Summary
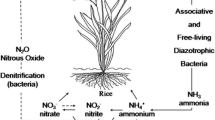
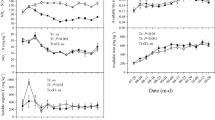
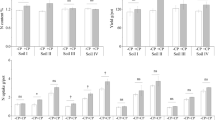
In situ measurements of nitrogenase activities in some rice soils, representing three different agroclimatic zones of Sri Lanka, demonstrated that there is a great potential for nitrogen fixation in these paddy soils, provided that they are continuously flooded and that nitrogenous fertilizer levels are relatively low. Under such conditions cyanobacterial (blue-green algal) fixation predominates. In certain areas of the wet zone, with highly organic soils, cyanobacterial fixation could probably meet a great part of the N-fertilizer input recommended. Heterotrophic rhizosphere fixation may also be significant, especially in the dry zone. Low concentrations of fertilizer-N were found to stimulate cyanobacterial numbers and total nitrogen fixation, at one site (dry zone), whereas high levels negatively affected total fixation at all sites investigated. In the absence of N-fertilizers, inoculation as well as additions of Mo, increased cyanobacterial numbers, nitrogen fixation activity and available ammonia levels substantially at the investigated site (dry zone). Rice grain yields did not vary significantly between treatments, because of too large a heterogeneity in the field with respect to water management.
Resumé
Des mesuresin situ d'activité de nitrogénase dans quelques sols de rizière, représentant trois zones agro-climatiques différentes du Sri Lanka, ont démontré qu'il y a une grande potentialité pour la fixation d'azote dans ces sols, pourvu qu'ils soient continuellement inondés et que le niveau de fertilisation azotée soit relativement bas. Dans ces conditions, la fixation par les cyanobactéries (algues bleu-vertes) prédomine. Dans certaines régions de la zone humide, aux sols à forte teneur en matière organique, la fixation par les cyanobactéries puet probablement satisfaire une grande partie du besoin recommandé en fertilisant azoté. La fixation par la rhizosphère hétérotrophe peut, elle aussi, être significative, surtout dans la zone sèche. Des concentrations faibles en fertilisant azoté ont révélé stimuler le nombre de cyanobactéries et la fixation totale d'azote, sur un site (zone sèche), tandis que des teneurs élevées affectaient négativement la fixation totale sur tous les sites étudiés. En absence de fertilisant azoté, l'inoculation ainsi que l'ajout de Mo ont augmenté le nombre de cyanobactéries, l'activité fixatrice d'azote et le niveau d'ammoniaque disponible, de manière substantielle sur le site étudié (zone sèche). Le rendement en graines de riz n'a pas varié de manière significative d'un traitment à l'autre, à cause d'une hétérogénéité trop grande sur le champ en matière de gestion d'eau.
Resumen
Medidas ‘in situ’ de las actividades nitrogenàsicas de algunos suelos arroceros representativos de tres zonas agroclimáticas distintas de Sri Lanka demostraron que existe un potencial considerable para la fijación de nitrógeno en estos suelos encharacados siempre y cuando permanezcan bajo el agua y la fertilización nitrógenada se mantenga relativamente baja. En estas condiciones la fijación predominante es la realizada por cianobacterias (algas verdeazules). En algunas areas de la zona húmeda con suelos muy orgánicos la fijación mediante cianobacterias podría suministrar una gran parte del aporte en nitrógeno recomendado. La fijación heterotrófa en la rizosfera puede también representar un aporte significativo, especialmente en la zona seca. Bajas concentraciones de fertilizante nitrogenado estimularon el número de cianobacterias y la fijación de nitrógeno total en uno de los suelos estudiados (zona seca) mientras que niveles elevados afectaron negativamente a la fijación en todos los suelos estudiados. En ausencia de fertilizantes nitrógenados la inoculación así como adiciones de Mo incrementaron sustancialmente el número de cianobacterias, la actividad fijadora de nitrógeno y los niveles de amonio disponibles en el suelo estudiado (zona seca). La cosecha de arroz no varió significativamente entre los distintos tratamientos debido a la excesiva heterogeneidad en el uso del agua.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anon. 1979 Report on the FAO/IAEA international Symposium on the Use of Isotopes and Radiation in Research on Soil-Plant relationships. Colombo, Sri Lanka, December 1978.FAO/IAEA Soils Newsletter 2, 19–24.
Anon. 1970IAEA Technical Report Series 108, 1–184.
Basilier, K. 1980 Fixation and uptake of nitrogen inSphagnum blue-green algal associations.Oikos 34, 239–242.
Becking, J. H. 1971 Biological nitrogen fixation and its economic significance. InNitrogen-15 in Soil-Plant Studies, Proceedings of a Research Co-ordination Meeting, Sofia 1–5 December 1969. IAEA Panel Proceedings series, STI/PUB278 189–222.
Becking, J. H. 1978Beijerinckia in irrigated rice soils. InEnvironmental Role of Nitrogen-fixing Blue-green Algae and Asymbiotic Bacteria. Ecological Bulletins, ed. Granhall, U. Swedish Natural Science Research Council, Liber Tryck, Stockholm26, 166–169.
Benemann, J. R. 1979 Production of nitrogen fertilizer with nitrogen-fixing blue-green algae.Enzyme Microbiology Technology 1, 83–90.
Bouldin, D. R. &Alimagno, B. V. 1976NH 3 Volatilization Losses from IRRI Paddies Following Broadcast Applications of Fertilizer Nitrogen. Los Baños, Philippines: Int. Rice Res. Inst.
Burns, R. C. &Hardy, R. W. F. 1975Nitrogen Fixation in Bacteria and Higher Plants. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Charyulu, P. B. B. N. &Rajaramamohan Rao, V. 1981 Influence of ammonium nitrogen on nitrogen fixation in paddy soils.Soil Science 131, 140–144.
Craswell, E. T. &Vlek, P. L. G. 1979 Fate of fertilizer nitrogen applied to watland rice. InNitrogen and Rice, pp. 175–193: Los Baños Philippines: Int. Rice Res. Inst.
De, P. K. 1936 The problems of the nitrogen supply of rice. 1. Fixation of nitrogen in the rice soils under waterlogged conditions.Indian Journal of Agricultural Science 6, 1237–1245.
de Datta, S. K., Magnaye, C. P. &Moomaw, J. C. 1968 Efficiency of fertilizer nitrogen (15-labelled) for flooded rice.Transactions 9th International Soil Science Congress, Adelaide, Australia,4, 67–76.
Diem, G., Rougier, M., Hamad-Fares, I., Balandreau, J. P. &Dommergues, Y. R. 1978 Colonization of rice roots by diazotrophic bacteria. InEnvironmental Role of Nitrogen-fixing Blue-green Algae and Asymbiotic Bacteria. Ecological Bulletins, ed. Granhall, U. Swedish Natural Science Research Council, Liber Tryck, Stockholm26, 305–311.
Dommergues, Y. R. &Rinaudo, G. 1979 Factors affecting N2 fixation in the rice rhizosphere. InNitrogen and Rice, pp 241–261. Los Baños, Philippines: Int. Rice Res. Inst.
Döbereiner, J. 1977 Biological nitrogen fixation in tropical grasses—possibilities for partial replacement of mineral N fertilizers.Ambio (Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences)6, 174–177.
Döbereiner, J., Burris, R. H. &Hollaender, A. (eds) 1978Limitations and Potentials for Biological Nitrogen Fixation in the Tropics. New York, London: Plenum Press.
Granhall, U. 1981 Biological nitrogen fixation in relation to environmental factors and functioning of natural eco-systems. InTerrestrial Nitrogen Cycles. Ecological Bulletins, ed. Clark, R. E. & Rosswall, T. Swedish Natural Science Research Council, Liber Tryck, Stockholm33, 131–144.
Granhall, U. &Lundgren, A. 1971 Nitrogen fixation in Lake Erken.Limnology and Oceanography 16, 711–719.
Henriksson, E. 1951 Nitrogen fixation by a bacteria-free symbioticNostoc strain isolated fromCollema.Physiologia Plantarum 4, 542–545.
Jackson, M. L. 1962Soil Chemical Analysis. London: Constable.
Jacq, V. &Roger, P. A. 1977 Diminuation des fontes des semis dues à la sulfatoréduction, par un prétraitement des graines de riz avec des cyanophycées.Cahiers ORSTOM Serie Biologique 12, 1–108.
Kar, S. &Singh, P. K. 1979 Detoxification of pesticides carbofuran and hexachlorocyclohexane by blue-green algaeNostoc muscorum andWollea bharadwaie.Microbios Letter 10, 111–114.
Kimura, M. Panichsakpatana, S., Wada, H. &Takai, Y. 1979 Influences of organic debri rice root on the nitrogen fixation in the submerged soil.Soil Science and Plant Nutrition 25, 637–640.
Kulasooriya, S. A., Hirimburegama, W. K. &de Silva, R. R. Y. 1980 Effect of light, temperature and phosphorus on the growth and nitrogen fixation inAzolla pinnata native to Sri Lanka.Acta Oecologia, Oecologie Plantarum 1, 355–365.
Kulasooriya, S. A. &de Silva, R. R. Y. 1981 Multivariate interpretation of the distribution of nitrogen-fixing blue-green algae in rice soils in Central Sri Lanka.Annals of Botany (London) 47, 31–52.
Kulasooriya, S. A., Roger, P. A., Barraquio, W. L. &Watanabe, I. 1981 Epiphytic nitrogen fixation on weeds in a rice field ecosystem. InNitrogen Cycling in S. E. Asian Wet Monsoonal Ecosystems, ed. Wetselaar, R. et al., pp. 55–60. Canberra: Australian Academy of Science.
Lee, K. K. &Watanabe, I. 1977 Problems of the acetylene reduction technique applied to water-saturated paddy soils.Applied and Environmental Microbiology 34, 654–668.
Lee, K. K. &Yoshida, T. 1977 An assay technique of measurement of nitrogenase activity in root zone of rice for varietal screening by the acetylene reduction method.Plant and Soil 46, 127–134.
Lännergren, C., Lundgren, A. &Granhall, U. 1974 Acetylene reduction and primary production in Lake Erken.Oikos 25, 365–369.
Matsugushi, T. 1977 Nitrogen transfer and the role of biological nitrogen fixation in paddy fields under intensive rice cultivation.Japanese Agricultural Research Quarterly 11, 204–210.
Matsuguchi, T. &Shimomura, T. 1977 Significance of biological nitrogen fixation in the intensive paddy rice cultivation. InProceedings of the International Seminar on Soil Environment and Fertility Management in Intensive Agriculture, Tokyo. pp. 204–210. The Society of the Science of Soil and Manure, Japan.
Mikkelsen, D. S. &De Datta, S. K. 1979 Ammonia volatilization from wetland rice soils. InNitrogen and Rice. pp. 135–156. Los Baños, Philippines: Int. Rice Res. Inst.
Mitsui, S. 1954Inorganic Nutrition Fertilization and Soil Amelioration, Tokyo: Yokendo.
Mohan, M. &Mukerji, K. G. 1979 Some biologically active extracellular products of blue-green algae.Phykos 18, 73–81.
Nayak, D. N. &Rajaramamohan Rao, V. 1977 Nitrogen fixation bySpirillum sp. from rice roots.Achives of Microbiology 115, 359–360.
Nayak, D. N. &Rajaramamohan Rao, V. 1980 Pesticides and heterotrophic nitrogen fixation in paddy soil.Soil Biology and Biochemistry 12, 1–4.
Okon, Y., Albrecht, S. L. &Burris, R. H. 1976 Carbon and ammonia metabolism ofSpirillum lipoferum.Journal of Bacteriology 128, 592–597.
Panabokke, C. R. 1978 Rice soil of Sri Lanka. InSoils and Rice, pp. 19–35. Los Baños, Philippines: Int. Rice Res. Inst.
Peterson, R. B. &Burris, R. H. 1976 Conversion of acetylene reduction rates to nitrogen fixation rates in natural populations of blue-green algae.Analytical Biochemistry 73, 404–410.
Prasad, R. &De Datta, S. K. 1979 Increasing fertilizer nitrogen efficiency in wetland rice. InNitrogen and Rice. pp. 465–485. Los Baños, Philippines: Int. Rice Res. Inst.
Reynaud, P. A. &Roger, P. A. 1979 Les hautes intensités lumineuses, facteur limitant l'activité fixatrice d'azote des Cyanobactéries.Comptes Rendus de l'Académie Scientific Paris 188, 1999–2002.
Roger, P. A., Kulasooriya, S. A., Barraquio, W. L. &Watanabe, I. 1979 Epiphytic nitrogen fixation on lowland rice plants. InNitrogen Cycling in S. E. Asian Wet monsoonal Ecosystems, ed. Wetseelar et al. pp. 62–67. Canberra: Australian Academy of Science.
Roger, P. A. &Kulasooriya, S. A. 1980Blue-Green Algae and Rice. Los Baños, Philippines: Int. Rice Res. Inst.
Roger, P. A., Kulasooriya, S. A., Tirol, A. C. &Craswell, E. T. 1981 Deep placement: A method of nitrogen fertilizer application compatible with algal nitrogen fixation in wetland rice soils.Plant and Soil 57, 137–142.
Roussos, S., Garcia, J.-L., Rinaudo, G. &Gauthier, D. 1980 Distribution de la microflore hétérotrophe aérobe et an particulier des bactéries dénitrifiantes et fixatrices d'azote libres dans la rhizosphere du riz.Annales de Microbiologie, l'Institut Pasteur 131A, 197–207.
Saito, M. &Watanabe, I. 1978 Organic matter production in rice field flood water.Soil Science and Plant Nutrition 28, 427–440.
Singh, P. K. 1977Azolla plants as fertilizer and feed.Indian Farming 27, 19–22.
Stewart, W. D. P. 1977 Present-day nitrogen-fixing plants.Ambio, (Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences)6, 166–173.
Stewart, W. D. P., Sampaio, M. J., Isichei, A. O. &Sylvester-Bradley, R. 1978 Nitrogen fixation by soil algae of temperature and tropical soil. InLimitations and Potentials for Biological Nitrogen Fixation in the Tropics, ed. Döbereiner et al. pp. 41–64. New York, London: Plenum Press.
Stewart, W. D. P., Rowell, P., Ladha, I. &Sampaio, M. I. A. M. 1979 Blue-green algae (cyanobacteria)—some aspects related to their role as sources of fixed nitrogen in paddy soils. InNitrogen and Rice. pp. 263–285. Los Baños, Philippines: Int. Rice Res. Inst.
Traore, T. M., Roger, P. A., Reynaud, P. A. &Sasson, A. 1978 Etude de la fixation de N2 par les cyanobactéries dans une rizière du Mali.Cahier ORSTOM Serie Biologique 13, 181–185.
Venkataraman, G. S. 1977 Blue-green algae as a biological nitrogen input in rice cultivation. InProceedings of the National Symposium of Nitrogen Assimilation and Crop Productivity, Hissar. pp. 132–142.
Venkataraman, G. S. 1979 Algal inoculations in rice fields. InNitrogen and Rice. pp. 311–321. Los Baños, Philippines: Int. Rice. Res. Inst.
Watanabe, A., Ito, R. &Sasa, T. 1955 Micro-algae as a source of nutrients for daphneids.Journal of General Applied Microbiology 1, 137–141.
Watanabe, I. 1976 Soil fertility management: microbiological studies. InAnnual Report 1976. pp. 31–49. Los Baños, Philippines: Int. Rice Res. Inst.
Watanabe, I. 1979 Biological nitrogen fixation in rice soils. InSoils and Rice. pp. 465–478. Los Baños, Philippines: Int. Rice Res. Inst.
Watanabe, I., Lee, K. K. &Alimagno, B. V. 1978a Seasonal change of N2-fixing rate in rice field assayed byin situ acetylene reduction technique. I. Experiments in long-term fertility plots.Soil Science and Plant Nutrition 24, 1–13.
Watanabe, I., Lee, K.-K. andDe Guzman, M. R. 1978b Seasonal change of N2-fixing rate in lowland rice assayed byin situ acetylene reduction technique. II. Estimate of nitrogen fixation associated with rice plants.Soil Science and Plant Nutrition 24, 465–471.
Watanabe, I., Barraquio, W. L., De Guzman, M. R. &Cabrera, D. A. 1979 Nitrogen fixing (acetylene reduction) activity and populations of aerobic nitrogen-fixing bacteria associated with wetland rice.Applied and Environmental Microbiology 37, 813–819.
Watanabe, I., De Guzman, M. R. &Cabrera, D. A. 1981 Effect of nitrogen fertilizer on N2-fixation in paddy fields measured byin situ acetylene reduction assay.Plant and Soil 52, 135–139.
Wilson, I., Greene, S. &Alexander, M. 1979 Effect of interactions among algae on nitrogen fixation by blue-green algae (cyanobacteria) in flooded soils.Applied and Environmental Microbiology 38, 916–921.
Yoshida, T. &Ancajas, R. R. 1973 Nitrogen-fixing activity in upland and flooded rice fields.Proceedings Soil Science Society of America 37, 42–46.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Granhall, U., Kulassoriya, S.A., Hirimburegama, W.K. et al. Nitrogen fixation in some rice soils in Sri Lanka. Mircen Journal 3, 367–388 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00935696
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00935696