Conclusions
-
1.
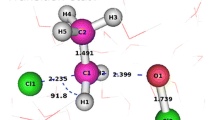
The sections of the potential energy surface (PES) for the model reaction Cl− +
in the gas phase and in aqueous solution were calculated by the quantum chemical MCSCF/VB method.
-
2.
Hydration increases the distance between the reagents in the prereaction complex and decreases the depth of the corresponding minimum on the PES but does not alter the path of movement of the reagents during the reaction and the geometry of the transition state.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
K. Ya. Burshtein and A. N. Isaev, Zh. Strukt. Khim.,25, 25 (1984).
K. Ya. Burshtein and A. N. Isaev, Theor. Chim. Acta,64, 397 (1984).
D. K. Bohme and G. J. Mackay, J. Am, Chem. Soc.,103, 978 (1981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Izvestiya Akademii Nauk SSSR, Seriya Khimicheskaya, No. 9, pp. 2005–2009, September, 1987.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burshtein, K.Y., Isaev, A.N. Quantum-chemical study of the effect of the solvent on the mechanism of nucleophilic substitution reactions which take place according to the Sn2 mechanism. Russ Chem Bull 36, 1858–1861 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00958330
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00958330