Abstract
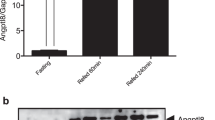
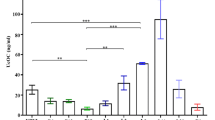
The effect of refeeding on the expression of Ca2+-binding protein regucalcin mRNA in the liver of fasted rats was investigated. When rats were fasted overnight, the hepatic regucalcin mRNA level was reduced about 70% of that in feeding rats. Refeeding produced a remarkable elevation of hepatic regucalcin mRNA level (about 150–170% of fasted rats). Liver regucalcin concentration was appreciably increased by refeeding, although it was not altered by fasting. The oral administration of glucose (2 g/kg body weight) to fasted rats caused a significant increase in hepatic regucalcin mRNA level. Moreover, hepatic regucalcin mRNA level was clearly elevated by a single subcutaneous administration of insulin (10 and 100 U/kg) to fasted rats. The hormonal effect was not further enhanced by the simultaneous administration of calcium chloride (250 mg Ca/kg) to fasted rats, although calcium administration stimulated regucalcin mRNA expression in the liver. The present study suggests that the expression of hepatic regucalcin mRNA stimulated by refeeding is significantly involved in the action of insulin and/or calcium as stimulating factors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheung WY: Calmodulin plays a pivotal role in cellular regulation. Science 202: 19–27, 1984
Nishizuka Y: Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science 233: 305–312, 1986
Yamaguchi M: A novel Ca2+-binding protein regucalcin and calcium inhibition: Regulatory role in liver cell function. In: K Kohama (ed.) Calcium Inhibition, Japan Sci Soc Press, Tokyo and CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1992, pp 19–41
Yamaguchi M, Tai H: Inhibitory effect of calcium-binding protein regucalcin on Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity in rat liver cytosol. Mol Cell Biochem 106: 25–30, 1991
Yamaguchi M, Mori S: Inhibitory effect of calcium-binding protein regucalcin on protein kinase C activity in rat liver cytosol. Biochem Med Metab Biol 43: 140–146, 1990
Yamaguchi M, Sakurai T: Inhibitory effect of calcium-binding protein regucalcin on Ca2+-activated DNA fragmentation in rat liver nuclei. FEBS Lett 279: 281–284, 1991
Shimokawa N, Yamaguchi M: Molecular cloning and sequencing of the cDNA coding for a calcium-binding protein regucalcin from rat liver. FEBS Lett 327: 251–255, 1993
Shimokawa N, Yamaguchi M: Expression of hepatic calcium-binding protein regucalcin mRNA is mediated through Ca2+/calmodulin in rat liver. FEBS Lett 316: 79–84, 1993
Chomczynski P, Saccki N: Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thyocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162: 156–159
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T: Northern hybridization. In: Molecular Cloning (2nd edn), Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, 1989, pp 7.39–7.52
Yamaguchi M, Yamamoto T Purification of calcium binding substance from soluble fraction of normal rat liver. Chem Pharm Bull 26: 1915–1918, 1978
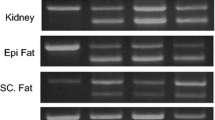
Yamaguchi M, Isogai M: Tissue concentration of calcium-binding protein regucalcin in rats by enzyme-linked immunoadsorbent assay. Mol Cell Biochem 122: 65–68, 1993
Shimokawa N, Yamaguchi M: Calcium administration stimulates the expression of calcium-binding protein regucalcin mRNA in rat liver. FEBS Lett 305: 151–154, 1992
Irvine F, Wallace AV, Sarawak SR, Houslay MD: Extracellular calcium modulates insulin's action on enzymes controlling cyclic AMP metabolism in intact hepatocytes. Biochem J 293: 249–253, 1993
Cooper DR, Hernandez H, Kuo JY, Farese RV: Insulin increases the synthesis of phospholipid and diacylglycerol and protein kinase C activity in rat hepatocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys 276: 486–494, 1990
Plehwe WE, Williams PF, Caterson ID, Harrison LC, Turtle JR: Calcium-dependence of insulin receptor phosphorylation. Biochem J 214: 361–366, 1983
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamaguchi, M., Oishi, K. & Isogai, M. Expression of hepatic calcium-binding protein regucalcin mRNA is elevated by refeeding of fasted rats: Involvement of glucose, insulin and calcium as stimulating factors. Mol Cell Biochem 142, 35–41 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00928911
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00928911