Abstract
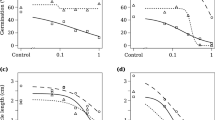
The aqueous eluate from fruits ofAmmi majus (Bishop's weed, Umbelliferae) remarkably inhibited germination of adjacent seeds ofAnastatica hierochuntica, lettuce, or tomato but had no effect on intact fruits ofAmmi. Similar inhibition was found in dark or in light, except that seeds ofA. hierochuntica were significantly more inhibited in the dark than in the light. Xanthotoxin was isolated, identified, and found to account for about a sixth of the inhibitory activity of the eluate. After fruits ofAmmi were submerged in a large volume of water for 4 days, the fruits still exuded enough inhibitors to prevent germination ofA. hierochuntica, lettuce, or tomato. Data support also the proposal that the phytotoxins are compartmentalized between the inner and the outer fruit envelopes. The inner layer excludes inhibitors from the embryo and autotoxicity is thus avoided, whereas the outer one ensures a gradual liberation of the phytotoxic compounds. This, as well as the high reactivity of the eluate, the high densities ofAmmi fruits in nature, and their relatively limited annual germination, suggest chemical inhibition of neighboring plant species other thanAmmi. Hence, in addition to their chemical protection against predators of either lower or higher organisms, furanocoumarins in fruits ofAmmi majus may contribute to its success as a weed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baskin, F.M., Ludlow, C.J., Harris, T.K., andWolf, F.T. 1967. Psoralen, an inhibitor in the seeds ofPsoralea subacaulis (Leguminosae).Phytochemistry 6:1209–1213.
Berenbaum, M. 1978. Toxicity of a furanocoumarin to armyworms: A case of biosynthetic escape from insect herbivores.Science 201:532–533.
Camm, L.E., Chi-Kit, W., andTowers, G.H.N. 1976. An assessment of the roles of furanocoumarins inHeradeum lanatum.Can. J. Bot. 54:2562–2566.
Chakraborty, D.P., Das Gupta, A., andRose, P.K. 1957. On the antifungal actions of some natural coumarins.Ann. Biochem. Exp. Med. 17:59.
Chaturvedi, S.N., andMuralia, R.N. 1975. Germination inhibitors in some umbellifer seeds.Ann. Bot. 39(164): 1125–1129.
Evenari, M. 1949. Germination inhibitors.Bot. Rev. 15(3):153–194.
Fowden, L., andLea, P.J. 1979. Mechanism of plant avoidance of autotoxicity by secondary metabolites, especially by nonprotein amino acids, pp. 135–160,in G.A. Rosenthal and D.H. Janzen (eds.). Herbivores, Their Interaction with Secondary Plant Metabolites. Academic Press, New York.
Fucushi, S. 1960. Components ofFicus carica IV. Influence of psoralen and bergapten on the germination of some vegetable seeds. Nippon Noeikagaku Kaishi 34:498–500;Chem. Abs. (1963) 58:119034.
Harper, J.L. 1977. Population Biology of Plants. Academic Press, London. 892 pp.
Ivie, G.W. 1978. Linear furanocoumarins (psoralens) from the seed of TexasAmmi majus L. (Bishop's weed).J. Agric. Food Chem. 26(6):1394–1403.
Mayer, A.M., andShain, Y. 1974. Control of seed germination.Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 25:169–193.
Rodighiero, G. 1954. Influence of natural furocoumarins on the germination of seeds and on the growth of lettuce sprouts and roots. Giorn. Biochem. 3:138–146.
Shina-Roy, S.P., andChakraborty, D.P. 1976. Psoralen, a powerful germination inhibitor.Phytochemistry 15:2005–2006.
Theobald, W.L. 1971. Comparative anatomical and developmental studies in the Umbelliferae, pp. 177–198,in N.H. Heywood (ed.). The Biology and Chemistry of the Umbelliferae. Academic Press, London.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Friedman, J., Rushkin, E. & Waller, G.R. Highly potent germination inhibitors in aqueous eluate of fruits of Bishop's weed (Ammi majus L.) and avoidance of autoinhibition. J Chem Ecol 8, 55–65 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00984005
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00984005