Abstract
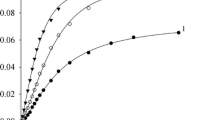
the polarographic waves corresponding to the reduction of the N=N-group of diazoaminobenzenes in methanolic solution are shifted to more positive potentials by addition of organic acids. The height of the prewave is approximately proportional to the concentration of the proton donor. Usually 4 equivalents of the acid per molecule of the depolarizer are needed to affect the shift of the whole wave towards more positive potentials. The remarkable shift corresponds to the participation of the proton of the acid in the potential determining step or the preprotonation of the depolarizer resp. The tendency of protonation increases with the electron donor intensity of the substituent in para-position of the depolarizer molecule.
The stability of triazenes in acid solution depends also of the nature of substituents and increases with electron acceptors and decreases with electron donors.
The limiting currents of p-cyano- and p-ethoxycarbonyl-diazoaminobenzenes in acidfree methanol are smaller as compared to the other investigated triazenes. However, in presence of organic acids the wave heights increase with the shift to more positive potential and reach the height corresponding to the 4e-reduction. The decrease in wave hight in methanol without acid is due to the reduction of a part of the depolarizer using protons of the residual molecules, whereby the resulting anions, or salts respectively, are reduced at considerably much more negative potential.
A mechanism for the reduction of triazenes is deduced.
Abstract
Die polarographischen Stufen der N=N-Reduktion von Triazenen in methanol. Lösung werden durch Zusatz organischer Protonendonatoren zu wesentlich positiveren Potentialen verlagert und erreichen dort wieder die Gesamthöhe der vierelektronigen Reduktion, wenn — bei ausreichendem pK der Säure — die Säurekonzentration das 4-fache der Depolarisatorkonzentration beträgt. Die beachtliche Positivierung ist auf die Beteiligung der Protonen am potentialbestimmenden Schritt, bzw. auf eine dem Elektronenübergang vorgelagerte Protonenaufnahme zurückzuführen. Die Protonierungstendenz steigt mit der Elektronendonatorwirkung von paraständigen Substituenten, wobei sich die Elektronendichte in der −N=N−NH-Gruppe erhöht.
Die Stabilität des Diazoaminobenzolmoleküls gegenüber Säuren erweist sich ebenfalls als von der Natur der Substituenten abhängig und ist bei Elektronenakzeptoren erhöht und dementsprechend bei Elektronendonatoren vermindert.
Die Grenzströme von p-Cyano-und p-Äthoxycarbonyl-diazoaminobenzol sind in säurefreiem Methanol niedriger als die der übrigen untersuchten Triazene, erreichen jedoch in den vorverlagerten Stufen bei ausreichender Säurekonzentration ebenfalls die Höhe der 4-elektronigen Reduktion. In protonenarmen Medien unterliegen diese Verbindungen teilweise einer Reduktion unter Verbrauch von Protonen des restlichen Teiles der Triazenmoleküle, die dann — als Anion, bzw. als Salz vorliegend — erst bei sehr negativen Potentialen reduziert werden.
Ein Mechanismus für die Reduktion der Triazene wird abgeleitet.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
L. Holleck undG. Kazemifard, J. Electroanal. Chem.35, 369 (1972).
G. Kazemifard, Dissertation Univ. Erlangen (1970).
D. Jannakoudakis undA. Wildenau, Z. Naturforsch.22 b, 118, 603 (1967).
L. Holleck, D. Jannakoudakis undA. Wildenau, Electrochim. Acta12, 1523 (1967).
L. Holleck undA. M. Shams El Din, Electrochim. Acta13, 199 (1968).
L. Holleck undH. J. Exner, Z. Elektrochem.56, 46 (1952).
L. Holleck undG. Kazemifard, Z. Naturforsch.26 b, 969 (1971).
L. Holleck, H. Marsen undH. J. Exner, Z. Naturforsch.9 b, 90 (1954).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Mit 3 Abbildungen
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holleck, L., Kazemifard, G. Der Einfluß von Protonendonatoren und von Substituenten auf die polarographische Reduktion von Diazoaminobenzolen (Triazenen) in methanolischen Lösungen. Monatshefte für Chemie 103, 1427–1437 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00904526
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00904526