Abstract
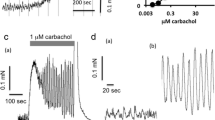
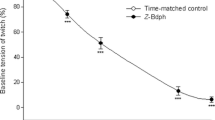
In vitro effects of VD-99-11 were examined using adultAngiostrongylus cantonensis and isolated frog rectus. InA. cantonensis, paralysis was elicited by VD-99-11 at 10−9–10−6 g/ml. The paralysis caused by VD-99-11 (10−8 g/ml) was antagonized by picrotoxin or bicuculline but not by phentolamine. A relationship between VD-99-11 and gabergic antagonists was observed in worm preparations contracted by eserine or pyrantel: VD-99-11 at higher concentrations (3×10−6 g/ml) caused a marked contraction. In worm preparations contracted with eserine or pyrantel, the only additional contraction induced by VD-99-11 (5×10−6 g/ml) was antagonized by strychnine. In experiments on the guanidine (2.5×10−3 M)-induced twitch responses in isolated frog rectus, marked stimulation was caused by VD-99-11 (3–5×10−6 g/ml). The stimulated responses induced by VD-99-11 were antagonized by tetrodotoxin,d-tubocurarine, strychnine, and hemicholinium-3, respectively. These results suggest that VD-99-11 seems superior to milbemycin D, milbemycin oxime, and ivermectin in some aspects, such as in vitro potency, though this new substance is similar to these drugs in having two different actions on the gabergic mechanism at lower concentrations and on the cholinergic mechanism at higher concentrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akao N, Konishi K, Kondo K (1991) Anthelmintic effects of milbemycin oxime on intestinal parasites of dogs and cats (in Japanese). J Vet Med 44:653–657
Aubry ML, Cowell P, Davey MJ, Shevde S (1970) Aspects of the pharmacology of a new anthelmintic: pyrantel. Br J Pharmacol 38:332–344
Lee HH, Terada M (1992) In vitro effects of milbemycin oxime: mechanism of action againstAngiostrongylus cantonensis andDirofilaria immitis. Parasitol Res 78:349–353
Lee HH, Sahara K, Terada M (1991) In vitro effects of milbemycin oxime: effects of the motility of various parasitic helminths. Jpn J Parasitol 40:424–431
Martin RJ, Kusel JR, Robertson SJ, Minta A, Haugland RP (1992) Distribution of a flourescent ivermectin probe, bodipy ivermectin, in tissues of the nematode parasiteAscaris suum. Parasitol Res 78:341–348
Sankyo Company Limited (1994) An outline of VD-99-11 (in Japanese). Sankyo Co. Ltd., Tokyo
Shoop WL (1993) Ivermectin resistance. Parasitol Today 9:154–159
Takiguchi Y, Mishima H, Okuda M, Terao M (1980) Milbemycin, a new family of macrolide antibiotics: fermentation, isolation and physicochemical properties. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 33:1120–1127
Takiguchi Y, Ono M, Matsumura, Ide J, Mishima H, Terao M (1983) Milbemycins, a new family of macrolide antibiotics: fermentation, isolation and physicochemical properties of milbemycin D, E, F, G and H. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 36:502–508
Terada M (1989) Classification and mode of action of anthelmitics (in Japanese). Saishin Igaku 44:695–701
Terada M, Ishii AI, Kino H, Sano M (1983) Studies on chemotherapy of parasitic helminths, XVIII. Mechanism of spastically paralyzing action of pyrantel inAngiostrongylus cantonensis. Experientia 39:1383–1385
Terada M, Ishii AI, Kino H, Sano M (1984)Angiostrongylus cantonensis: paralysis due to avermectin B1a and ivermectin. Exp Parasitol 57:149–157
Terada M, Dharejo AM, Sano M (1986) Effects of milbemycin D on the motility ofAngiostrongylus cantonensis andA. costaricensis. Jpn J Parasitol 35:497–504
Terada M, Chen W, Wang HH, Kachi S, Lee HH (1994) Effects of gabergic anthelmintics at higher concentrations on the guanidine-induced twitch responses in isolated frog rectus. Parasitol Res 80:575–580
Turner MJ, Schaeffer JM (1989) Mode of action of ivermectin. In Campbell WC (ed) Ivermectin and abamectin. Springer, New York Berlin Heidelberg, pp 73–88
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, H.H., Shyu, L.Y. & Terada, M. In vitro effects of VD-99-11 onAngiostrongylus cantonensis and isolated frog rectus. Parasitol Res 81, 615–621 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00932029
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00932029