Abstract
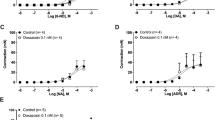
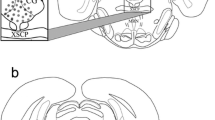
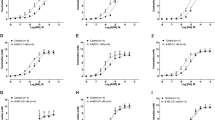
The concentrations of dopamine (DA), 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) and noradrenaline (NA) in the rat vas deferens divided in eight or four sections were determined by high performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. Dopamine and NA had the same regional distribution; their concentrations were maximal near the prostatic end and decreased towards the epididymis. The concentration of 5-HT also decreased from the prostatic to the epididimal end, but 5-HT did not follow the same regional distribution as DA and NA. Reserpine (0.02 or 0.2 mg/kg, i.p., 24 hr) and 6-hydroxydopamine (2×80 mg/kg, i.v., 6 days) decreased the contents of DA and NA; the concentrations of both amines were modified to a similar extent. Reserpine also diminished the content of 5-HT. Pargyline (200 mg/kg, i.p., 2 hr) increased the concentration of 5-HT whilep-chlorophenylalanine (300 mg/kg, oral, 3 days) decreased the contents of the amine in some sections of the vas deferens. This study suggests that DA and NA co-exist in the same sympathetic neurons. Some of the 5-HT could be stored in mast cells as previously proposed, but the finding that tissue content of 5-HT changes after inhibiting the deamination or synthesis of the amine suggests that other source(s) of 5-HT distinct from mast cells exist in the rat vas deferens.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sjostrand, N. O. 1965. The adrenergic innervation of the vas deferens and the accessory male genital glands. Acta Physiol. Scand. Vol. 65 Suppl 257.
Norberg, K.-A. 1967. Transmitter histochemistry of the sympathetic adrenergic system. Brain Res. 5:125–170.
Zieher, L. M., and Jaim-Etcheverry, G. 1971. Regional variations in the distribution of noradrenaline along the rat vas deferens. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 23:61–63.
Bell, C., and Gillespie, J. S. 1981. Dopamine and noradrenaline levels in peripheral tissues of several mammalian species. J. Neurochem. 36:703–706.
Oishi, R., Mishima, S., and Kuriyama, H. 1983. Determination of norepinephrine and its metabolites released from rat vas deferens using high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. Life Sci. 32:933–940.
Simon, A., and Van Maanen, E. F. 1976. Dopamine receptors and dopaminergic nerves in the vas deferens of the rat. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. 222:4–15.
Tayo, F. M. 1979. Prejunctional inhibitory α-adrenoceptors and dopaminoceptors of the rat vas deferens and the guinea-pig ileum in vitro. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 58:189–195.
Favre, R., de Haut, M., Dalmaz, Y., Pequignot, J. M., and Peyrin, L. 1986. Peripheral distribution of free dopamine and its metabolites in the rat. J. Neural Transmission 66:135–149.
Bell, C., Gillespie, J. S., and Macrae, I. M. 1984. Release of noradrenaline and dopamine by nerve stimulation in the guinea pig and rat vas deferens. Br. J. Pharmacol. 81:503–509.
Bell, C. 1988. Dopamine release from sympathetic nerve terminals. Progress Neurobiol. 30:193–208.
Fuenmayor, L., Gomez, J., Campos, H. A., and Romero, E. 1976. Presence of serotonin in the rat vas deferens: its influence on contractile responses. Neuroscience 1:197–203.
Kapur, H., and Mottram, D. R., 1979. A pre-synaptic inhibitory effect of 5-hydroxytryptamine on the electrically induced twitch response of the rat vas deferens. Biochem. Pharmacol. 28:951–952.
Hay, D. W. P., and Wadsworth, R. M. 1982. The contractile effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine on the rat isolated vas deferens. Br. J. Pharmacol. 77:605–613.
Moritoki, H., Fukuda, H., Kanaya, J., and Ishida, Y. 1986. Ketanserin potentiates the prejunctional inhibitory effect of 5-hydroxytryptamine on rat vas deferens. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 38:737–741.
Moritoki, H., Iwamoto, T., Kanaya, J., Ishida, Y., and Fukuda, H. 1986. Age-related change in serotonin-mediated prejunctional inhibition of rat vas deferens. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 132:39–46.
Yu, P. H., Bailey, B. A., Durden, D. A., and Boulton, A. A. 1986. Stereospecific deuterium substitution at the α-carbon position of dopamine and its effect on oxidative deamination catalyzed by MAO-A and MAO-B from different tissues. Biochem. Pharmacol. 35:1027–1036.
Sokal, R. R., and Rohlf, F. J. 1981. Biometry. The Principles and Practice of Statistics in Biological Research, 2nd Ed., W. H. Freeman and Co., New York.
Björklund, A., Cegrell, L., Falck, B., Ritzén, M., and Rosengreen, E. 1970. Dopamine containing cells in sympathetic ganglia. Acta Physiol. Scand. 78:334–338.
Norberg, K.-A., Ritzén, M., and Ungerstedt, V. 1966. Histochemical studies on a special catecholamine—containing cell type in sympathetic ganglia. Acta Physiol. Scand. 67:260–270.
Thoenen, H., and Tranzer, J. P. 1968. Chemical sympathectomy by selective destruction of adrenergic nerve endings with 6-hydroxydopamine. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. Exp. Path. 261:271–288.
Laverty, R., Sharman, D. F., and Vogt, M. 1965. Action of 2,4,5-trihydroxyphenylethylamine on the storage and release of noradrenaline. Br. J. Pharmacol. Chemother. 24:549–560.
Mueller, R. A., Thoenen, H., and Axelrod, J. 1969. Adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase: compensatory increase in activity after chemical sympathectomy with 6-hydroxydopamine. Science 163:468–469.
Padawer, J. 1974. Mast cells: extended lifespan and lack of granule turnover under normal in vivo conditions. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 20:269–280.
Wingren, U., Wasteson, Å., and Enerbäck, L. 1983. Storage and turnover of histamine, 5-hydroxytryptamine and heparin in rat peritoneal mast cells in vivo. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immun. 70:193–199.
Ibrahim, M. Z. M., and Koshayan, D. S. 1981. The mast cells of the mammalian central nervous system. VIII. Uptake of35S and3H-5-hydroxytryptophan inside and outside the CNS. Cell Tissue Res. 220:529–538.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Celuch, S.M., Sloley, B.D. Regional distribution of dopamine, 5-hydroxytryptamine, and noradrenaline in the rat vas deferens. Neurochem Res 13, 967–972 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00970770
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00970770