Abstract
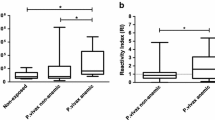
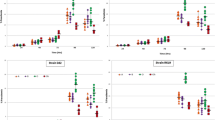
Red blood cell (RBC) negative charges and resistance to linoleic acid (LNA)-induced lysis were studied inPlasmodium yoelii-infected mice and in malaria (P. falciparum)-affected individuals. RBCs from mice infected withP. yoelii showed a progressive decrease in the net surface negative charges at 24 h after infection, reaching a minimal value on day 3, followed by a second phase that was characterised by a recovery to normal levels on day 6. Resistance to linoleic acid follows similar kinetics. These alterations preceded the appearance of parasites in the peripheral blood. A similar increase in LNA-induced lysis was observed in RBCs from malaria-affected individuals. These early membrane alterations of uninfected RBCs could be responsible for spreading of infection and RBC lysis during infection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aceti A, Bonincontro A, Cametti C, Celestino D, Leri O (1990) Electrical conductivity of human erythrocytes infected withPlasmodium falciparum and its modifications following quinine therapy. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 84:671–672
Aikawa M, Miller LH (1983) Structural alteration of the erythrocyte membrane during malaria parasite invasion and intraerythrocytic development. In: Ciba foundation Symposium 94 (eds), Malaria and the red cell. Pitman, London, pp 45–63
Beaumelle B, Vial HJ (1988) Uninfected red cells from malaria-infected blood: alteration of fatty acid composition involving a serum protein: an in vivo and in vitro study. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 24:711–718
Clark IA, Hunt NN (1983) Evidence for reactive oxygen intermediates causing hemolysis and parasite death in malaria. Infect Immun 39:1–6
Gupta CM, Alam A, Mathur PN (1982) A new look at nonparasitized red cells of malaria-infected monkeys. Nature 299:259–261
Kaufmann R, Steiner R, Hoffmann W (1979) Lacypher — a new laser cytopherometer for measuring the electrophoretic mobility of particles and cells. In: Preece AW, and Sabolovic' D (eds). Cell electrophoresis: clinical applications and methodology. Elsevier/North-Holland Amsterdam New York Oxford, pp 435–444
Krogstad DJ, Sutera SP, Boylan CW, Gluzman IY, Qian FF, Rao PR (1991) Intraerythrocytic parasites and red cell deformability. Blood Cells 17:209–221
Macpherson GG, Warrell MJ, White NJ, Looareesuwan S, Warrell DA (1985) Human cerebral malaria. A quantitative ultrastructural analysis of parasitised erythrocyte sequestration. Am J Pathol 119:385–401
Maguire PA, Prudhomme J, Sherman IW (1991) Alteration in erythrocyte membrane phospholipid organisation due to the intracellular growth of the human malaria parasite,Plasmodium falciparum. Parasitology 102:179–187
Sabolovic' D, Hashimoto N (1992) Alterations of uninfected red blood cell membranes during in vitro and in vivo parasite growth. Physicochem Biol 36:1–6
Sabolovic' D, Canque B, Berbiguier N, Galey L (1991) Stage-dependent alterations of negative charges of uninfected erythrocytes inPlasmodium falciparum culture. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 27:595–596
Simchon S, Jan KM, Chien S (1988) Studies on sequestration of neuraminidase-treated red blood cells. Am J Physiol 254: 1167–1171
Simoes AP, Fiebig S, Wunderlich F, Vial H, Roelofsen B, Op den Kamp JAP (1993)Plasmodium chabaudi-parasitized erythrocytes: phosphatidylcholine species of parasites and host cell membranes. Mol Biochem Parasitol 57:343–348
Sherman IW (1983) Metabolism and surface transport of parasitised erythrocytes in malaria. In: Ciba Foundation symposium 94 (eds), Malaria and the red cell. Pitman, London, pp 206–221
Tenforde TS, Yee JP, Mel HC (1978) Electrophoretic detection of reversible chlorpromazine-HCl binding at the human erythrocyte surface. Biochim Biophys Acta 511:152–155
Weatherall DJ, Abdalla S, Pippard MJ (1983) The anaemia ofPlasmodium falciparum malaria. In: Ciba Foundation Symposium 94 (eds), Malaria and the red cell. Pitman, London, pp 74–97
Wright IG, Goodger BV, Clark IA (1988) Immunopathophysiology ofBabesia bovis andPlasmodium falciparum infections. Parasitol Today 4:214–218
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sabolovic', D., Bouanga, J.C., Danis, M. et al. Alterations of uninfected red blood cells in malaria. Parasitol Res 80, 70–73 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00932627
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00932627