Abstract
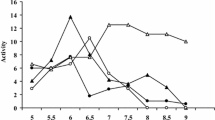
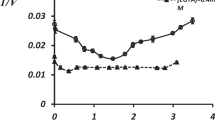
The rates of phosphate activated glutaminase activity in finely homogenised cerebral cortex and synaptosomes were measured. Activity was 25–50% higher at pH 7.0 than at pH 8.0. Glutamate inhibited activity with a Ki of 2–3 mM while aspartate had little effect. Calcium (1 mM) activated the enzyme but magnesium was without action. The pH profiles of the effects of these modulators of glutaminase activity in these finely ground preparations showed that all agents were more effective at pH 7.0 than at pH 8.0.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradford, H. F., Ward, H. K., andThomas, A. J. 1978. Glutamine—a major substrate for nerve endings. J. Neurochem. 30:1453–1459.
Hamberger, A. C., Chiang, G. H., Nylén, E. S., Scheff, S. W., andCotman, C. W. 1979. Glutamate as a CNS transmitter. I. Evaluation of glucose and glutamine as precursors for the synthesis of preferentially released glutamate. Brain Res. 168:513–530.
Reubi, J. C., Van Den Berg, C. J., andCuénod, M. 1978. Glutamine as precursor for the GABA and glutamate transmitter pools. Neurosci. Lett. 10:171–174.
Tapia, R., andGonzález, R. M. 1978. Glutamine and glutamate as precursors of the releasable pool of GABA in brain cortex slices. Neurosci. Lett. 10:165–169.
Kvamme, E., andLenda, K. 1982. Regulation of glutaminase by exogenous glutamate, ammonia and 2-oxoglutarate in synaptosomal enriched preparation from rat brain. Neurochem. Res. 7:667–678.
Benjamin, A. M. 1981. Control of glutaminase activity in rat brain cortex in vitro: Influence of glutamate, phosphate, ammonium, calcium and hydrogen ions. Brain Res. 208:363–377.
Bradford, H. F., andWard, H. K. 1976. On glutaminase activity in mammalian synaptosomes. Brain Res. 110:115–125.
Weil-Malherbe, H. 1969 Activators and inhibitors of brain glutaminase. J. Neurochem. 16:855–864.
Kvamme, E., Svenneby, G., andTorgner, I. AA. 1983 Calcium stimulation of glutamine hydrolysis in synaptosomes from rat brain. Neurochem. Res. 8:23–36.
Bradford, H. F., Bennet G. W., andThomas, A. J. 1973. Depolarizing stimuli and the release of physiologically active amino acids from suspensions of mammalian synaptosomes. J. Neurochem. 21:495–505.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., andRandall, R. J. 1951. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193:265–275.
Kvamme, E., andLenda, K. 1981. Evidence for compartmentalization of glutamate in rat brain synaptosomes using the glutamate sensitivity of phosphate-activated glutaminase as a functional test. Neurosci. Lett. 25:193–198.
Edsall, J. T., andWyman, J. 1958. Page 452,Biophysical Chemistry Vol I Academic Press, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Henry McIlwain.