Summary
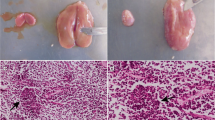
Trophozoites ofEntamoeba histolytica maintained in vitro in Pavlova's medium were inoculated by deep intramuscular injection into the proximal left hindleg of hamsters. Thioglycollate medium was utilized as a successful vehicle to induce the infection. The invasion of the muscular tissue by the vegetative forms caused the formation of abscesses with great destruction of muscular fibers. The lesions were limited to the muscular tissue of the femoral area. The number of trophozoites, the medium of thioglycollate as a vehicle, the volume of the inoculum and the trauma caused by the needle were important elements in the evolution of the muscular amebic abscesses. A limited trial of the amebicidal activity of metronidazole utilizing the amebic intramuscular infection was also performed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atchley, F.O.: Experimental infection of rats withEntamoeba histolytica. Am. J. Hyg.,23, 410 in W.R. Jones, 1946. The experimental infection of rats withEntamoeba histolytica: with a method for evaluating the anti-amoebic properties of new compounds. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol.40, 130–140 (1936)
Bos, H.J., Van de Griends, R.D.: Virulence and toxicity of axenicEntamoeba histolytica. Nature265, 341–343 (1977)
Brandt, H., Perez-Tamayo, R.: Pathology of human amebiasis. Hum. Pathol.1, 351–385 (1970)
Chaia, G., Silva, E.F., Vilela, C.C., Chiari, L.: Isolation and maintenance of a strain ofEntamoeba histolytica. Schaudinn, 1903 and the possibility of its utilization in screening of drugs. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo (in press)
Chiang, S.F.: The rats as possible carrier of the dysentery amoeba. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. Wash.11, 399 (1925)
Cunha, A.S.: Patogenia da Amebiase. Tese professor titular. Faculdade Medicina da Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Brasil, 160 pp. (1975)
Duncan, D.B.: A Bayesian approach to multiple comparisons. Technometrics7, 171–222 (1965)
Ghione, M., Sanfilippo, A.: Pathogenic and therapeutic problems of amebic infections. G. Mall. Infet. Parassit.20, 993–1004 (1968)
Jarumilinta, R., Maegraith, B.G.: Intestinal amoebiasis associated with amoebic liver abscess produced by intracaecal inoculation ofEntamoeba histolytica in hamsters. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol.55, 383–388 (1961)
Maegraith, B., Harinasuta, C.: Experimental amebiasis in the guinea pig. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg.47, 582–583 (1953)
Meleney, H.E., Frye, W.W.: Studies ofEntamoeba histolytica and other intestinal protozoa in Tennessee. V. A comparison of five strains ofE. histolytica with reference to their pathogenicity for kittens. Am. J. Hyg.27, 637–655 (1933)
Neal, R.A.: Some observations on the variation of virulence and response to chemotherapy of strains ofEntamoeba histolytica in rats. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg.44, 439–452 (1951)
Neal, R.A.: Virulence ofEntamoeba histolytica. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg.66, 514–515 (1972)
Pavlova, E.A.: Sur les méthodes de la culture d'Entamoeba histolytica. Med. Parasit. Dis. Moscow7, 224–227 (1938). French summary in Trop. Dis. Bull.36, 286 (1939)
Phillips, B.P., Wolfer, R., Bartgis, I.L.: Studies in the amoeba-bacteria relationship in amebiasis. II. Some concepts on the etiology of the disease. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg.7, 392–399 (1958)
Phillips, B.P., Diamond, L.S., Bartgis, I.L., Stuppler, S.A.: Results of the intracaecal inoculation of germfree and conventional guinea pigs and germfree rats with axenically cultivatedEntamoeba histolytica. J. Protozool.19, 498–499 (1972)
Raetler, W.: Intrahepatikale Infektionsversuche am Goldhamster mitEntamoeba histolytica. Crithidia Kulturen mit und ohne Beteiligung von Bakterien. Z. Parasitenkd.36, 335–345 (1971)
Ross, G.W. and Knight, R.: Dietary factors affecting the pathogenicity ofEntamoeba histolytica in rats. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg.67(4), 560–567 (1973)
Silva, E.F.: Studies ofEntamoeba moshkovskii. II. New foci in Brazil and Uruguai. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo16, 203–221 (1974)
Singh, B.N., Srivastava, R.V.N., Dutta, G.P.: Virulence of strains ofEntamoeba histolytica to rats and the effect of cholesterol, rat caecal and hamster liver passage on the virulence of non-invasive strains. Indian J. Exp. Biol.9, 21–27 (1971)
Stewart, G.T., Jones, W.R.: The pathology of an experimental amoebic in the rat. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol.42, 33–45 (2947)
Swartzwelder, J.C.: Experimental studies onEntamoeba histolytica in the dog. Am. J. Hyg.29, 89–109 (1939)
Tobie, J.E.: Experimental infection of the rabbit withEntamoeba histolytica. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg.29, 859–570 (1949)
Westphal, A.: Die intrazakale Infektion der Maus mitEntamoeba histolytica. Tropenmed. Parasitol.21, 220–230 (1970)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Deceased
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiari, L., Guerrero, J. & Negrão dos Santos, C. Experimental muscular amebiasis in hamsters as a biological model. Z. Parasitenkd. 56, 107–114 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00930741
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00930741