Abstract
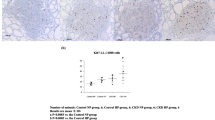
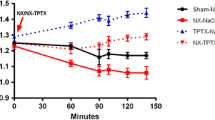
The expression of calcium-binding protein regucalcin mRNA in the kidney cortex of rats was investigated. The change of regucalcin mRNA levels was analyzed by Northern blotting using liver regucalcin complementary DNA (0.9 kb of open-reading frame). Regucalcin mRNA was expressed in the kidney cortex, and this expression was clearly increased by a single intraperitoneal administration of calcium chloride solution (5–15 mg Ca/100 g body weight) in rats; this increase was remarkable at 60–120 min after the administration. Thyroparathyroidectomy (TPTX) caused a slight decrease of regucalcin mRNA levels in the kidney cortex. However, the administration of calcium (10 mg/100 g) in TPTX rats produced a clear increase of regucalcin mRNA levels in the kidney cortex. The subcutaneous administration of calcitonin (10–100 MRC mU/100 g) or parathyroid hormone [1–34] (1–10 U/100 g) in TPTX rats which received calcium (10 mg/100 g) administration did not cause an appreciable alteration of regucalcin mRNA levels in the kidney cortex, suggesting that the mRNA expression is not stimulated by calcium-regulating hormones. The administration of trifluoperazine (TFP; 5 mg/100 g), an inhibitor of Ca2+/calmodulin action, completely blocked the expression of regucalcin mRNA stimulated by calcium administration. Now, calcium content in the kidney cortex was significantly elevated by a single intraperitpneal administration of calcium (10 mg/100 g) in rats. The present study clearly demonstrates that the expression of regucalcin mRNA in the kidney cortex is stimulated by calcium administration in rats. This expression may be mediated through Ca2+/calmodulin action in the kidney cortex.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Williamson JR, Cooper RH, Hoek JB: Role of calcium in the hormonal regulation of liver metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta 639: 243–245, 1981
Kraus-Freidman N: Calcium sequestration in the liver. Cell Calcium 11: 625–640, 1990
Reihart PH, Taylor WM, Bygrave FL: The role of calcium ions in the mechanisms of action of α-adrenergic agonists in rat liver. Biochem J 223: 1–13, 1984
Cheung WY: Calmodulin plays a pivotal role in cellular regulation. Science 202: 19–27, 1980
Berridge MJ: Inositol triphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J 220: 345–360, 1984
Yamaguchi M: A novel Ca2+-binding protein regucalcin and calcium inhibition: Regulatory role in liver cell function. In: K. Kohama (ed.). Calcium Inhibition. Japan Sci Soc Press, Tokyo and CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1992, p 19–41
Shimokawa N, Yamaguchi M: Molecular cloning and sequencing of the cDNA coding for a calcium-binding protein regucalcin from rat liver. FEBS Lett 327: 251–255, 1993
Shimokawa N. Yamaguchi M: Expression of hepatic calcium binding protein regucalcin mRNA is mediated through Ca2+/ calmodulin in rat liver. FEBS Lett 316: 79–84, 1993
Yamaguchi M, Isogai M: Tissue concentration of calcium binding protein regucalcin in rats by enzyme-linked immunoadsorbent assay. Mol Cell Biochem 122: 65–68, 1993
Yamaguchi M, Mori S: Effect of calcium-binding protein regucalcin on hepatic protein synthesis: inhibition of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase activity. Mol Cell Biochem 99: 25–32, 1990
Yamaguchi M, Mori S: Inhibitory effect of calcium-binding protein regucalcin on protein kinase C activity in rat liver cytosol. Biochem Med Metab Biol 43: 140–146, 1990
Yamaguchi M, Sakurai T: Inhibitory effect of calcium-binding protein regucalcin on Ca2+-activated DNA fragmentation in rat liver nuclei. FEBS Lett 279: 281–284, 1991
Yamaguchi M, Takei Y, Yamamoto T: Effect of thyrocalcitonin in liver of intact and thyroparathyroidectomized rats. Endocrinology 96: 1004–1008, 1975
Willis JB: Determination of calcium in blood serum by atomic absorption spectroscopy. Nature (London) 186: 249–250, 1960
Shimokawa N, Yamaguchi M: Calcium administration stimulates the expression of calcium-binding protein regucalcin mRNA in rat liver. FEBS Lett 305: 151–154, 1992
Takahashi H, Yamaguchi M: Regucalcin modulates hormonal effect on (Ca2+-Mg2+)-ATPase activity in rat liver plasma membranes. Mol Cell Biochem 125: 171–177, 1993
Van Os CH: Transcellular calcium transport in intestinal and renal epithelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 906: 195–222, 1987
Taylor CW: Calcium regulation in vertebrates: An overview. Comp Biochem Physiol 82A: 249–255, 1985
Azria M: The Calcitonins: Physiology and Pharmacology. Karger, Basel, 1989
Vincenzi FF: Pharmacology of calmodulin antagonism. In: T. Godfraind, A. Albertini, R. Paoletti (ed.). Calcium Modulators. Elsevier Biomedical Press, Amsterdam, 1982, p 67–80
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamaguchi, M., Kurota, H. Expression of calcium-binding protein regucalcin mRNA in the kidney cortex of rats: The stimulation by calcium administration. Mol Cell Biochem 146, 71–77 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00926884
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00926884