Abstract
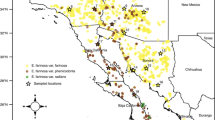
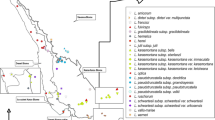
Nuclear DNAs extracted from individuals of the kelpCostaria costata (Phaeophyta) were studied using a small-subunit ribosomal DNA probe (pCc 18). On the basis of annealing analysis of rDNA variation within and among individuals and between populations, polymorphisms detected by pCc 18 appeared to indicate population identity. These rDNA polymorphisms were used to chart the distribution ofCostaria breeding groups in the northeast Pacific. 20 sites were sampled and eight distinct populations resolved. One variant (Variant A) identified a southern group with plants from 13, loosely clustered sites sharing this banding pattern. The other seven variants, found in the northern portion of the study area, were unique and population-specific.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, E. K., North, W. K., 1966: In situ studies of spore production and dispersal in the giant kelpMacrocystis. — Proc. 5th Int. Seaweed Symp.5: 73–86.
Angst, L., 1927: Gametophytes ofCostaria costata. — Publ. Puget Sd. Biol. Sta.5: 293–307.
Bhattacharya, D., 1988: Molecular biological analysis of morphological variation, populations and phylogeny of the kelpCostaria costata (Phaeophyta). — Ph.D. Thesis, Burnaby: Simon Fraser University.
—,Druehl, L. D., 1988: Phylogenetic comparison of the small-subunit ribosomal DNA sequence ofCostaria costata (Phaeophyta) with those of other algae, vascular plants andOomycetes. — J. Phycol.24: 539–543.
Clague, J. J., 1981: Late quaternary geology and geochronology of British Columbia. 2: Summary and discussion of radiocarbon-dated quaternary history. — Geol. Surv. Canada Paper80–85: 1–41.
Dayton, P. K., 1973: Dispersion, dispersal, and persistence of the annual intertidal algaPostelsia palmaeformis Ruprecht. — Ecology54: 433–438.
Dover, G., 1982: Molecular drive: a cohesive mode of species evolution. — Nature299: 111–117.
Druehl, L. D., 1970: The pattern ofLaminariales distribution in the northeast Pacific. — Phycologia9: 237–247.
—, 1981: The distribution ofLaminariales in the north Pacific with reference to environmental influences. — Proc. 2nd Int. Cong. Syst. Evol. Biol.2: 55–67.
Fain, S. R., Druehl, L. D., Baillie, D. L., 1988: Repeat and single copy sequences are differentially conserved in the evolution of kelp chloroplast DNA. — J. Phycol.24: 292–302.
Flavell, R. B., O'Dell, M., Sharp, P., Nevo, E., Beiles, A., 1986: Variation in the ribosomal DNA of wild wheat,Triticum dicococcoides, in Israel. — Mol. Biol. Evol.3: 547–558.
Ingle, J., Timmis, J. N., Sinclair, J., 1975: The relationship between satellite deoyribonucleic acid, ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene redundancy, and genome size in plants. — Pl. Physiol.55: 496–501.
Jorgensen, R. A., Cuellar, R. E., Thompson, W. F., Kavanagh, T. A., 1987: Structure and variation in ribosomal RNA genes of pea. — Pl. Mol. Biol.8: 3–12.
Kain, J. M., 1964: Aspects of the biology ofLaminaria hyperborea. 3. Survival and growth of gametophytes. — J. Mar. Biol. Ass. U.K.44: 415–433.
—, 1969: The biology ofLaminaria hyperborea. 5. Comparison with early stages of competitors. — J. Mar. Biol. Ass. U.K.49: 455–473.
Learn, G. H., Jr.,Schaal, B. A., 1987: Population subdivision for ribosomal DNA repeat variants inClematis fremontii. — Evolution41: 433–438.
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E. F., Sambrook, J., 1982: Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual. — Cold Spring Harbor, New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory.
Matsch, C. L., 1976: North America and the great ice age. — New York: McGraw-Hill.
Mathews, W. H., Fyles, J. G., Nasmith, H. W., 1970: Postglacial crustal movements in southwestern British Columbia and adjacent Washington State. — Canad. J. Earth Sci.7: 690–702.
Moss, B. L., Tovey, D., Court, P., 1981: Kelps as fouling organisms on North Sea platforms. — Bot. Marina24: 207–209.
Mullineaux, D. R., Waldron, H. H., Rubin, M., 1965: Stratigraphy and chronology of late interglacial and early Vashon glacial time in the Seattle area, Washington. — U.S. Geol. Surv.1194-0.
Obrien, S. C. P., 1972: Morphological variation ofCostaria Greville in southwest British Columbia coastal waters. — M. Sc. Thesis, Burnaby: Simon Fraser University.
Oono, K., Sugiura, M., 1980: Heterogeneity of the ribosomal RNA gene clusters in rice. — Chromosoma76: 85–89.
Pace, N. R., Olsen, G. J., Woese, C. R., 1986: Ribosomal RNA phylogeny and the primary lines of evolutionary descent. — Cell45: 325–326.
Polans, N. O., Weeden, N. F., Thompson, W. F., 1986: Distribution, inheritence and linkage relationships of ribosomal DNA spacer length variants in pea. — Theor. Appl. Genet.72: 289–295.
Rigby, P. W. J., Dieckmann, M., Rhodes, C., Berg, P., 1977: Labelling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. — J. Mol. Biol.113: 237–251.
Rogers, S. O., Bendich, A. J., 1987a: Heritability and variability in ribosomal RNA genes ofVicia faba. — Genetics117: 285–295.
—, 1987b: Ribosomal RNA genes in plants: Variability in copy number and in the intergenic spacer. — Pl. Molec. Biol.9: 509–520.
Round, F. E., 1981: The ecology of algae. — Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Saghai-Maroof, M. A., Soliman, K. M., Jorgensen, R. A., Allard, R. W., 1984: Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: Mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location, and population dynamics. — Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.81: 8014–8018.
Schaal, B. A., Leverich, W. J., 1987: Ribosomal DNA variation in the native plantPhlox divaricata. — Molec. Biol. Evol.4: 611–621.
Smith, G. E., Summers, M. D., 1980: The bidirectional transfer of DNA and RNA to nitrocellulose or DBM paper. — Anal. Biochem.109: 123–129.
Sundene, O., 1962: The implications of transplant and culture experiments on the growth and distribution ofAlaria esculenta. — Nytt. Mag. Bot.9: 155–174.
Systma, K. J., Schaal, B. A., 1985: Phylogenetics of theLisianthus skinneri (Gentianaceae) species complex in Panama utilizing DNA restriction fragment analysis. — Evolution39: 594–608.
Thomson, R. E., 1981: Oceanography of the British Columbia coast. — Canad. Spec. Publ. Fish. Aquat. Sci.56: 1–291.
Van den Hoek, C., 1987: The possible significance of long-range dispersal for the biogeography of seaweeds. — Helgolander Meeresunters.41: 261–272.
Worton, R. G., Sutherland, J., Sylvester, J. E., Willard, H. F., Bodrug, S., Dube, I., Duff, C., Kean, V., Ray, P. N., Schmickel, R. D., 1988: Human ribosomal RNA genes: orientation of the tandem array and conservation of the 5′ end. — Science239: 64–68.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhattacharya, D., Baillie, D.L. & Druehl, L.D. Population analysis of the kelpCostaria costata (Phaeophyta) using a polymorphic ribosomal DNA probe. Pl Syst Evol 170, 177–191 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00937702
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00937702