Summary
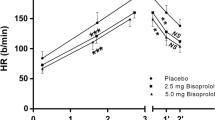
Previous studies have shown that the intrinsic heart rate (IHR) may undergo changes, e.g., decrease after long-term endurance training. The mechanism for this adaptation is not known. In this study, rats were subjected to long-term oral treatment with the beta receptor stimulating drug prenalterol. During the treatment period heart rates at rest and during submaximal exercise were measured. Heart rate after 30 min rest and also 2 min after exercise was higher in the treated animals, due to the beta stimulation. The treated rats had a significantly lower heart rate increase during exercise than untreated controls, consistent with a partial beta-blocking effect of the drug in states with a high endogenous sympathetic activity. Therefore, the animals were not trained but only exposed to the increased stimulation of cardiac beta receptors accomplished by the drug while at rest. After 25 weeks, prenalterol was withdrawn and the IHR was measured in situ after a denervation procedure. The treatment with prenalterol had not altered the IHR. Our previous results from training studies indicate that a heart rate increase above a certain level or the stimulation of cardiac beta receptors are not the main stimuli for a lower setting of the IHR as seen after endurance training. In this study chronic beta receptor stimulation with prenalterol did not influence the IHR, which supports that hypothesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnard RJ, Corre K, Cho H (1976) Effect of training on the resting heart rate of rats. Eur J Appl Physiol 35: 285–289
Bolter CP, Hughson RL, Critz JB (1973) Intrinsic rate and cholinergic sensitivity of isolated atria from trained and sedentary rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 144: 364–367
Corre KA, Cho H, Barnard RJ (1976) Maximum exercise heart rate reduction with maturation in the rat. J Appl Physiol 40: 741–744
Dahlström U, Atterhög J-H, Jorfeldt L (1983) Hemodynamics and leg muscle metabolism at rest and during exercise in young healthy volunteers after intravenous prenalterol. Clin Pharmacol Ther 33: 701–709
De Champlain J, van AmeringenMR (1972) Regulation of blood pressure by sympathetic nerve fibres and adrenal medulla in normotensive and hypertensive rats. Circ Research 31: 617–628
Frick MH, Elovainio RO, Somer T (1967) The mechanism of bradycardia evoked by physical training. Cardiologia 51: 46–54
Gauthier P, Nadeau R, de Champlain J (1972) Acute and chronic cardiovascular effects of 6-hydroxydopamine in dogs. Circ Res 31: 207–217
Harri MNE, Narvola I (1979) Physical training under the influence of beta blockade in rats: Effects on adrenergic responses. Eur J Appl Physiol 41: 199–210
Harri M, Kuusela P (1982) Effects of the adrenergic nervous system on training-induced cardiac enlargement and on the intrinsic rate and phenylephrine sensitivity of isolated rat atria. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 60: 1125–1130
Harri M, Kuusela P, Oksanen-Rossi R (1982) Modification of training-induced responses by repeated norepinephrine injections in rats. J Appl Physiol 53: 665–670
Hedberg A, Carlsson E, Fellenius E, Lundgren B (1982) Cardiostimulatory effects of oral prenalterol, a beta-1 adrenoceptor selective partial agonist, in vivo and in vitro. Correlation between physiological effects and adenylate cyclase activity. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 318: 185–191
Hjalmarson å, Abelardo N, Caidahl K, Reyes C, Waagstein F, Wallentin I, Wikstrand J (1982) Effects of prenalterol administered orally in patients with congestive heart failure. Acta Med Scand [Suppl] 659: 201–220
Hughson RL, Sutton JR, Fitzgerald JD, Jones NL (1977) Reduction of intrinsic sinoatrial frequency and norepinephrine response of the exercised rat. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 55: 813–820
Kenakin TD, Beek D (1980) Is prenalterol (H133/80) really a selective beta 1 adrenoceptor agonist? Tissue selectivity resulting from differences in stimulus-response relationships. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 213: 406–413
Lewis SF, Nylander E, Gad P, Areskog N-H (1980) Non-autonomic component in bradycardia of endurance trained men at rest and during exercise. Acta Physiol Scand 109: 297–305
Manders WT, Vatner SF, Braunwald E (1980) Cardioselective beta adrenergic stimulation with prenalterol in the conscious dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 215: 266–270
Mattson H, Hedberg A, Carlsson E (1982) Basic pharmacological properties of prenalterol. Acta Med Scand [Suppl] 659: 9–37
Nadeau RA, de Champlain J, Tremblay CM (1971) Supersensitivity of the isolated rat heart after chemical sympathectomy with 6-hydroxydopamine. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 49: 36–44
Nylander E (1981) Effect of beta-adrenergic receptor blockade on development of training-induced bradycardia in rats. Acta Physiol Scand 112: 449–454
Nylander E, Areskog N-H (1982) New aspects on training bradycardia. Upsala J Med Sci 87: 1–10
Nylander E, Sigvardsson K, Kilbom å (1982) Training-induced bradycardia and intrinsic heart rate in rats. Eur J Appl Physiol 48: 189–199
Shipley RE, Tilden JH (1947) A pithed rat preparation suitable for assaying pressor substances. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 64: 453–455
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nylander, E., Dahlström, U. Influence of long-term beta receptor stimulation with prenalterol on intrinsic heart rate in rats. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 53, 48–52 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00964689
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00964689