Abstract
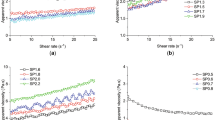
A method is proposed for measuring the rheology of cement paste under conditions that suppress shear flow, i.e. squeezing. This method is based on squeezing samples in a servohydraulic compression-tension testing machine, and is different from the commonly used shear flow experiments. Possible artefacts such as the buoyancy of the piston that penetrates the paste, sedimentation of cement paste, geometry of the container, and friction at the interface between the top plate (or piston) and sample are investigated. Plots of stress versus apparent strain were obtained and compared with results from standard shear flow experiments. Because cement paste has both viscoelastic and viscoplastic characteristics, results are analysed in terms of both solid-like deformation and liquid-like flow behaviour. A first-approximation theoretical analysis is developed, based on the assumption that cement paste behaves as a non-Newtonian liquid, and results are compared with the experimental results.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(\dot \gamma\) :
-
Shear strain rate in power law fluid model
- γ zr :
-
Shear strain converted from ε zr
- \(\dot \gamma _{zr}\) :
-
Shear strain rate
- έ:
-
Normal strain rate
- ε zr :
-
Component of shear strain
- έ zr :
-
Component of shear strain rate
- ε zz :
-
Component of normal strain
- η:
-
Viscosity
- ϱ:
-
Density of cement paste (3.2 g cm−3)
- σCav :
-
Calculated average normal stress of cement paste
- σNav :
-
Calculated average normal stress of power law fluid
- σm :
-
Measured normal stress of cement paste
- σ zz :
-
Normal stress in z direction
- Τeq :
-
Equivalent shear stress converted from normal stress
- Τ rz :
-
Shear stress in momentum equation
- a i :
-
Coefficients in polynomial function of geometric factor for cement paste
- B :
-
Buoyancy force
- CGF :
-
Geometric factor for cement paste
- d o :
-
Amplitude of squeeze motion
- F N :
-
Load in normal direction
- g :
-
Gravitational constant
- h :
-
Sample height
- h o :
-
Initial sample height
- \(\dot h\) :
-
Velocity of platen
- k :
-
Order of polynomial function of geometric factor for cement paste
- m :
-
Consistency in power-law fluid model
- n :
-
Power index in power-law fluid model
- P :
-
Pressure
- P a :
-
Atmospheric pressure
- PGF :
-
Geometric factor for power-law fluid model
- r :
-
Radial direction in cylindrical coordinates
- R :
-
Radius of sample
- s :
-
1/n
- V :
-
Volume of the top platen submerged into cement paste
- v r :
-
Velocity inr direction
- v z :
-
Velocity in z direction
- z :
-
Vertical direction in cylindrical coordinates
References
B. H. Min, L. Erwin, andH. M. Jennings,Ceram. Trans. 16 (1990) 337.
Idem,Korean J. of Rheol., in press.
G. H. Tattersall,Nature 175 (1955) 166.
R. Lapsin,Cemento 4 (1982) 243.
W. Vom Berg, in Proceedings of 8th Internationl Congress on Rheology, Vol. 3 (Plenum, New York, 1980) p. 665.
I. Odler, T. Becker andB. Weiss,Cemento (1978) 303.
P. F. G. Banfill,Mag. Concr. Res. 33 (1981) 37.
T. E. R. Jones, G. Brindly andB. C. Patel, in “Hydraulic Cement Pastes: Their Structure and Properties”, Proceedings of Conference, University of Sheffield, 1976, p. 135.
A. R. Cusen andJ. Harris, in Proceedings of RILEM, on “Fresh concrete; important properties and their measurements, Sem”. Leeds, England, 1973. Vol. 1 (Dept. of Civil Engng. University of Leeds, Leeds, England, 1973) p. 2.8.1.
T. M. Chow, L. V. McIntire, K. R. Kunze andC. E. Cooke,SPE Prodn Engng 3(4) (1988) 543.
P. F. G. Banfill andD. R. Kitching, in Proceedings of International Congress on Rheology of Fresh Cement and Concrete, edited by P. F. G. Banfill (University Press, Cambridge, 1991) p. 125.
G. J. Dienes andH. F. Klemm,J. Appl. Phys. 17 (1946) 458.
G. J. Dienes,J. Coll. Sci. 2 (1947) 131.
R. J. Grimm,AIChE J. 24 (1978) 427.
K. S. Gandhi andR. Burns,Trans. Soc. Rheol. 20 (1976) 489.
R. J. Silva-Nietto, B. C. Fisher andA. W. Birly,Polym. Engng Sci. 21 (1981) 499.
E. J. Dickenson andH. P. Witt,Trans. Soc. Rheol. 13 (1969) 485.
A. N. Gent,Br. J. Appl. Phys. 11 (1960) 85.
M. J. Foster,J. Appl. Phys. 26 (1955) 1104.
S. H. Chatraei, C. W. Macosko andH. H. Winter,J. Rheol. 25 (1981) 433.
A. Terentyev andG. Kunnos, in Proceedings of International Congress on Rheology of Fresh Cement and Concrete, edited by P.F.G. Banfill (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1990) p. 93.
M. Reiner, in “Rheology”, Vol. 3, edited by F. R. Eirich (Academic, New York, 1960) p. 351.
R. B. Bird, R. C. Armstrong andO. Hassager, “Dynamics of Polymeric Liquids”, Vol. 1, (Wiley, New York 1977) p. 429.
W. Ostwald, V. Kolloid-Z. 36 (1925) 99.
A. De Waele,Oil & Color Chem. Assoc. J. 6 (1923) 23.
P. J. Leider andR. B. Bird, in “Industrial Engineering Chemical Fundamentals”, Vol. 13 (American Chemical Society, Washington, 1974) p. 336.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Min, B.H., Erwin, L. & Jennings, H.M. Rheological behaviour of fresh cement paste as measured by squeeze flow. J Mater Sci 29, 1374–1381 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00975091
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00975091