Abstract
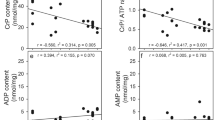
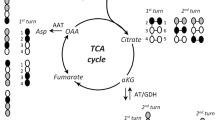
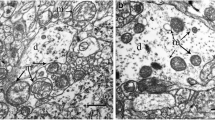
In attempts to distinguish between direct and indirect effects of Ca on brain cell metabolism, respiration, glycolysis, ATP, phosphocreatine, incorporation of [14C] leucine into protein, and accumulation of45Ca was determined in brain slices. Incubation was carried out in normal salt-balanced medium, in high-potassiumor ouabain-containing medium under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Calcium ions inhibited slightly glycolysis and respiration in normal medium and activated amino acid incorporation into proteins. Levels of ATP and phosphocreatine remained normal. These effects were interpreted as due to a stabilization of plasma membranes by Ca ions to prevent their spontaneous depolarization. Incubation of slices in high-potassium and ouabain media in aerobic conditions in the presence of Ca resulted in activation of respiration and glycolysis, decrease of ATP and phosphocreatine levels, and inhibition of amino acid incorporation into proteins. The disturbances in energy metabolism, caused by the respiration-linked Ca uptake in brain mitochondria and concomitant inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation, may lead to the inhibition of amino acid incorporation into proteins. An increase in Ca levels in the cytoplasm may only be expected in anaerobic conditions during the incubation in high-potassium and ouabain media. This is manifested by a direct inhibition of glycolysis by Ca ions and a drastic decrease of ATP and phosphocreatine in slices. The results suggest that stimulation of aerobic glycolysis and inhibition of anaerobic glycolysis by Ca may explain the unknown mechanism of the so-called “reversed Pasteur effect” of brain slices incubated in high-potassium media.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, P. E., 1972. Transport and metabolism of calcium ions in nerve. Progr. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 24:177–223.
Banay-Schwartz, M., Teller, D. N., Gergely, A., andLajtha, A. 1974. The effects of metabolic inhibitors on amino acid uptake and the levels of ATP, Na+ and K+ in incubated slices of mouse brain. Brain Res. 71:117–131.
Basi, M., andBarnelli-Zazzera, A. 1960. Effect of potassium ions on brain respiration and amino acid incorporation into brain proteins in vitro. Experientia 16:430.
Blaustein, M. P. 1974. The interrelationship between sodium and calcium fluxes across cell membranes. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 70:33–82.
Blaustein, M. P. 1975. Effects of potassium, veratridine and scorpion venom on calcium accumulation and transmitter release by nerve terminals in vitro. J. Physiol. 247:617–655.
Blaustein, M. P., andEctor, A. C. 1976. Carrier-mediated sodium-dependent and calcium-dependent calcium efflux from pinched-off presynaptic nerve terminals (synaptosomes) in vitro. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 419:295–308.
Brown, H. M., Pemberton, J. P., andOwen, J. D. 1976. A calcium-sensitive microelectrode suitable for intracellular measurement of calcium (II) activity. Anal. Chim. Acta 85:261–276.
Bull, R. J., andCummings, J. T. 1973. Influence of potassium on the steady-state redox potential of the electron transport chain in slices of rat cerbral cortex and the effect of ouabain. J. Neurochem. 21:913–937.
Carnay, L., andGrundfest, S. 1974. Excitable membrane stabilization by diphenylhydantoin and calcium. Neuropharmacology 13:1097–1108.
Charnock, J. S. 1963. The accumulation of calcium by brain cortex slices. J. Neurochem. 10:219–223.
Cohen, S. R. 1972. The estimation of extracellular space of brain tissue in vitro. Pages 179–219,in Marks, N., and Rodnight, R. (eds.), Research Methods in Neurochemistry, Vol. 1, Plenum Press, New York.
Cocke, W. J., andRobinson, J. D. 1971. Factors influencing calcium movements in rat brain slices. Am. J. Physiol. 221:218–225.
De Almeida, D. F., Chain, E. B., andPocchiari, F. 1965. Effect of ammonium and other ions on the glucose-dependent active transport ofl-histidine in slices of rat brain cortex. Biochem. J. 95:793–796.
De Belleroche, J. S., andBradford, H. F. 1972. Metabolism of beds of mammalian cortical synaptosomes: Response to depolarizing influences. J. Neurochem. 19:585–602.
Dickens, F., andGreville, G. D. 1935. The metabolism of normal and tumour tissue. XIII. Neutral salt effects. Biochem. J. 29:1468–1483.
Dunlop, D. S., van Elden, W., andLajtha, A. 1975. Optimal conditions for protein synthesis in incubated slices of rat brain. Brain Res. 99:303–318.
Glazer, R. I., andWeber, G. 1971. The effect ofl-phenylalanine and phenylpyruvate on glycolysis in rat cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 33:439–450.
Gordon, J., andLipmann, F. 1967. Role of divalent ions in poly U-directed phenylalanine polymerization. J. Mol. Biol. 23:23–33.
Hertz, L. 1973. Ion effects on metabolism in the adult mammalian brain in vitro. Evidence of a potassium-induced, stimulation of active uptake of KCl into neuroglial cell. Pages 1–207. F.A.D.L's Forlag A/S, Copenhangen.
Huttunen, M. O. 1969. Protein and ribonucleic acid metabolism in rat brain cortex slices. Thesis, Helsinki.
Huttunen, M. O. 1973. General model for the molecular events in synapses during learning. Persp. Biol. Med. 17:103–108.
Joanny, P., andHillman, H. 1964. Further studies on the potassium and sodium concentrations of mammalian cerebral slices in vitro. J. Neurochem. 11:413–422.
Katz, R. I., Chase, T. N., andKopin, I. J. 1969. Effect of ions on stimulus-induced release of amino acids from mammalian brain slices. J. Neurochem. 16:961–967.
Lahiri, S., andLajtha, A. 1964. Cerebral amino acid transport in vitro. I. Some requirements and properties of uptake. J. Neurochem. 11:77–86.
Lazarewicz, J. W., Haljamäe, H., andHamberger, A. 1974. Calcium metabolism in isolated brain cells and subcellular fractions. J. Neurochem. 22:33–45.
Lazarewicz, J. W., Kanje, M., Sellström, Å., andHamberger, A. 1977. Calcium fluxes in cultured and bulk isolated neuronal and glial cells. J. Neurochem. 29:495–502.
Lehninger, A. L. 1971. Mitochondria and the physiology of Ca2+. Trans. Am. Clin. Climatol. Assoc. 83:83–94.
Lehninger, A. L., Carafoli, E., andRossi C. 1967. Energy-linked ion movements in mitochondrial systems. Adv. Enzymol. 29:259–320.
Lolley, R. N. 1963. The calcium content of isolated cerebral tissue and their steadystate exchange of calcium. J. Neurochem. 10:665–676.
Lowry, O. H., Passoneau, J. V., Hasselberger, F. X., andSchulz, D. W. 1964. Effect of ischemia on known substrates and cofactors of the glycolytic pathway in brain. J. Biol. Chem. 239:18–30.
Mase, K., Takahashi, Y., andOgata, K. 1962. The incorporation of [14C]-glycine into the protein of guinea pig brain cortex slices. J. Neurochem. 9:281–288.
Mc Ilwain, H. 1952. Phosphates of brain during in vitro metabolism. Effects of oxygen glucose, glutamate, glutamine and calcium and potassium salts. Biochem. J. 52:289–295.
Mulder, A. H., Van Den Berg, W. B., andStoof, J. C. 1975. Calcium-dependent release of radiolabeled catecholamines and serotonin from rat brain synaptosomes in a superfusion system. Brain Res. 99:419–424.
Quastel, J. H. 1962. Effects of electrolytes on brain metabolism. Pages 226–237,in Elliott, K. A. C., Page, I. H., and Quastel, J. H. (eds.), Neurochemistry, Charles C. Thomas, Springfield.
Rao, K. N., de Smet, M., Howells, A. J., andBygrave, F. L. 1974. Inhibition by calcium of tRNA aminoacylation in preparations from rat liver. FEBS Lett. 41:185–188.
Rasmussen, H. 1970. Cell communication, calcium ion and cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Science 170:404–411.
Rossi, C. S., andLehninger, A. L. 1964. Stoichiometry of respiratory stimulation, accumulation of Ca++ and phosphate, and oxidative phosphorylation in rat liver mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 239:3971–3980.
Simkiss, K. 1974. Calcium translocation by cells. Endeavour 33:119–123.
Stahl, W. L., andSwanson, P. F. 1971. Movements of calcium and other cations in isolated cerebral tissues. J. Neurochem. 18:415–427.
Swanson, P. D. 1968. Effect of ouabain on acid-soluble phosphates and electrolytes of isolated cerebral tissues in presence and absence of calcium. J. Neurochem. 15:57–67.
Takagaki, G. 1968. Control of aerobic glycolysis and pyruvate kinase activity in cerebral cortex slices. J. Neurochem. 15:903–916.
Takemori, A. E. 1964. The influence of morphine on glucose utilization in cerebral preparations of rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 145:20–26.
Tower, D. B. 1968. Ouabain and the distribution of calcium and magnesium in cerebral tissues in vitro. Exp. Brain Res. 6:273–283.
Tsukada, Y., Nagata, Y., Hirano, S., andMatsutani, T. 1963. Active transport of amino acid into cerebral cortex slices. J. Neurochem. 10:241–256.
Vernie, L. N., Bont, W. S., andEmmelot, P. 1972. Differences in Mg2+ and Ca2+ dependence of amino acid incorporation by free and membrane-bound polyribosomes isolated from liver, and an effect of the hepatocarcinogen dimethylnitrosamine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 281:253–262.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Łazarewicz, J.W., Zalewska, T., Haljamäe, H. et al. Effect of calcium on brain metabolism in vitro. Neurochem Res 3, 683–698 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00965992
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00965992