Abstract
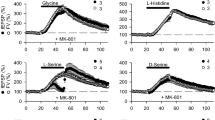
The release of previously accumulated [3H]taurine and [14C]GABA from crude synaptosomal (P2) fractions isolated from rat cerebral cortex was studied using a superfusion system. The spontaneous efflux of [3H]taurine and [14C]GABA was stimulated by elevated concentrations of K+ (15–133 mM) in a concentration-dependent manner. This K+-stimulated release of [14C]GABA but not of [3H]taurine was enhanced in the presence of Ca2+. However, addition of 3 mM Ca2+ to the superfusion medium in the presence of the ionophore A 23187 resulted in a stimulation of the release of both [3H]taurine and [14C]GABA. These results are discussed in connection with the cellular localization of tourine in the central nervous system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbeau, A., andHuxtable, R. (eds.) 1978. Taurine and Neurological Disorders, Raven Press, New York.
Blaustein, M. P., Johnson, E. R., Jr., andNeedleman, P. 1972. Calcium dependent norepinephrine release from presynaptic nerve endings in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., U.S.A. 69:2237–2240.
Borg, J., Balcar, V. J., andMandel, P. 1976. High affinity uptake of taurine in neuronal and glial cells. Brain Res. 118:514–516.
Clark, R. M., andCollins, G. G. S. 1976. The release of endogenous amino acids from the rat visual cortex. J. Physiol. 262:383–400.
Collins, G. G. S., andTopiwala, S. H. 1974. The release of [14C]-taurine from slices of rat cerebral cortex and spinal cord evoked by electrical stimulation and high potassium ion concentrations. Br. J. Pharmacol. 50:451–452.
Cotman, C. W., Herschman, H., andTaylor, D. 1971. Subcellular fractionation of cultured flial cells. J. Neurobiol. 2:169–180.
Cotman, C. W., Haycock, J. W., andFrost White, W. 1976. Stimulus-secretion coupling processes in the brain: analysis of noradrenaline and gamma-aminobutyric acid release. J. Physiol. 254:475–505.
Curtis, D. R., andWatkins, J. C. 1965. The pharmacology of amino acids related to γ-aminobutyric acid. Pharmacol. Rev. 17:347–391.
de Belleroche, J. S., andBradford, H. F. 1973. Amino acids in synaptic vesicles from mammalian cerebral cortex: A reappraisal. J. Neurochem. 21:441–451.
Ehinger, B. 1973. Glial uptake of taurine in the rabbit retina. Brain Res. 60:512–516.
Hammerstad, J. P., Murray, J. E., andCutler, R. W. P. 1971. Efflux of amino acid neurotransmitters from rat spinal cord slices. II. Factors influencing the electrically induced efflux of [14C]glycine and [3H]GABA. Brain Res. 35:357–367.
Henn, F. A., andHamberger, A. 1971. Glial cell function: Uptake of transmitter substances. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 68:2686–2690.
Henn, F. A., Goldstein, M. N., andHamberger, A. 1974. Uptake of the neurotransmitter candidate glutamate by glia. Nature 249:663–664.
Hruska, R. E., Padjen, A., Bressler, R., andYamamura, H. I. 1978. Taurine: Sodium-dependent, high-affinity transport into rat brain synaptosomes. Mol. Pharmacol. 14:77–85.
Huxtable, R., andBarbeau, A. (eds.) 1976. Taurine, Raven Press, New York.
Jacobsen, J. G., andSmith, L. H. 1968. Biochemistry and physiology of taurine and taurine derivatives. Physiol. Rev. 48:425–511.
Jasper, H. H., andKoyama, I. 1969. Rate of release of amino acids from the cerebral cortex in the cats as affected by brainstem and thalamic stimulation. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 47:889–905.
Kaczmarek, L. K., andDavison, A. N. 1972. Uptake and release of taurine from rat brain slices. J. Neurochem. 19:2355–2362.
Kontro, P., andOja, S. S. 1978. Sodium dependence of taurine in rat brain synaptosomes. Neuroscience 3:761–765.
Lähdesmäki, P., Pasula, M., andOja, S. S. 1975. Effect of electrical stimulation and chlorpromazine on the uptake and release of taurine, γ-aminobutyric acid and glutamic acid in mouse brain synaptosomes. J. Neurochem. 25:675–680.
Levi, G., Roberts, P. J., andRaiteri, M. 1976. Release and exchange of neurotransmitters in synaptosomes: effects of the ionophore A 23187 and of ouabain. Neurochem. Res. 1:409–416.
McBride, W. J., Nadi, N. S., Altman, J., andAprison, M. H. 1976. Effects of selective doses of X-irradiation on the levels of several amino acids in the cerebellum of the rat. Neurochem. Res. 1:141–152.
McCaman, R., andStetzler, J. 1977. Determination of taurine in individual neurones ofAplysia california. J. Neurochem. 29:739–741.
McLennan, H. 1976. The autoradiographic localization ofl-[3H]glutamate in rat brain tissue. Brain Res. 115:139–144.
Minchin, M. C. W., andIversen, L. L. 1974. Release of [3H]gamma-aminobutyric acid from glial cells in rat dorsal root ganglia. J. Neurochem. 23:533–540.
Mulder, A. H., andSnyder, S. H. 1974. Potassium-induced release of amino acids from cerebral cortex and spinal cord slices of the rat. Brain Res. 76:297–308.
Oja, S. S., andLähdesmäki, P. 1974. Is taurine an inhibitory neurotransmitter? Med. Biol. 52:138–143.
Pasantes-Morales, H., Urban, P. F., Klethi, J., andMandel, P. 1973. Light stimulated release of [35S]-taurine from chicken retina. Brain Res. 51:375–378.
Placheta, P., Singer, E., Schönbeck, G., Heckl, K., andKarobath, M. 1979. Reduction of endogenous level, uptake and release of taurine after intrastriatal kainic acid injection. Neuropharmacology 18:399–402.
Pressman, B. C. 1973. Properties of ionophores with broad range cation selectivity. Fed. Proc. 32:1698–1703.
Raiteri, M., Angelini, F., andLevi, G. 1974. A simple apparatus for studying the release of neurotransmitters from synaptosomes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 25:411–414.
Redburn, D. A., Shelton, D., andCotman, C. W. 1976. Calcium-dependent release of exogenously loaded γ-amino-[U-14C]butyrate from synaptosomes: Time course of stimulation by potassium, veratridine, and the calcium ionophore A 23187. J. Neurochem. 26:297–303.
Richelson, E., andThompson, E. J. 1973. Transport of neurotransmitter precursors into cultured cells. Nature (London), New Biol. 241:201–204.
Rubin, R. P. 1970. The role of calcium in the release of neurotransmitter substances and hormones. Pharmacol. Rev. 22:389–428.
Schmid, R. Sieghart, W., andKarobath, M. 1975. Taurine uptake in synaptosomal fractions of rat cerebral cortex. J. Neurochem. 25:5–9.
Schon, F., andKelly, J. S. 1974. Autoradiographic localization of [3H]GABA and [3H]glutamate over satellite glial cells. Brain Res. 66:275–288.
Schrier, B. K., andThompson, E. J. 1974. On the role of glial cells in the mammalian nervous system. Uptake, excretion and metabolism of putative neurotransmitters by cultured glial tumor cells. J. Biol. Chem. 249:1769–1780.
Sellström, A., andHamberger, A. 1975. Neuronal and glial systems for γ-aminobutyric acid transport. J. Neurochem. 24:847–852.
Sellström, A., andHamberger, A. 1977. Potassium-stimulated γ-aminobutyric acid release from neurons and glia. Brain Res. 119:189–198.
Sieghart, W., andKarobath, M. 1974. Evidence for specific synaptosomal localization of exogenous accumulated taurine. J. Neurochem. 23:911–915.
Sieghart, W., andHeckl, K. 1976. Potassium-evoked release of taurine from synaptosomal fractions of rat cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 116:538–543.
Sieghart, W., andKarobath, M. 1976. Uptake of taurine into subcellular fractions of C-6 glioma cells. J. Neurochem. 26:981–986.
Sieghart, W., Sellström, A., andHenn, F. 1978. Sedimentation characteristics of subcellular vesicles derived from three glial systems. J. Neurochem. 30:1587–1589.
Weinreich, D., andHammerschlag, R. 1975. Nerve impulse-enhanced release of amino acids from nonsynaptic regions of peripheral and central nerve trunks of bullfrog. Brain Res. 84:137–143.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Placheta, P., Singer, E., Sieghart, W. et al. Properties of [3H]taurine release from crude synaptosomal fractions of rat cerebral cortex. Neurochem Res 4, 703–712 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00964467
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00964467