Abstract
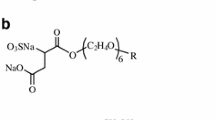
The hydrophobicity of myelinic, synaptosomal and mitochondrial surfaces in the rat brain was measured using the nonionic surfactant, C18H37O(CH2CH2O)13H. This method is based on the adsorption of the hydrophobic alkyl group of the surfactant by the hydrophobic sites on the surfaces. Each preparations was mixed with an excess of the surfactant and the surfactant remaining in the supernatants was determined spectrophotometrically by measuring the absorbance of tetrabromophenolphthalein ethylester at 690 nm. The greatest amount was adsorbed by myelin, followed by synaptosomes and mitochondria. The hydrophobicity is shown to be a reflection of the surface lipids. This method showed good reproducibility and was useful for the quantitative determination of hydrophobicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harris, R. A., and Schroeder, F. 1981. Ethanol and the physical properties of brain membranes. Fluoresence studies. Mol. Pharmacol. 20:128–137.
Rowe, E. S. 1983. Lipid chain length and temperature dependence of ethanol-phosphatidylcholine interactions. Biochemistry 22:3299–3305.
Fernandez, Y. J., Boigegrain, R-A. M., Cambon-Gros, C. D., and Mitjavila, S. E. 1984. Sensitivity of Na+-couples D-glucose uptake, Mg2+-ATPase and sucrose to perturbations of the fluidity of brush-border membrane vesicles induced by n-aliphitic alcohols. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 770:171–177.
Kreishman, G. P., Graham-Brittain, C., Hitzemann, R. J. 1985. Determination of ethanol partition coefficients to the interior and the surface of dipalmityl-phosphatidylcholine liposomes using deuterium nuclear magnetic resonane spectroscopy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 130:301–305.
Hitzemann, R. J., Schueler, H. E., Graham-Brittain, C., and Kreishman, G. P. 1986. Ethanol-induced changes in neuronal membrane order. An NMR study. Biochim. Biophs. Acta 859:189–197.
Pope, J. M., and Dubro, D. W. 1986. The interaction of nalkanes and n-alcohols with lipid bilayer membranes: a2HNMR study. Biochim. Biophs. Acta 858:243–253.
Seeman, P. 1972. The membrane actions of anesthetics and tranquilizers. Pharmacol. Rev. 24:583–655.
Miller, K. W., and Pang, K-Y. Y. 1976. General anaesthetics can selectively perturb lipid bilayer membranes. Nature 263:253–255.
Rosenberg, P. H., Jansson, S-E., and Gripenberg, J. 1977. Effects of halothane, thiopental, and lidocaine on fluidity of synaptic plasma membranes and artificial phospholipid membranes. Anesthesiology 46:322–326.
Trudell, J. R. 1977. A unitary theory of anesthesia based on lateral phase separations in nerve membranes. Anesthesiology 46:5–10.
Mountcastle, D. B., Biltonen, R. L., and Halsey, M. J. 1978. Effect of anesthetics and pressure on the thermotropic behavior of multilamellar dipalmitoylphosphatudylcholine liposomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 75:4906–4910.
Janoff, A. S., and Miller, K. W. 1982. A critical assessment of the lipid theories of general anaethetic action. Pages 417–476,in Chapman, D. (Ed.), Biological Membranes, vol. 4, Academic Press, London.
Jain, M. K., Wu, N. Y.-M., and Wray, L. V. 1975. Druginduced phase changes in bilayer as possible mode of action of membrane expanding drugs. Nature 255:494–496.
Noda, Y., and Kanemasa, Y. 1986. Determination of hydrophobicity on bacterial surfaces by nonionic surfactants. J. Bacteriol. 167:1016–1019.
Folch, J., Lees, M., and Sloane-Stanley, G. H. 1975. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 226:497–509.
Rathbone, L., and Maroney, P. M. 1963. Preparation of phosphatidylserine. Nature 200:887–888.
Rouser, G., Kritchevsky, G., and Yamamoto, A. 1967. Column chromatographic and associated procedures for separation and determination of phosphatides and glycolipids. Pages 99–162,in Marimetti, G. V. (ed.), Lipid Chromatographic Analysis, Marcel Dekker, New York.
Gray, E. G., and Whittaker, V. P. 1962. The isolation of nerve endings from brain: An electron-microscopic study of cell fragments derived by homogenization and centrifugation. J. Anat. 96:79–88.
Whittaker, V. P., and Baker, L. A. 1972. The subcellular fractionation of synaptosomes and their component organelles. Pages, 1–52,in Fried, R. (ed.), Method of Neurochemistry, vol. 2, Marcel Dekker, New York.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., and Randall, R. J. 1951. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193:265–275.
Cuzner, M. L., Davison, A. N., and Grefson, N. A. 1965. Chemical and metabolic studies of rat myelin of the central nervous system. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 122:86–94.
Norton, W. T. 1972. Formation, structure, and biochemistry of myelin. Pages, 76–79,in Siegel, G. J., Albers, R. S., Agranoff, B. W., and Katsman, R. (ed.), Basic Neurochemistry, Little, Brown and Co., Boston.
Norton, W. T., and Poduslo, S. E. 1973. Myelination in rat brain: Changes in myelin composition during brain maturation. J. Neurochem. 21:759–773.
Seminario, L. M., Hren, H., and Gomez, C. J. 1964. Lipid distribution in subcellular fractions of the rat brain. J. Neurochem. 11:197–207.
Dikerson, J. W. T. 1968. The composition of nervous tissues. Pages, 48–115, in Davison, A. N., and Dobbing, J. (ed.), Applied Neurochemistry, Blackwell Sci. Pub. Oxford-Edinburgh.
Lapetina, E. G., Soto, E. F., and Derobertis, E. 1968. Lipids and proteolipids in isolated subcellular membranes of rat brain cortex. J. Neurochem. 15:437–445.
Noda, Y., Tôei, K., and Mori, A. 1987. Effect of alcohol on the hydrophobicity of the myelinic, synaptosomal and mitochondrial surfaces in the rat brain. Med. Sci. Res. 1987 15:579–580.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noda, Y., Tôei, K. & Mori, A. Determination of hydrophobicity of myelinic, synaptosomal, and mitochondrial surfaces in the rat brain. Neurochem Res 13, 557–560 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00973297
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00973297