Abstract
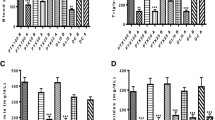
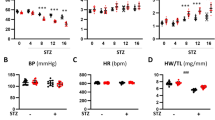
Chronic treatment with the antihypertensive drug hydralazine did not affect the hyperglycemic state of streptozotocin (STZ)-diabetic rats but did prevent the serum hyperlipidemia that is synonymous with these diabetic animals. After 6 weeks, untreated STZ-diabetic rats exhibited a 659% increase in serum triglycerides and 292% increase in serum cholesterol versus age-matched non-diabetic rats. Hydralazine-treated STZ-diabetic rats had serum triglyceride and cholesterol levels that did not differ from controls. Myocytes from control rats showed a preference for binding of the unsaturated fatty acid analog cis-parinaric acid vs the saturated fatty acid analog trans-parinaric acid. This preference was not altered in STZ-diabetic rat myocytes; hydralazine-treatment of STZ-diabetic rats also showed no change in fatty acid preference. STZ-diabetes caused a decrease in the affinity (Kd) for the trans, but not the cis-parinaric acid. However, total binding of both analogs was increased in STZ-diabetes. Hydralazine treatment of STZ-diabetic rats resulted in even greater total binding of both analogs. Affinity for the trans analog was further decreased in these hydralazine-treated rats, but the affinity for the cis analog was increased beyond control animals. These results suggest that the diabetic state influences the binding characteristics of the myocardial PM-FABP and that hydralazine, while reducing serum lipids in diabetes, has complex effects on the fatty acid binding by this protein.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PM-FABP:
-
plasma membrane fatty acid binding protein
- ACE:
-
angiotensin converting enzyme
- c-PNA:
-
cis-parinaric acid
- t-PNA:
-
trans-parinaric acid
References
Heyliger CE, Rodrigues B, McNeill JH: An assessment of choline and methionine treatment on the cardiac dysfunction of diabetic rats. Diabetes 35: 1152–1157, 1986
Xiang H. Heyliger CE, McNeill JH: Effect of myo-inositol and T3 on myocardial lipids and cardiac function in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes 37: 1542–1548, 1988
Dhalla NS, Elimban V, Rupp H: Paradoxical role of lipid metabolism in heart function and dysfunction. Mol Cell Biochem 116: 3–9, 1992
Rodrigues B, Goyal RK, McNeill JH: Effects of hydralazine on streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: Prevention of hyperlipidemia and improvement in cardiac function. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 237: 292–299, 1986
Stremmel W: Fatty acid uptake by isolated rat heart myocytes represents a carrier-mediated transport process. J Clin Invest 81: 844–852, 1988
vyska K, Meyer W, Stremmel W, Notohamiprodio G, Minami K, Machullo H-J, Gleichmann M, Meyer H, Korfer R: Fatty acid uptake in normal human myocardium. Circ Res 69: 857–870, 1991
Diede HE, Rodilla-Sala E, Gunaman J, Manns M, Stremmel W: Identification and characterization of a monoclonal antibody to the membrane fatty acid binding protein. Biochem Biophys Acta 1125: 13–20, 1992
Kryski A, Kenno KA, Severson DL: Stimulation of lipolysis in rat heart myocytes by isoproterenol. Am J Physiol 248: H208-H216, 1985
Schroeder F: Hormonal effects on fatty acid binding and physical properties of rat liver plasma membranes. J Membrane Biol 68: 1–10, 1982
Opie L: Carbohydrates and lipids. In: The Heart. Grune and Stratton, Inc, Orlando FL, 1986, Chap 10
Randle PJ, Hales CN, Garland PB, Newsholme EA: The glucosefatty acid cycle: Its role in insulin sensitivity and the metabolic disturbances of diabetes mellitus. Lancet 1: 785–789, 1963
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heyliger, C.E., Powell, D.M. & Skau, K.A. Effect of hydralazine on myocardial plasma membrane fatty acid binding protein (PM-FABP) during diabetes mellitus. Mol Cell Biochem 148, 39–44 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00929501
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00929501