Abstract
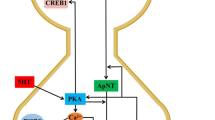
The role of polyamines (PA) synthesis in NMDA receptor-mediated45Ca2+ fluxes and norepinephrine release was studied in rat hippocampal synaptosomes. NMDA (50μM) caused a sharp (>2-fold) transient increase in PA synthesis regulating enzyme, ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) activity with concomitant elevation in PA levels in the order putrescine>spermidine>spermine. ODC inhibitor, α-difluoromethylornithine (DFMO), and NMDA antagonist, 2-amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid (D-AP5), both blocked increases in ODC activity and PA levels. Activation of NMDA receptors induced a sharp (3 to 4-fold) and quick (15 seconds) increase in45Ca2+ uptake by synaptosomes within 15 seconds of exposure at 37°C. The efflux of45Ca2+ and3H-norepinephrine (NE) release at 22°C from pre-loaded synaptosomes was also significantly (2 to 4-fold) enhanced by NMDA within 15 seconds. These NMDA receptor-mediated effects on calcium fluxes and NE release were blocked by NMDA receptor-antagonists (DAP-5 and MK-801) and PA synthesis inhibitor, DFMO and the DFMO inhibition nullified by exogenous putrescine. These observations establish that ODC/PA cascade play an important role in transduction of excitatory amino acid mediated signals at NMDA receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Collingridge, G. L., and Lester, R. A. J. 1989. Excitatory amino acid receptors in the vertebrate central nervous system. Physiol. Rev. 40:143–210.
Mayer, M. L., Vycklicky, L., and Sernagor, E. 1989. A physiologist's view of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor: an allosteric ion channel with multiple regulatory sites. Drug Development Res. 17:263–280.
Monaghan, D. T., Bridges, R.J., and Cotman, C. W. 1989. The excitatory amino acid receptors: their classes, pharmacology and distinct properties in function of the central nervous system. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 29:365–402.
Ransom, R. W. and Stec, N. L. 1988. Comparative modulation of [3H]MK-801 binding to the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-ion channel complex by L-glutamate, glycine, and polyamines. J. Neurochem. 51:830–836.
Reynolds, I. J. and Miller, R. J. 1989. Ifenprodil is a novel type of N-methyl-D-asparate receptor antagonist interaction with polyamines. Mol. Pharmacol. 36:758–765.
Sacaan, A. I. and Johnson, K. M. 1990. Characterization of the stimulatory and inhibitory effects of polyamines on [3H]TCP binding to the NMDA receptor iouophore complex. Mol. Pharmacol. 37:572–577.
Williams, K., Romano, C., and Molinoff, P. B. V. 1989. Effects of polyamines on the binding of3H-MK-801 to the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. Pharmacological evidence for the existence of a polyamine recognition site. Mol. Pharmacol. 36:575–581.
Collingridge, G. L. and Singer, W. 1990. Excitatory amino acid receptors and synaptic plasticity. Tr. Pharm. Sci. 11:290–296.
Lipton, S. A., and Kater, S. B. 1989. Neurotransmitter regulation of neuronal outgrowth, plasticity and survival. Tr. Neurosci. 12:265–270.
Dingledine, R., MacBain, C. J., and McNamara, J. O. 1990. Excitatory amino acid receptors in epilepsy. Tr. Pharm. Sci. 11:334–338.
Choi, D. W. 1988. Glutamate neurotoxicity and diseases of the nervous system. Neuron 1, 623–634.
Durand, G. M., Bennett, M. V. and Zukin, R. S. 1993. Splice variants of the NMDA receptor NR1 identify domains involved in regulation by polyamines and protein kinase C. Proc. Natl. Acad. Scie. (US) 6731–6735.
Mayer, M. L., and Miller, R. J. 1990. Excitatory amino acid receptors, second messengers and regulation of intracellular Ca2+ in mammalian neurons. Tr. Pharm. Sci. 11:254–260.
Nicoletti, F., Wroblewski, J. T., Novelli, A., Acho, H., Guidotti, A., and Costa, E. 1986. The activation of inositol phospholipid metabolism as a signal transducing system for excitatory amino acids in primary cultures of cerebellar granule cells. J. Neurosci. 6:1905–1911.
Sladeczek, F., Pin, J. P., Recasens, M., Bockaert, J., and Weiss, S. 1985. Glutamate stimulates inositol phosphate formation in striatal neurons. Nature 317:717–719.
Vaccarino, F., Guidotti, A., and Costa, E. 1987. Ganglioside inhibition of glutamate-mediated protein kinase C translocation in primary cultures of cerebellar neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:8707–8711.
Dumuis, A., Sebben, M., Haynes, L., Pin, J.-P., and Bockaert, J. 1988. NMDA receptors activate the arachidonic acid cascade system in striatal neurons. Nature 336:68–70.
Lazarewicz, J. W., Wroblewski, J. R., and Costa, E. 1990. N-Methyl-D-asparate-sensitive glutamate receptors induce calciummediated arachidonic acid release in primary cultures of cerebellar granule cells. J. Neurochem. 55:1875–1881.
Chetkovich, D. M., Gray, R., Johnston, D., and Sweatt, J. D. 1991. N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor activation increases cAMP levels and voltage-gated Ca2+ channel activity in area CA1 of hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88:6696–6700.
Garthwaite, J., Charles, S. L., and Chess-Williams, R. 1988. Endothelium derived relaxing factor release on activation of NMDA receptors suggests its role as intracellular messenger in the brain. Nature 336:385–388.
Novelli, A., Nicoletti, F., Wroblewski, J. T., Acho, H., Costa, E., and Guidotti, A. 1987. Excitatory amino acid receptors coupled with guanylate cyclase in primary cultures of cerebellar granule cells. J. Neurosci. 7:40–47.
Klamm, E., Chen, S.-J., and Sweatt, J. D. 1991. Persistent protein kinase activation in the maintenance phase of long-term potentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 266:24253–24256.
Bading, H., and Greenberg, M. E. 1991. Stimulation of protein tyrosine phosphorylation by NMDA receptor activation. Science 253:912–914.
Szekeley, A. M., Barbaccia, M. L., Alho, H., and Costa, E. 1989. In primary cultures of cerebellar granule cells the activation of NMDA-sensitive glutamate receptors induces c-fos mRNA expression. Molec. Pharmacol. 35:401–408.
Fagg, G. E., and Matus, A. 1984. Selective association of N-methyl-aspartate and quisqualate types of L-glutamate receptor with brain postsynaptic membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81:6876–6880.
Greenamyre, J. T., and Young, A. B. 1989. Synaptic localization of striatal NMDA, quisqualate and kainate receptors. Neurosci. Lett. 101:133–137.
Monaghan, D. T., and Cotman, C. W. 1986. Identification and properties of NMDA receptors in rat brain synaptic membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:7532–7536.
Errington, M. L., Lynch, M. A., and Bliss, T. V. P. 1987. Longterm potentiation in the dentate gyrus: induction and increased glutamate release are blocked byd-amino-phosphonovalerate. Neuroscience 20:279–284.
Koenig, H., Iqbal, Z., Goldstone, A., Siddiqui, F., and Lu, C. Y. 1989. NMDA receptor transduction: polymines as 2nd messengers mediating agonist-stimulated Ca2+ influx and transmitter release. J. Neurochem. 52(Suppl), S42.
Koening, H., Iqbal, Z., Goldstone, A., and Lu, C. 1991. Polyamines mediate presynaptic NMDA receptor responses in synaptosomes. J. Neurochem. 57(Suppl.), S15.
Martin, D., Bustos, G. A., Bowe, M. A., Bray, S. D., and Nadler, J. V. 1991. Autoreceptor regulation of glutamate and aspartate release from slices of the hippocampal CA1 area. J. Neurochem. 56:1647–1655.
Young, M. J., and Bradford, H. F. 1991. N-Methyl-D-aspartate releases excitatory amino acids in rat corpus striatum in vivo. J. Neurochem. 56:1677–1683.
Nicholls, D. G. 1989. Release of glutamate, aspartate, and aminobutyric acid from isolated nerve terminals. J. Neurochem. 52:331–341.
Clow, D. W., and Jhamandas, K. 1989. Characterization of L-glutamate action on the release of endogenous dopamine from the rat caudate-putamen. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Therap. 248:722–728.
Krebs, M. O., Desce, J. M., Kemel, M. L., Gauchy, C., Godeheu, G., Cheramy, A., and Glowinski, J. 1991. Glutamatergic control of dopamine release in the rat striatum:evidence for presynaptic N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors on dopaminergic nerve terminals. J. Neurochem. 56:81–85.
Wang, J. K. T. 1991. Presynaptic glutamate receptors modulate dopamine release from striatal synaptosomes. J. Neurochem. 57:819–822.
Fink, K., Bonisch, H., and Gothert, M. 1990. Presynaptic NMDA receptors stimulate noradrenaline release in the cerebral cortex. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 185:115–117.
Pittaluga, A., and Raiteri, M. 1990. Release-enhancing glucinedependent presynaptic NMDA receptors exist on noradrenergic terminals of hippocampus. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 191:231–234.
Iqbl Z. 1989. Role of calcium and polyamines in neuronal signal transduction. Plenary lecture at the 58th Annual Meeting of the Society of Biological Chemists (India).
Wang, J. K. T., Andrews, H., and Thukral, V. 1992. Presynaptic glutamate receptors regulate noradrenaline release from isolated nerve terminals. J. Neurochem. 58:204–211.
Augustine, G. J., Charlton, M. P., and Smith, S. J. 1987. Calcium action in synaptic transmitter release. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 10:633–693.
Retz, K. C., Young, A. C., and Coyle, J. T. 1982. Glutamate stimulation of45Ca2+ uptake by rat striatal synaptosomes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 79:319–322.
Simonato, M., Jope, R. S., Bianchi, C., and Beani, L. 1989. Lack of excitatory amino acid-induced effects on calcium fluxes measured with45Ca2+ in rat cerebral cortex synaptosomes. Neurochem. Res. 14:667–682.
Adamson, P., Hajimohammadreza, I., Brammer, M. J., Campbell, I. C., and Meldrum, B. S. 1990. Presynaptic glutamate/quisqualate receptors: effects on synaptosomal free calcium concentrations. J. Neurochem. 55:1850–1854.
Daniell, L. C. 1991. N-Methyl-D-aspartate increases cytoplasmic free calcium in mouse hippocampus. Neuropharmacology. 30:539–545.
Tabor, C. W. and Tabor, H. 1984. Polyamines. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 53:749–790.
Koenig, H., Goldstone, A. D., and Lu, C. Y. 1983. Polyamines regulate calcium fluxes in a rapid plasma membrane response. Nature 305:530–534.
Koenig, H., Ean, C.-C., Goldstone, A. D., Lu, C. Y., and Trout, J. J. 1989. Polyamines mediate androgenic stimulation of calcium fluxes and membrane transport in rat heart myocytes. Circ. Res. 64:415–426.
Koenig, H., Goldstone, A. D., Lu, C. Y., Iqbal, Z., Fan, C.-C., and Trout, J. J. 1989. Polyamines, hormone receptors and calcium fluxes,in The Physiology of Polymines (Bachrach U. and Heimer, Y. M., eds), CRC Press, vol. 1, pp. 57–81.
Fan C.-C. and Koenig H. 1988. The role of polyamines in β-adrenergic stimulation of calcium influx and membrane transport in rat heart. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 20:789–799.
Koenig, H., Goldstone, A. D., and Lu, C. Y. 1983. β-Adrenergic stimulation of Ca2+fluxes, endocytosis, hexose tranpport and amino acid transport in mouse kidney cortex is mediated by polyamine synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80:7210–7214.
Koenig, H., Goldstone, A. D., and Lu, C. Y. 1988. Polyamines are intracellular messengers in the β-adrenergic regulation of Ca2+ fluxes, [Ca2+]i and membrane transport in rat heart myocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 153:1179–1185.
Koenig, H., Goldstone, A. D., and Lu, C. Y. 1987. Neurotransmitters modulate Ca2+ influx and transport processes in brain capillaries: a new model for blood-brain barrier regulation (Abstr.), Ann. Neurol. 22:137–138.
Iqbal, Z., and Koenig, H. 1985. The role of polyamine synthesis in epilepsy induced by electroconvulsive shock and methionine sulfoximine. J. Neurochem. 44(Suppl.):S88.
Iqbal, Z., Koenig, H., Zimmerman, R., and Chisholm, R. 1991. ECS seizures, NMDA receptors and the ODC/polyamine cascade, Neurchem, Internat. 16:120.
Iqbal, Z., Siddiqui, F., Lu, C. and Koenig, H. 1993. Polyamines and NMDA receptors in electroconvulsive shock induced epileptic seizures. Soc. Neuroscie. Abstr. 19:1134.
Iqbal, Z., and Koenig, H. 1985. Polyamines appear to be second messengers in mediating calcium fluxes and neurotransmitter release in potassium depolarized synaptosomes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 133:563–573.
Djuhuus, R. 1981. Ornithine decarboxylase assay based on the retention of putrescine by a strong cation-exchange paper. Anal. Biochem. 113:352–353.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., and Randall, R. J. 1951. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193:265–275.
Watkins, J. C., and Olverman, H. J. 1987. Agonists and antagonists for excitatory amino acid receptors. Tr. Neurosci. 10:265–272.
Metcalf, B. W., Bey, P., Danzin, C., Jung, M. J., Casara, P., and Vevert, J. P. 1978. Catalytic irreversible inhibition of mammalian ornithine decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.17) by substrate and product analogues. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 100:2552–2553.
Fage, D., Voltz, C., Scatton, B. and Carter, C. 1992. Selective release of spermine and spermidine from the rat striatum by NMDA receptor activators in vivo. J. Neurochem. 58:2170–2175.
Iversen, L. L. 1994. MK-801 (Dizocilpine maleate)-NMDA receptor antagonist. Neurotransmissions. 10:1–4.
Wong, E. H. F., Kemp, J. A., Priestly, T., Knight, A. R., Woodruff, G. N., and Iversen, L. L. 1986. The antagonist MK-801 is a potent N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:7104–7108.
McNamara, J. O., Russell, R. D., Rigsbee, L., and Cohnhaus, D. W. 1988. Anticonvulsant and antiepileptogenic actions of MK-801 in the kindling and electroshock models. Neuropharmacology 27:563–568.
Wilmot, C. A. 1989. Excitatory amino acid antagonists:behavioral and biochemical approaches for the development of new central neuron system therapeutic agents. Drug Development Res. 17:339–365.
Trout, J. J., Koenig, H., Goldstone, A. D., Iqbal, Z., and Siddiqui, F. 1993. NMDA receptor excitotoxicity involves activation of polyamine synthesis: protection by α-difluoromethylornithine. J. Neurochem. 60:352–355.
McGurk, J. F., Bennett, M. V. L., and Zukin, R. S. 1990. Polyamines potentiate responses of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:9971–9974.
McCann, P., Pegg, A. E., and Sjoerdsma, A. (eds.) Inhibition to Polyamine Synthesis. Academic Press, San Diego, Ca, pp 1–371.
Seiler, N., and Dezeuse, F. 1988. Polyamine transport in mammalian cells. Int. J. Biochem. 22:211–218.
Starke, K. A. 1981. Presynaptic Receptors. (Review) Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 21:7–31.
Jones, P. G. and Roberts, P. J. 1990. Ibotenate stimulates glutamate release from guinea pig cerebrocortical synaptosomes: inhibition by L-2-amino-4-phosphono-butyrate (L-AP4), Neurosci. Lett. 111:228–232.
Shimizu, N., Shumin, D., Hori, T., and Domura, Y. 1990. Glutamate modulates dopamine release in the striatum as measured by brain microdialysis. Brain Res. Bull. 25:99–102.
Koenig, H., Goldstone, A. D., Lu, C. Y., and Trout, J. J. 1991. Regulation of brain capillary permeability by neurotransmitters: Role of ODC/polyamine cascade. J. Cereb. Blood Flow and Metab. 11:S494.
Cotman, C. W., Bridges, R. J., Taube, J. S., Clark, A. S., Geddes, J. W., and Monaghan D. T. 1989. The role of the NMDA receptor in central neurons system plasticity and pathology. J. NIH Res. 1: 65–74.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Special issue dedicated to Dr. Sidney Ochs.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siddiqui, F., Iqbal, Z. Regulation of N-Methyl-d-aspartate receptor-mediated calcium transport and norepinephrine release in rat hippocampus synaptosomes by polyamines. Neurochem Res 19, 1421–1429 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00972471
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00972471
Key Words
- D-AP5, 2-amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid
- DFMO, α-difluoromethylornithine
- EGTA, ethylene-bis-(oxyethelene nitrilo) tetra acetic acid
- Hepes, N-2-hydroxyethyl piperazine-N′-2-ethane sulfonic acid
- NMDA, N-methyl-D-aspartate
- NE, Norepinephrine
- ODC, Ornithine decarboxylase
- PA, Polyamines
- PSS, Physiological saline solution
- Tris, Tris (hydoxymethyl)amino methane