Abstract
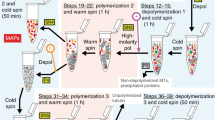
The changes in the levels of microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) during advanced embryonic stages, neonatal and adult organisms reflect the importance of these cytoskeletal proteins in relation to the morphogenesis of the central nervous system. MAP-1B is found in prenatal brains and it appears to have the highests levels in neonatal rat brains, being a developmentally-regulated protein. In this research, a fast procedure to isolate MAP-1B, as well as MAP-2 and MAP-3 from neonatal rat brains was designed, based on the differential capacity of poly L-aspartic acid to release MAPs during temperature-dependent cycles of microtubule assembly in the absence of taxol. The high molecular weight MAP-1B was recovered in the warm supernatants after microtubular protein polymerization in the presence of low concentrations of polyaspartic acid. Instead, MAP-2 and a 180 kDa protein with characteristics of MAP-3 remained associated to the polymer after the assembly. Further purification of MAP-1B was attained after phosphocellulose chromatography. Isolation of MAP-2 isoforms together with MAP-3 was achieved on the basis of their selective interactions with calmodulin-agarose affinity columns. In addition, MAP-2 and MAP-3 were also purified on the basis of their capacities to interact with the tubulin peptide β-II (422–434) derivatized on an Affigel matrix. However, MAP-1B did not interact with the β-II tubulin fragment, but it showed interaction with the Affigel-conjugated β-I (431–444) tubulin peptide. The different MAPs componentes were characterized by western blots using specific monoclonal antibodies. A salient feature of neonatal rat brain MAP-3 was its interactions with site-directed antibodies that recognize binding epitopes on the repetitive sequences of tau and MAP-2. However, these site-specific antibodies did not interact with MAP-1B from the neonatal rat brain tissue.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PAA:
-
poly (L-aspartic acid)
- HMW-MAPs:
-
high molecular weight microtubule associated proteins
References
Riederer B, Matus A: Differential expression of distinct microtubule-associated proteins during brain development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:6006–6009, 1985
Garner C, Garner A, Huber G, Kozak C, Matus A: Molecular cloning of microtubule-associated protein 1 (MAP-1A) and microtubule-associated protein 5 (MAP-1B): Identification of distincts genes and their differential expression in developing brain. J Neurochem 55:146–154, 1990
Crandall JE, Fischer I: Developmental regulation of microtubule-associated protein 2 expression in regions of mouse brain. J Neurochem 53:1910–1917, 1989
Nunez J: Differential expression of microtubule components during brain development. Devl Neurosci 8:421–457, 1986
Kosik K, Orecchio L, Bakalis S, Neve R: Developmental regulated expression of specific tau sequences. Neuron 2:1389–1397, 1989
Maccioni RB, Rivas C, Vera J: Differential interaction of synthetic peptides from carboxyl-terminal regulatory domain of tubulin with microtubule-associated proteins (MAPS). EMBO J 7:1957–1963, 1988
Vallee RB, Bloom G, Luca FC: Differential structure and distribution of the high molecular weight brain microtubule-associated proteins, MAP-1 and MAP-2. In: Soifer D (ed.) Dynamic aspects of microtubule biology. Ann New York Acad Sci, USA v 466:134–147, 1986
Paschal B, Obar R, Vallee R: Interaction of brain citoplasmic dynein and MAP-2 with a common sequence at the C-terminus of tubulin. Nature 342:569–572, 1989
Cross D, Domínguez J, Avila J, Maccioni RB: MAP-1 and MAP-2 binding sites at C-terminus of beta tubulin. Studies with synthetic tubulin peptides. Biochemistry 30:4362–4366, 1991
Herrmann H, Dalton JM, Wiche G: Microheterogenity of microtubule-associated proteins MAP-1 and MAP-2, and differential phosphorylation of individual subcomponents. J Biol Chem 260: 5797–5803, 1985
Fujii T, Nakamura A, Ogoma Y, Yoshiyuki K, Arai T: Selective purification of microtubule associated proteins 1 and 2 from rat brain using poly(L-aspartic acid). Anal Biochem 184:268–273, 1990
Cross D, Vial C, Maccioni RB: A tau-like protein mediates interactions between microtubules and actin filaments in human and rodent cell lines. J Cell Sci 105:51–60, 1993
Vera JC, Rivas C, Maccioni RB: Biochemical dissection of the role of the 1 kDa C-terminal domain of tubulin subunits in the assembly of microtubules. Biochemistry 28:333–339, 1989
Weingarten M, Lockwood A, Hwo S, Kirschner M: A protein factor essential for microtubule assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72:1858–1862, 1975
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of the bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685, 1970
Rivas C, Vera J, Maccioni RB: Anti-idiotypic antibodies reacting with MAPs in the sera of rabbits immunized with synthetic peptides from tubulin's regulatory domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:6092–6096, 1988
Farías G, Vial C, Maccioni RB: Specific macromolecular interactions between tau and the microtubule system. Mol Cell Biochem 112:81–88, 1992
Vera J, Rivas C, Maccioni RB: Heat-stable microtubule protein MAP-1 binds to microtubules and induces microtubule assembly. FEBS Lett 232:159–162, 1988
Nakamura A, Arai T, Kondo Y, Fujii T: Inhibitory effects of poly (L-aspartic acid) on the assembly of brain microtubules and the interaction of microtubule associated protein 2 with F-actinin vitro. J Biochem 106:93–97, 1989
Maccioni RB, Serrano L, Avila J, Cann JR: Characterization and structural aspects of the enhanced assembling capacity of tubulin after removal of its carboxyl-terminal domain. Eur J Biochem 154: 427–435, 1985
Rivas-Berrios A, Hernández M, Domínguez J, Avila J, Maccioni RB: Common antigenic determinants of the tubulin binding domains of the microtubule-associated proteins MAP-2 and tau. Biochem Biophys Acta 1040:382–390, 1990
Maccioni RB, Vera J, Domínguez J, Avila J: A discrete repeated sequence defines a tubulin binding domain on microtubule-associated protein tau. Arch Biochem Biophys 275:568–579, 1989
Vera JC, Rivas C, Maccioni RB: Antibodies to synthetic peptides from the tubulin's regulatory domain interact with tubulin and microtubules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:6763–6767, 1988
Binder LI, Frankfurter A, Kim H, Cáceres A, Payne MR, Rebhun LI: Heterogeneity of microtubule-associated protein 2 during rat brain development. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 81:5613–5617, 1984
Riederer B, Cohen R, Matus A: MAP-5: A novel microtubule-associated protein under strong developmental regulation. J Neurocytol 15:763–775, 1986
Herzog w, Weber K: Fractionation of brain microtubule-associated proteins. Isolation of two different proteins which stimulate tubulin polymerizationin vitro. Eur J Biochem 92:1–8, 1978
Vallee R: A taxol-dependent procedure for the isolation of microtubules and microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs). J Cell Biol 92:435–442, 1982
Maccioni RB, Arechaga J: The cytoskeleton in cell differentiation and development. ICSU Press-IRL (Oxford University Press), 1987; pp 397
Matus A: Microtubule-associated proteins and neuronal morphogenesis. J Cell Sci 15:61–67, 1991
Maccioni RB, Vial C, Cross D, González M: Specific macromolecular interactions modulating the cytoskeleton organization. In: Becerra J (ed.) Progress in cell biology. Servicio Editorial Universidad de Málaga, 1992
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guzman, L., Bustos, R. & Maccioni, R.B. Purification and characterization of the high molecular weight microtubule associated proteins from neonatal rat brain. Mol Cell Biochem 131, 105–113 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00925946
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00925946