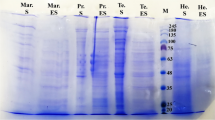
Abstract
Groups of eight miniature pigs were infected either with 1,500 embryonated eggs each ofAscaris suum orToxocara canis or with 1,000 eggs each of both nematodes. Sera were sampled before the infection as well as three and six weeks postinfection and then investigated in the ELISA on microtitre plates against antigens of various developmental stages. When extracts of adultAscaris andToxocara worms were used as antigens, distinct reactions were registered both in the infected and in the uninfected control groups. Antigens isolated from either embryonated eggs or larvae of both worms produced distinctly positive reactions with sera of the infected animals, including those pigs with heterologous infections but not with sera from uninfected controls. After saturation with heterologous antigens, the sera showed distinct antibody reactions against homologous antigen extracts and in this way infections with the two nematode species could be serologically differentiated.
Zusammenfassung
Je 8 Miniaturschweine wurden mit 1500 embryonierten Eiern vonAscaris suum oderToxocara canis bzw. mit je 1000 Eiern der beiden Spulwurmarten infiziert. Seren der Tiere wurden vor der Infektion sowie 3 und 6 Wochen post infectionem mit dem ELISA in Mikrotiterplatten gegen Antigene verschiedener Entwicklungsstadien untersucht. Bei Verwendung von Extrakten adulterAscaris undToxocara als Antigene waren sowohl bei den infizierten als auch bei den nichtinfizierten Kontrollen deutliche Reaktionen nachweisbar. Antigene aus embryonierten Eiern bzw. Larven beider Askaridenarten erzeugten nur bei den infizierten Tieren deutliche positive Reaktionen einschließlich bei den heterolog infizierten Schweinen, jedoch nicht bei den nicht infizierten Kontrolltieren.
Nach Absättigung der Seren mit den jeweils heterologen Antigenen konnten mit homologen Antigenextrakten deutliche Antikörperreaktionen nachgewiesen werden. Auf diese Weise gelang es, Infektionen mit den beiden Nematodenarten serologisch zu differenzieren.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Ambroise-Thomas P, Desgeorges PT (1978) Diagnostic immuno-enzymologique (ELISA) des maladies parasitaires par une microméthode modifiée. I. Modalités techniques. Bull Wld Hlth Org 56:609–613
Annen JM, Eckert J, Hess U (1975) Eine einfache Methode zur Gewinnung von Toxocara canis-Antigen für die indirekte Immunofluoreszenz-Technik. Acta trop 32:37–47
De Savigny DH, Voller A, Woodruff AW (1979) Toxocariasis: Serological diagnosis by enzyme immunoassay. J clin Path 32:284–288
Cypess RH, Glickman LT (1976) Visceral Larva migrans: a significant zoonosis? Mod vet Pract 57:462–464
Cypess RH, Karol MH, Zidian JL, Glickman LT, Gitlin D (1977) Larva specific antibodies in patients with visceral Larva migrans. J infect Dis 135:633–640
Glickman L, Schantz P, Dombroske R, Cypess R (1978) Evaluation of serodiagnostic tests for visceral Larva migrans. Am J trop Med Hyg 27:492–498
Hogarth-Scott RS (1966) Visceral Larva migrans—an immunofluorescent examination of rabbit and human sera for antibodies to the ES antigens of the second stage larvae of Toxocara canis, Toxocara cati and Toxascaris leonina (Nematoda). Immunology 10:217–223
Krupp JM (1974) Hemagglutination test for the detection of antibodies specific for Ascaris and Toxocara antigens in patients with suspected visceral Larva migrans. Am J trop Med Hyg 23:378–384
Lamina J (1968) “Larva migrans visceralis”. Entwicklung und Möglichkeit der Diagnostik am Beispiel von Ascaris lumbricoides var. suis (Linné 1758) und Toxocara canis (Werner 1782). Med Habil Schr Frankfurt/M
Lamina J (1974) Die Immundiagnostik durch den Hundespulwurm Toxocara canis (Werner 1782) hervorgerufener Larva-migrans-visceralis-Infektionen. Dt med Wschr 99:1070–1073
Ruitenberg EJ, Buys J (1976) An immunofluorescence technique for the detection of Toxocara canis antibodies. Vet Parasit 1:231–237
Stevenson P, Jacobs DE (1977) Toxocara infection in pigs. The use of indirect fluorescent antibody tests and an in vitro larval precipitate test for detecting specific antibodies. J Helminth 51:149–154
Weiland G, Schwarzhuber A (1978) Untersuchungen zum Nachweis von Larva migrans visceralis mit dem Peroxydase-Test (ELISA) und der Immunofluoreszenz. Berl Münch Tierärztl Wschr 91:209–213
Wilson MB, Nakane PK (1978) In: Knapp W et al. Immunofluorescent and related staining techniques, 215, Biomedical Press, Elsevier, North Holland
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Herrn Prof. Dr. G. Piekarski zum 70 Geburtstag giwidmet
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grelck, H., Hörchner, F. & Unterholzner, J. Zur serologischen Differenzierung vonAscaris suum- undToxocara canis-Infektionen beim Schwein. Z. Parasitenkd. 65, 277–282 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00926721
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00926721