Abstract
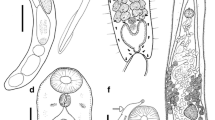
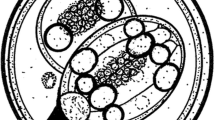
Goussia cichlidarum n. sp. (Barrouxiidae, Apicomplexa) is a coccidian parasite found in the epithelial lining of the swimbladder in a variety of cichlid fish, most commonly inSarotherodon galilaeus. Infected fish were found in Lake Kinneret and in fish ponds in Israel and in Uganda. Natural infections were investigated as well as experimental infections obtained in the laboratory. Merogony and gamogony is completed within a hypertrophic host cell. The latter is displaced to the surface of the epithelial layer and during the parasitization process is reduced to a membranous envelope. This cell remains attached to the epithelial layer up until the stage of oogony. Oocysts complete their differentiation free in the swimbladder lumen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker JR (1960) Trypanosomes and dactylosomes from the blood of freshwater fish in East Africa. Parasitology 50:515–526
Baker JR (1963) Three new species ofMyxosoma (Protozoa, Myxosporidia) from East African freshwater fish. Parasitology 53:285–292
Boulard Y (1977) Description d'Eimeria quenteni n. sp., parasite intranucleaire du péritoine de la raie:Aetobatis narinari (Chondrichthyens, Myliobatidae) en Malaisie. Protistologica 13:529–533
Copeland DE (1969) Fine structure of gas secretion in the physoclistous swim bladder ofFundulus heteroclitus andGadus callarias and in the euphysoclistous swimbladder ofOpsanus tau. Z Zellforsch 93:305–331
Desser SS (1981) The challenge of fish coccidia. J Protozool 28:260–261
Du Pont (1981) Instruction manual, staining procedures for plastic embedded tissue. Sorval microtome biomedical division — DuPont instruction publications 45603-6, Feb. 1983
Dyková I, Lom J (1981) Fish coccidia: critical notes of life cycles, classification and pathogenicity. J Fish Dis 4:487–505
Dyková I, Lom J (1983) Fish coccidia: an annotated list of described species. Folia Parasitol (Praha) 30:193–208
Fiebiger J (1913) Studien über die Schwimmenblasen-Coccidien derGadusarten (Eimeria gadi n. sp.). Arch Protistenkd 31:95–137
Fournie JW, Overstreet RM (1983) True intermediate hosts forEimeria funduli (Apicomplexa) from estuarine fishes. J Protozool 30:627–675
Hoare CA (1930) On a newDactylosoma occurring in fish of Lake Victoria Nyanza. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 24:241–248
Horton-Smith O, Long PL (1963) Coccidia and coccidiosis in the domestic fowl and turkey. Adv Parasitol 1:67–107
Landau I, Marteau M, Golvan Y, Chabaud AG, Boulard Y (1975) Hétéroxenie chez les coccidies intestinales de poissons. CR Acad Sci Paris D 281:1721–1723
Landsberg JH (1985) Myxosporean infections of cultured tilapias in Israel. J Protozool (in press)
Léger M, Léger A (1914) Hemogrégarine et trypanosome d'un poisson du Niger,Tilapia lata. CR Soc Biol Paris 77:183–184
Levine ND (1983) The generaBarrouxia Defretinella andGoussia of the coccidian family Barrouxiidae (Protozoa, Apicomplexa). J Protozool 30:542–547
Lom J, Dyková I (1982) Some marine fish coccidia of the generaEimeria Schneider,Epieimeria Dyková and Lom andGoussia Labbé. J Fish Dis 5:309–321
Lulham CN (1979) Glycol methacrylate embedding for light microscopy. J Histotechnol 2:68–71
Marinček M (1973) Development d'Eimeria subepithelialis (Sporozoa: Coccidia) parasite de la carpe. Acta Protozool 12:195–215
Millonig G (1976) Laboratory manual of biological electron microscopy. Mario Saviolo-Editore, Vercelli C.P. 182, Italy, pp 67
Molnar K (1981) Some peculiarities of oocyst rejection of fish coccidia. In: Fish, pathogens and environment in European polyculture, Fisheries Research Institute, Szarvas, Hungary, pp 170–183
Odense PH, Logan VH (1976) Prevalence and morphology ofEimeria gadi Fiebiger 1913 in the haddock. J Protozool 23:564–571
Overstreet RM (1981) Species ofEimeria in non epithelial sites. J Protozool 28:258–260
Paperna I (1973) Occurrence of Cnidospora infections in freshwater fishes in Africa. Bull Inst Fondam Afr Noire (A-Sci Nat) 35:509–521
Paperna I (1980) Parasites, infection and diseases of fish in Africa. CIFA Tech Rep (7) pp 216
Solangi MA, Overstreet RM (1980) Biology and pathogenesis of the coccidiumEimeria funduli infecting killifishes. J Parasitol 66:513–526
Todd KS, Lepp DL (1971) The life cycle ofEimeria vermiformis Ernst, Chobotar and Hammond 1971 in the mouseMus musculus. J Protozool 18:332–337
Woodland WNF (1911) On the structure and function of the gas gland and retia mirabilia associated with the gas bladder of some teleostean fishes with notes on the teleost pancreas. Proc Zool Soc Lond 183–247 Plates II-IX
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Landsberg, J.H., Paperna, I. Goussia cichlidarum n. sp. (Barrouxiidae, Apicomplexa), a coccidian parasite in the swimbladder of cichlid fish. Z. Parasitenkd. 71, 199–212 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00926270
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00926270