Summary
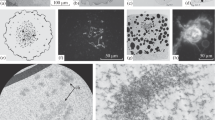
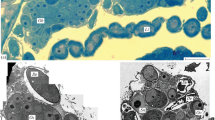
Octagonal symmetry in the pore margin has been demonstratedin situ in annulate lamellae and the nuclear envelope of germ cells. The annular material is located to variable extent within the pore and also extends beyond the pore margin; in the latter case it may be continuous with extra-pore annular material of some adjacent pores. In thin sections of fixed material, the annular material of both the nuclear envelope and annulate lamellae appears to be composed of a matrix within which are embedded thin filaments and small granules, the disposition and interrelationship of which are described and discussed. The so-called intra-annular granule is described as consisting of a number of smaller units (similar to the granular component of the annular material) which become aggregated in the center of some pores in both the nuclear envelope and annulate lamellae. The possible significance of intra-annular granules is discussed in terms of binding and movement of macromolecules.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afzelius, B.A.: The ultrastructure of the nuclear membrane of the sea urchin oocyte as studied with the electron microscope. Exp. Cell Res.8, 147–158 (1955).
—: Electron microscopy on the basophilic structures of the sea urchin egg. Z. Zellforsch.45, 660–675 (1957).
Bretschneider, L.H.: The electron-microscopic investigations of tissue sections. Int. Rev. Cytol.1, 305–322 (1952).
Callan, H. G., andS. G. Tomlin: Experimental studies on amphibian oocyte nuclei by means of the electron microscope, I. Investigation of the structure of the nuclear membrane. Proc. roy. Soc. B137, 367–378 (1950).
Du Praw, E. J.: The organization of nuclei and chromosomes in honeybee embryonic cells. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.)53, 161–168 (1965).
Esser, K.: Elektronenmikroskopisch-cytochemische Untersuchungen an der Kernmembran vonStreptotheca thamesis. Experientia (Basel)24, 61–62 (1968).
Feldherr, C.M.: The nuclear annuli as pathways for nucleocytoplasmic exchanges. J. Cell Biol.14, 65–72 (1962).
—: Binding within the nuclear annuli and its possible effect on nucleocytoplasmic exchanges. J. Cell Biol.20, 188–191 (1964).
—: The effect of the electron-opaque pore material on exchanges through the nuclear annuli. J. Cell Biol.25, 43–54 (1965).
Friend, D.S., andM.G. Farquhar: Functions of coated vesicles during protein absorption in the rat vas deferens. J. Cell Biol.35, 357–376 (1967).
Gall, J. G.: Observations on the nuclear membrane with the electron microscope. Exp. Cell Res.7, 197–200 (1954).
—: Electron microscopy of the nuclear envelope. Protoplasmatologia5, 4–25 (1964).
—: Octagonal nuclear pores. J. Cell Biol.32, 391–400 (1967).
Hartmann, J.F.: An electron optical study of sections of central nervous system. J. comp. Neurol.99, 201–250 (1953).
Karnovsky, M.J.: A formaldehyde-glutaraldehyde fixative of high osmolality for use in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol.27, 137 A (1965).
Kessel, R. G.: Electron microscope studies on the origin of annulate lamellae in oocytes ofNecturus. J. Cell Biol.19, 391–414 (1963).
—: Intranuclear annulate lamellae in oocytes of the tunicate,Styela partita. Z. Zellforsch.63, 37–51 (1964).
—: Intranuclear and cytoplasmic annulate lamellae in tunicate oocytes. J. Cell Biol.24, 471–487 (1965).
—: Fine structure of annulate lamellae. J. Cell Biol.36, 658–664 (1968a).
- Annulate lamellae. J. Ultrastruct. Res., Suppl. 10 (1968b).
—: Octagonal pores in annulate lamellae ofRana pipiens oocytes. Proc. 26th Ann. Meeting Electron Micros. Soc. Amer. (C. J. Arceneaux, editor), pp. 132–133. Baton Rouge, Louisiana: Claitor's Publishing Division 1968c.
Krishan, A., D. Hsu, andP. Hutchins: Hypertrophy of granular endoplasmic reticulum and annulate lamellae in Earle's L cells exposed to vinblastine sulfate. J. Cell Biol.39, 211–216 (1968).
Luft, J.H.: Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol.9, 409–414 (1961).
Merriam, R. W.: The origin and fate of annulate lamellae in maturing sand dollar eggs. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol.5, 117–122 (1959).
—: On the structure and composition of the nuclear envelope. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol.11, 559–570 (1961).
Reynolds, E. S.: The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol.17, 208–211 (1963).
Sjöstrand, F. S., andJ. Rhodin: The ultrastructure of the proximal convoluted tubules of the mouse kidney as revealed by high resolution electron microscopy. Exp. Cell Res.4, 426–456 (1953).
Watson, M.L.: The nuclear envelope. Its structure and relation to cytoplasmic membranes. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol.1, 257–270 (1955).
—: Staining of tissue sections for electron microscopy with heavy metals. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol.4, 474–478 (1958).
—: Further observations on the nuclear envelope of the animal cell. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol.6, 147–156 (1959).
Wischnitzer, S.: An electron microscope study of the nuclear envelope of amphibian oocytes. J. Ultrastruct. Res.1, 201–222 (1958).
Yoo, B.Y., andS.T. Bayley: The structure of pores in isolated pea nuclei. J. Ultrastruct. Res.18, 651–660 (1967).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This investigation was supported by research grants (HD-00699, GM-09229) and a Career Development Award from the National Institutes of Health, U. S. Public Health Service. The author acknowledges the skillful technical assistance of Mrs.Robert Decker.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kessel, R.G. Fine structure of the pore-annulus complex in the nuclear envelope and annulate lamellae of germ cells. Z.Zellforsch 94, 441–453 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00936051
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00936051