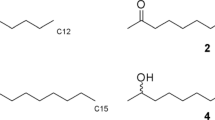
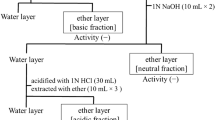
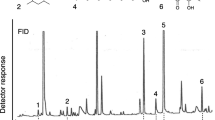
Abstract
The major component of the trail pheromone ofT. impurum is methyl 2-hydroxy-6-methylbenzoate (methyl 6-methyl salicylate). The poison reservoir of each worker contains about 1.0 ng of this substance in the venom. To ascertain the degree of specificity of the substance as pheromone and to determine any correlation between structure and biological activity, 38 synthetic analogs were tested in a bioassay. Sixteen compounds showed activity at 100 ng per artificial trail. The importance of the methyl group and methyl ester were demonstrated, while the hydroxyl group has a relatively small effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anslow, W.K., andRaistrick, H. 1931. Studies on the biochemistry of microorganisms XIX 6-hydroxy-2-methylbenzoic acid, a product of the metabolism of glucose byPenicillium griseo-fulvum Dierckx.Biochem. J. 25:39–44.
Attygalle, A.B., andMorgan, E.D. 1983. Trail pheromone of the antTetramorium caespitum (L.).Naturwissenschaften 70:364–365.
Attygalle, A.B., andMorgan, E.D. 1985. Ant trail pheromones.Adv. Insect Physiol. 18:1–30.
Attygalle, A.B., andMorgan, E.D. 1988. Pheromones in nanogram quantities: Structure determination by combined microchemical and gas Chromatographie methods.Angew. Chem. Internat. Ed. English, 27:460–478.
Billen, J.P.J., Evershed, R.P., Attygalle, A.B., Morgan, E.D., andOllett, D.G. 1986. The contents of the Dufour glands of workers of three species ofTetramorium (Hymenoptera: Formicidae).J. Chem. Ecol. 12:669–685.
Brand, J.M., Fales, H.M., Sokoloski, F.A., Macconnell, J.G., Blum, M.S., andDuffield, R.M. 1973. Identification of mellein in the mandibular gland of carpenter ants.Life Sci. 13:201–211.
Evershed, R.P., Morgan, E.D., andCammaerts, M.C. 1982. 3-Ethyl-2,5-dimethylpyrazine, the trail pheromone from the venom gland of eight species ofMyrmica ants.Insect Biochem. 12:383–391.
Gnanasunderam, C., Young, H., andBenn, M.H. 1984. Defensive secretions of New Zealand tenebrionids-III. The identification of methyl esters of 6-methyl and 6-ethylsalicylic acid inChrysopephus expolitus (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae).Insect Biochem. 14:159–161.
Hauser, P.M., andPogany, S.A. 1980. 2-Hydroxy-6-methylbenzoic acid derivatives.Synth. Commun. 814–815.
Jackson, B.D., Wright, P.J., andMorgan, E.D. 1989. 3-Ethyl-2,5-dimethylpyrazine, a component of the trail pheromone of the antMessor bouvieri.Experientia 45:487–489.
Kannangara, C.G., Henningssen, K.W., Stumpf, P.K., andVon Wettstein, D. 1971. 6-Methylsalicylic acid synthesis by isolated barley chloroplasts.Eur. J. Biochem. 21:334–338.
Kunesch, G., Zagatti, P., Pouvreau, A., andCassini, R. 1987. A fungal metabolite as the male wing gland pheromone of the bumble-bee wax moth,Aphomia sociellaL.Z. Naturforsch. 42c:657–659.
Lloyd, H.A., Schmuff, N.R., andHefetz, A. 1984. Chemistry of the male mandibular gland secretion of the carpenter ant,Camponotus thoracicus fellah Emery.Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B: Comp. Biochem. 78B:687–689.
Morgan, E.D. 1990a. Insect trail pheromones: A perspective of progress, pp. 259–270,in A.R. McCaffrey and I.D. Wilson (eds.). Chromatography and Isolation of Insect Hormones and Pheromones. Plenum Press, New York.
Morgan, E.D. 1990b. Preparation of small scale samples from insects for chromatography.Anal. Chim. Acta. 236:227–235.
Morgan, E.D., andOllett, D.G. 1987. Methyl 6-methylsalicylate, trail pheromone of the antTetramorium impurum.Naturwissenschaften 74:596–597.
Morgan, E.D., andWadhams, L.J. 1972. Gas chromatography of volatile compounds in small samples of biological materials. 7.Chromatogr. Sci. 10:528–529.
Pasteels, J.M., andVerhaeghe, J.C., 1974. Dosage biologique de la phéromone de piste chez les fourrageures et les reines deMyrmica rubra.Insectes Soc. 21:167–180.
Pasteels, J.M., Verhaeghe, J.C., Ottinger, R., Braekman, J.C., andDaloze, D. 1981. Absolute configuration of (3R,4S)-4-methyl-3-hexanol-a pheromone from the head of the antTetramorium impurum Foerster.Insect Biochem. 11:675–678.
Riley, R.G., Silverstein, R.M., Carroll, B., andCarroll, R. 1974. Methyl 4-methylpyrrole-2-carboxylate: A volatile trail pheromone from the leaf-cutting ant,Atta cephalotes.J. Insect Physiol. 20:651–654.
Sexton, W.A. 1963. Chemical Constitution and Biological Activity, 3rd ed. Spon, London, pp. 161–163.
Siegel, S., andCastellan, N.J. 1988. Non-Parametric Statistics for the Behavioural Sciences. McGraw-Hill, Singapore, p. 128.
Sonnet, P.E., andMoser, J.C. 1972. Synthetic analogs of the trail pheromone of the leaf-cutting ant,Atta texana (Buckley).J. Agric. Food Chem. 20:1191–1194.
Sonnet, P.E., andMoser, J.C. 1973. Trail pheromone: Responses of the Texas leaf-cutting ant,Atta texana to selected halo- and cyanopyrrole-2-aldehydes, ketones, and esters.Environ. Entomol. 2:851–854.
Tecle, B., Brophy, J.J., andToia, R.F. 1986. Biosynthesis of 2-hydroxy-6-methylacetophenone in an Australian ponerine ant,Rhytidoponera aciculata (Smith).Insect Biochem. 16:333–336.
Tumlinson, J.H., Moser, J.C., Silverstein, R.M., Brownlee, R.G., andRuth, J.M. 1972. A volatile trail pheromone of the leaf-cutting antAtta texana.J. Insect Physiol. 18:809–814.
Weiss, U., andEdwards, J.M. 1980. The Biosynthesis of Aromatic Compounds, Wiley, New York. pp. 356–358.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
In part presented at the Fourth Annual Meeting of the International Society of Chemical Ecology, July 13–17, 1987, Hull, England.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morgan, E.D., Jackson, B.D., Ollett, D.G. et al. Trail pheromone of the antTetramorium impurum and model compounds: Structure-activity comparisons. J Chem Ecol 16, 3493–3510 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00982113
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00982113