Abstract
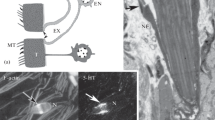
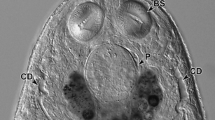
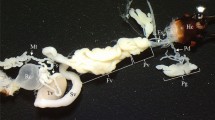
The excretory system ofDiphyllobothrium dendriticum was studied morphologically and functionally. In living plerocercoids, one of the large excretory ducts was injected with latex-based stain. The excretory system was found to consist of a peripheral network of ducts, a central system of two longitudinal ducts, communicating through transverse ducts, a capillary plexus in the scolex and the excretory bladder and pore in the tail. The central and peripheral duct systems were both found to communicate with the capillary plexus in the scolex. In the peripheral network the stain was mainly spread by those contractions of the plerocercoid, which start in the neck region and are propagated through the body. The flow in the central ducts was usually independent of the contractions. Occasional reverse contractions led to a rapid flush in the central ducts. From the peripheral and central ducts the stain was transported out through the excretory bladder and pore. The distributive role of the excretory system is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonsdorff C-H von, Forssten T, Gustafsson MKS, Wikgren B-J (1971) Cellular composition of plerocercoids ofDiphyllobothrium dendriticum (Cestoda). Acta Zool Fenn 132:1–25
Howells RE (1969) Observations on the nephridial system of the cestodeMoniezia expansa (Rud., 1805). Parasitology 59:449–459
Hyman LH (1951) The invertebrates: Platyhelminthes and Rhynchocoela, McGraw-Hill Book Co Inc, New York, Vol 2
Lee DL, Tatchell RJ (1964) Studies on the tapewormAnoplocephala perfoliata (Goeze, 1782). Parasitology 54:467–479
Malmberg G (1971) On the procercoid protonephridial systems of threeDiphyllobothrium species (Cestoda, Pseudophyllidea) and Janicki's cercomer theory. Zool Scripta 1:43–56
Pantelouris EM, Threadgold LT (1963) The excretory system of the adultFasciola hepatica L. Cellule 64:63–67
Parshad VR, Guraya SS (1977) Comparative histochemical observations on the excretory system of helminth parasites. Z Parasitenkd 52:81–89
Siddiqi AH (1961) Studies on the morphology ofCotugnia dignopora Pasquale 1890 (Cestoda: Davaineidae). IV. Excretory system. Z Parasitenkd 21:93–100
Šlais J (1973) Functional morphology of cestode larvae. Adv Parasitol 11:395–480
Sulgostovska T (1972) The development of organ systems in cestodes. I. A study of histology ofHymenolepis diminuta (Rudolphi, 1819) (Hymenolepididae). Acta Parasitol Pol 20:449–462
Webster LA (1972) Absorption of glucose, lactate and urea from the protonephridial canals ofHymenolepis diminuta. Comp Biochem Physiol 41A:861–868
Wilson RA, Webster LA (1974) Protonephridia. Biol Rev 49:127–160
Zernecke E (1896) Untersuchungen über den feineren Bau der Cestoden. Zool Jahrb Anat 9:92–161
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lindroos, P., Gardberg, T. The excretory system ofDiphyllobothrium dendriticum (Nitzsch 1824) plerocercoids as revealed by an injection technique. Z. Parasitenkd. 67, 289–297 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00927664
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00927664