Summary
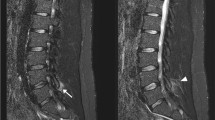
We report on 16 cases of suspected spondylitis in which we used magnetic resonance (MR) imaging to confirm or exclude the diagnosis. MR has several advantages, one of which is to permit diagnosis of this disease in the early stages without major risks. In addition, MR permits recognition of complications such as paravertebral or intraspinal abscess formation with a high security and accuracy. Moreover, it is possible to show spondylitic alterations in three different planes. To differentiate this disease from metastatic or tumorous lesions the technique with T1- and T2-weighted images is helpful. As a result, MR imaging can shorten the time between onset and diagnosis of spondylitis.
Zusammenfassung
Es wird über 16 Patienten mit hämatogener bakterieller Spondylitis oder Verdacht auf einen entzündlichen Wirbelsäulenprozeß berichtet, bei denen die Magnetresonanztomographie (MR) diagnostisch angewandt wurde. Diese Methode erlaubt aufgrund ihrer technischen Bedingungen unabhängig von Röntgenstrahlen eine Spondylitis frühzeitig zu erfassen und kann entsprechende Veränderungen in drei verschiedenen Ebenen abbilden. Außerdem kann das Ausmaß eventueller begleitender paravertebraler und/oder intraspinaler Abszesse mit hoher Genauigkeit und Sicherheit dargestellt werden. Dies ist besonders für die operative Therapie vorteilhaft. Weiterhin ist aufgrund der Zuhilfenahme sog. T1- und T2-gewichteter Bilder die Differential-diagnostik zu anderen Erkrankungen der Wirbelsäule möglich. Auch können ausgeprägtere Veränderungen der kalkhaltigen Gewebsanteile dargestellt werden. Im Vergleich zu anderen diagnostischen Methoden besitzt die MR mehrere Vorteile in einer Methoden Dies dürfte einen wesentlichen Beitrag zur Frühdiagnose dieser Krankheit leisten.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arrington JA, Murtagh FR, Silbiger ML, Rechtine GR, Nokes SR (1986) Magnetic resonance imaging of postdiscogram discitis and osteomyelitis in the lumbar spine: a case report. J Fla Med Assoc 73:192–194
Bruns J, Hemker T, Dahmen G (1986) Pilzinduzierte Spondylitis. Z Orthop 124:96–101
Bruschwein DA, Brown ML, McLeod RA (1980) Gallium scintigraphy in the evaluation of disk space infections: concise communication. J Nucl Med 21:925–927
Burke DR (1985) CT of pyogenic spine infections. Neuroradiology 27:131–137
Digby JM, Kersley JB (1979) Pyogenic non-tuberculous spinal infection: an analysis of thirty cases. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 61:47–55
Griffiths HED, Jones DM (1971) Pyogenic infections of the spine. A review of twenty-eight cases. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 53:383–391
Hermann G, Mendelson DS, Cohen BA, Train JS (1983) Role of computed tomography in the diagnosis of infectious spondylitis. J Comput Assist Tomogr 7:961–968
Jäger M, Springer HH (1981) Die entzündlichen Erkrankungen der Wirbelsäule. Orthopäde 10:106–113
Jend HH, Helmle K, Heller M, Kühne D (1982) Die Computertomographie bei Fehlbildungen, entzündlichen und degenerativen Veränderungen der Wirbelsäule. RöFo 137:523–529
Lardè D, Mathieu D, Frija J, Gaston A, Vasile N (1982) Vertebral osteomyelitis: disk hypodensity on CT. Am J Radiol 239:963–967
Lingg G, Nebel G (1982) Computertomographische und szintigraphische Diagnostik der bakteriellen Spondylitis. RöFo 137:692–699
McCain GA, Harth M, Bell DA (1981) Septic discitis. J Rheumatol 8:100–109
Modic MT, Weinstein MA, Paclicek W, Starnes DL, Duchesneau PM, Boumphrey F, Hardy RJ (1983) Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging of the spine. Radiology 148: 757–762
Modic MT, Paclicek W, Weinstein MA, Boumphrey F, Ngo F, Hardy R, Duchesneau PM (1984) Magnetic resonance imaging of intervertebral disk disease. Radiology 152:103–111
Modic MT, Feiglin DH, Piraino DW, Boumphrey F, Weinstein MA, Duchesneau PM, Rehm S (1985) Vertebral osteomyelitis: assessment using MR. Radiology 157:157–166
Norris S, Ehrlich MG, Keim DE, Guiterman H, McKusick KA (1978) Early diagnosis of disc-space infections using Gallium-67. J Nucl Med 19:384–396
Price AC, Allen JH, Eggers FM, Shaff MI, James AE (1983) Intervertebral disk-space infection: CT changes. Radiology 149:725–729
Reiser M, Kahn T, Weigert F, Lukas P, Büttner F (1986) Diagnostik der Spondylitis durch die MR-Tomographie. RöFo 145:320–325
Stuhler T, Küsswetter W, Nichterlein G, Stankovic P (1982) Hämatogene Osteomyelitis—eine Langzeitstudie. In: Schlegel KF (ed) Hämatogene Osteomyelitis und post-traumatische Osteitis. Buchreihe für Orthopädie und orthopädische Grenzgebiete. Med Lit Verl Ges, Uelzen, pp 112–114
Waldvogel FA, Medoff G, Swartz MN (1970) Osteomyelitis: a review of clinical features, therapeutic considerations and unusual aspects. N Engl J Med 282:198–206 (part I), 260–266 (part II), 316–322 (part III)
Waldvogel FA, Vasey H (1980) Osteomyelitis: the past decade. N Engl J Med 303:360–370
Wimmer B, Friedburg H, Hennig J, Kauffmann GW (1986) Moglichkeiten der diagnostischen Bildgebung durch Kernspintomographie. Radiologe 26:137–143
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bruns, J., Maas, R. Advantages of diagnosing bacterial spondylitis with magnetic resonance imaging. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 108, 30–35 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00934154
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00934154