Abstract
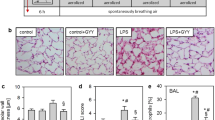
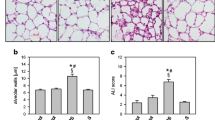
Recent evidence indicates that under in vitro conditions, superoxide anion and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) are unstable in the presence of manganese ion (Mn2+). The current studies snow that in the presence of Mn2+, H2O2-mediated injury of endothelial cells is greatly attenuated. A source of bicarbonate ion and amino acid is required for Mn2+ to exert its protective effects. Injury by phorbol ester-activated neutrophils is also attenuated under the same conditions. EDTA reverses the protective effects. Acute lung injury produced in vivo in rats by intratracheal instillation of glucose-glucose oxidase is almost completely blocked in rats treated with Mn2+ and glycine. Conversely, treatment of rats with EDTA, a chelator of Mn2+, markedly accentuates lung injury caused by glucose-glucose oxidase. These data are consistent with the findings of others that Mn2+ can facilitate direct oxidation of amino acids with concomitant H2O2 disproportionation. This could form the basis of a new therapeutic approach against oxygen radical-mediated tissue injury.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheton, P. B. L., andF. S. Archibald. 1988. Manganous complexes and the generation and scavenging of hydroxyl free radicals.Free Radical Biol. Med. 5:325–330.
Gutteridge, J. M. C., andJ. V. Bannister. 1986. Copper + zinc and manganese Superoxide dismutase inhibit deoxyribose degradation by the superoxide-driven fenton reaction at two different stages.Biochem. J. 234:225–231.
Stadtman, E. S., B. S. Berlett, andP. B. Chock. 1990. Manganese-dependent disproportionation of hydrogen peroxide in bicarbonate buffer.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87:384–390.
Berlett, B. S., P. B. Chock, M. B. Yim, andE. R. Stadtman. 1990. Manganese (II) catalyzes the bicarbonate dependent oxidation of amino acids by hydrogen peroxide and the amino acid-facilitated dismutation of hydrogen peroxide.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87:389–395.
Yim, M. B., B. S. Berlett, P. B. Chock, andE. R. Stadtman. 1990. Manganese (II) bicarbonate-mediated catalytic activity for hydrogen peroxide dismutation and amino acid oxidation: Detection of free radical intermediates.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87:394–398.
Phan, S. H., D. E. Cannon, J. Varani, U. S. Ryan, andP. A. Ward. 1989. Xanthine oxidase activity in rat pulmonary artery endothelial cells and its alteration by activated neutrophils.Am. J. Pathol. 134:1201–1211.
Varani, J., S. H. Phan, D. F. Gibbs, U. S. Ryan, andP. A. Ward. 1990. H2O2-mediated cytotoxicity of rat pulmonary artery endothelial cells: Changes in ATP and purine products and effects of protective interventions.Lab. Invest. 63:683–689.
Varani, J., S. E. G. Fligiel, G. O. Till, R. G. Kunkel, U. S. Ryan, andP. A. Ward. 1895. Pulmonary endothelial cell killing by human neutrophils: Possible involvement of hydroxyl radical.Lab. Invest. 53:656–661.
Varani, J., M. J. Bendelow, D. E. Sealey, S. L. Kunkel, D. E. Gannon, U. S. Ryan, andP. A. Ward. 1988. Tumor necrosis factor enhances susceptibility of vascular endothelial cells to neutrophil-mediated killing.Lab. Invest. 59:292–296.
Johnson, K. J., andP. A. Ward. 1974. Acute immunologie alveolitis.J. Clin. Invest. 54:349–356.
Yamazaki, I., andL. H. Piette. 1990. ESR spin-trapping studies on the reaction of Fe2+ with H2O2-reactive species in oxygen toxicity in biology.J. Biol. Chem. 265:13589–13594.
Beckman, J. S., R. L. Minor, Jr., andB. A. Freeman. 1986. Augmentation of antioxidant enzymes in vascular endothelium.Free Radical Biol. Med. 2:359–363.
Beckman, J. S., R. L. Minor, Jr., C. W. White, J. E. Repine, G. M. Rosen, andB. A. Freeman. 1988. Superoxide dismutase and catalase conjugated to polyethylene glycol increases endothelial enzyme activity and oxidant resistance.J. Biol. Chem. 263:6884–6890.
Freeman, B. A., S. L. Young, andJ. D. Cropo. 1983. Liposome-mediated augmentation of superoxide dismutase in endothelial cells prevents oxygen injury.J. Biol. Chem. 258:12534–12538.
Parenti, M., L. Rusconi, V. Cappabianca, E. A. Parati, andA. Groppetti. 1988. Role of dopamine in manganese neurotoxicity.Brain Res. 473:236–242.
Skreb, Y., andB. Nagy. 1984. Cell survival after the combined action of manganese (MnCl2) and X-rays in synchronized Chinese hamster cells.Arch. Toxlcol. 56:29–36.
Chandra, S. V., andG. S. Shukla, andR. C. Murthy. 1979. Effect of stress on the response of rat brain to manganese.Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 47:603–608.
Halatcheva, L., andP. Kinolova. 1980. The effect of heavy metais (lead, manganese, mercury) on the concentration of free amino acids in the liver of rats.Arch. Toxicol. (Suppl) 4:355–359.
Webster, W. S., andA. A. Valois. 1987. Reproductive toxicology of manganese in rodents, including exposure during the postnatal period.Neurotoxicology 8:437–442.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Varani, J., Ginsburg, I., Gibbs, D.F. et al. Hydrogen peroxide-induced cell and tissue injury: Protective effects of Mn2+ . Inflammation 15, 291–301 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00917314
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00917314