Abstract
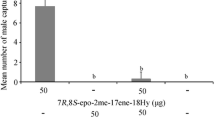
Pheromone traps baited with (+)-disparlure,cis-7,8-epoxy-2methyocta-decane, captured males ofLymantria dispar, L. monacha, andL. mathura in northeastern People's Republic of China.L. dispar responded to the addition of olefin to (+)-disparlure-baited traps in a negative doseresponse manner. Observations on site and seasonal capture ofL. dispar andL. mathura are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cardé, R.T., Roelofs, W.L., andDoane, C.C. 1973. Natural inhibitor of the gypsy moth sex attractant.Nature 241:474–475.
Cardé, R.T., Doane, C.C., Granett, J., andRoelofs, W.L. 1975. Disruption of pheromone communication in the gypsy moth; Some behavioral effects of disparlure and an attractant modifier.Environ. Entomol. 4:793–796.
Klimetzek, D. Loskant, G., Vité, J.P., andMori, K. 1976. Disparlure: Differences between gypsy moth and nun moth.Naturwissenschaftern 63:582–583.
Kovalev, B.G., Bedny, V.D., andCardé, R.T. 1980. Attractancy of disparlure enantiomers for the gypsy moth and the nun moths.Insect Chemoreception (Mechanisms of Pheromone Reception) 5:109–112 (Lithuanian Academy of Sciences, (in Russian).
Paszek, E. 1984. Bioassay of aged and unaged samples of 1981–1984 Hercon disparlure dispensers. USDA, APHIS Laboratory Report, 1983–1984. Otis Methods Development Center, Otis AFB, Maine.
Schneider, D., Lange, R., Schwarz, F., Beroza, M., andBierl, M.A. 1974. Attraction of male gypsy moth and nun moth to disparlure and some of its chemical analogues.Oecologia 14:19–36.
Schwalbe, C.P. 1981. Disparlure baited traps for survey and detection, pp. 542–548.,in C.C. Doane and M.L. McManus (eds.). The Gypsy Moth: Research toward Integrated Pest Management.U.S. Department of Agriculture Technical Bulletin 1584.
Vité, J.P., Klimetzek, D., Loskant, G., Hedden, R., andMori, K. 1976. Chirality of insect pheromones: Response interruption by inactive antipodes.Naturwissenschaften 63:582–583.
Wallner, W.E., Cardé, R.T., Xu, C., Weseloh, R.M., Sun, X., Yan, J., andSchaefer, P.W. 1984. Gypsy moth (Lymantria dispar L.) attraction to disparlure enantiomers and the olefin precursor in the People's Republic of China.J. Chem. Ecol. 10:753–757.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Lepidoptera: Lymantriidae.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Odell, T.M., Xu, CH., Schaefer, P.W. et al. Capture of gypsy moth,Lymantria dispar (L.), andLymantria mathura (L.) males in traps baited with disparlure enantiomers and olefin precursor in the People's Republic of China. J Chem Ecol 18, 2153–2159 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00984942
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00984942