Conclusion
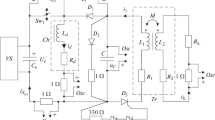
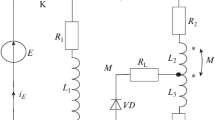
The study of the operation of the pulsed inductive converter led to expressions for the calculation and design of such devices. Inspection of these expressions revealed the well-established advantages of pulsed operation of parametric converters [4]. Furthermore, it was shown that it is possible to measure in circuits with varying inductivity. The signal amplitude delivered from the converter and the converter sensitivity are independent of spurious capacities; this is particularly important when small movable converters must be employed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
L. V. Kamenev and A. V. Antoshin, Author's Certificate (Soviet Patent) No. 143,467, Byul. Izobr., No. 24 (1961).
L. V. Kamenev, Automation of Chemical Production, No. 1, Moscow, Editorial GK SM USSR for Chem. (1962).
V. I. Pakhomov, Izmeritel. Tekh., No. 1 (1966).
Yu. I. Semko, Izmeritel. Tekh., No. 2 (1966).
Ya. S. Itskhoki, Pulsed Instruments, Moscow, Sov. Radio (1959).
Additional information
Translated from Izmeritel'naya Tekhnika, No. 12, pp. 53–55, December, 1969.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peredel'skii, G.I. Pulse-operated inductive converter. Meas Tech 12, 1726–1729 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00979975
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00979975