Summary
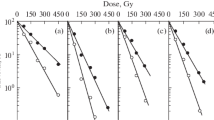
InNeurospora crassa X- and gamma-ray induced inactivation- and reversion-rates for conidia of HNO2 induced mutants were measured. With constant radiation dose inactivation rate is lowest for conidia of medium moisture content. It increases for higher and also for very low moisture content. The semilogarithmic plot of inactivation data for conidia irradiated in suspension or at medium moisture content results in a shouldered curve. A formal analysis using the number of nuclei of multinucleated conidia as numerical reference indicates that ca. 0.5 hits per nucleus are needed to inactivate such a conidium. The data for extremely dry conidia plotted from 0–210 kr likewise closely approximate a single hit curve with a steeper slope than that of the corresponding curve for conidia of medium moisture content.
Reversion rates of 5 among 7 mutants checked run parallel with inactivation with low figures for conidia of medium and increasing figures for higher as well as for very low moisture contents (class I). The reversion rate of conidia of very low moisture content of the other 2 mutants is equal or nearly equal to that of conidia of medium moisture content (class II).
Possible explanations for the data obtained are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Caldecott, R. S.: Effects of ionizing radiations on seeds of barley. Radiat. Res.2, 339 (1955).
—: Effects of hydration on X-ray sensitivity in Hordeum. Radiat. Res.3, 316 (1955).
Ehrenberg, A., andL. Ehrenberg: The decay of X-ray induced free radicals in plant seeds and starch. Ark. Fysik14, 133 (1958).
Ehrenberg, L.: The radiation induced growth inhibition in seedlings. Bot. Not. (Lund)108, 184 (1955).
—: Factors influencing radiation induced lethality, sterility, and mutations in barley. Hereditas (Lund)41, 123 (1955).
Franklin, R. E., andR. G. Gossling: The structure of sodium thymonucleate fibres. I. The influence of the water content. Acta Cryst.6, 673 (1953).
——: The structure of sodium thymonucleate fibres. III. The threedimensional Patterson function. Acta Cryst.8, 151 (1955).
Gafford, R. D.: The observation of two-process survival curves in gamma-irradiatedNeurospora conidia. Radiat. Res.9, 248 (1958).
Giles, N. H.: Studies on the mechanism of reversion in biochemical mutants ofNeurospora crassa. Cold Spr. Harb. Symp. quant. Biol.16, 283 (1951).
Harm, W.: Gene-controlled reactivation of ultraviolet-inactivated bacteriophage. J. cell. comp. Physiol., Suppl.1, 69 (1961).
—: Repair of lethal UV-damage in phage DNA. Repair from genetic radiation damage (F. H. Sobels, ed.), p. 107. London: Pergamon Press 1963.
Horowitz, N. H., andG. W. Beadle: J. biol. Chem.150, 325 (1943).
Kaplan, R. W.: Mutation und Tötung durch UV in Bakterien verschiedenen Wassergehalts. Naturwissenschaften42, 184 (1955a).
—: Influence of the water content on the UV-sensitivity of DNA and its bearing on biological UV-effects. Naturwissenschaften42, 466 (1955b).
—, andCh. Kaplan: Influence of water content on UV-induced s-mutation and killing in Serratia. Exp. Cell Res.11, 378 (1956).
Klingmüller, W.: Zur Moglichkeit eines nachträglichen Strahlenschutzes bei Samen vonVicia faba. Z. Naturforsch.14b, 268 (1959).
Klingmüller, W.: Modification of radiation damage and electronspin-resonance measurements inVicia faba seeds. Proc. 3rd Intern. Congr. Photobiol. Kopenhagen 1960a, p. 261.
Klingmüller, W.: Radiation damage inVicia faba seeds. Proc. Sympos. on the effects of ionizing radiations on seeds, Karlsruhe 1960b, p. 67.
—: Modification of radiation damage in seeds by post treatment. Nature (Lond.)189, 413 (1961).
—: Strahlenbiologische Untersuchungen anVicia faba-Samen. Der Einfluß des Wassergehaltes, der Sauerstoffzufuhr und der Lagerungszeit auf primäre und sekundäre Strahleneffekte. Int. J. Radiat. Biol.4, 255 (1962a).
—: Influence of graded moisture content on survival and back mutation rate of X-rayedNeurospora crassa conidia. Radiat. Res.16, 575 (1962b).
Klingmüller, W.: Influence of graded moisture content on survival and back mutation rate of X-rayedNeurospora crassa conidia. 2nd Intern. Congr. Rad. Res. Harrogate 1962c, Abstracts of papers p. 197.
—: A damaging effect of drying onNeurospora crassa conidia and its reversibility. Z. Naturforsch.18b, 55 (1963).
—,G. R. Lane, M. C. Saxena, andD. J. E. Ingram: Free radicals in X-rayed seeds of high and low water content, as measured by electronspin resonance. Nature (Lond.)184, 464 (1959).
—, u.M. C. Saxena: Nachweis freier Radikale in röntgenbestrahlten Samen vonVicia faba mittels Elektronspin-Resonanz-Absorption. Naturwissenschaften46, 475 (1959).
Metzger, K.: Der Einfluß des Wassergehaltes auf Inaktivierung und Mutabilität vonSerratia marcescens durch UV- und Röntgenbestrahlung. Z. allg. Mikrobiol.1, 29 (1960).
Miltenburger, H., u.H. Bauer: Inaktivierung vonNeurospora-Conidien durch Röntgenstrahlen unter verschiedenen Bedingungen. Strahlentherapie116, 57 (1961).
Powers, E. L.: Reversibility of X irradiation-induced effects in dry biological systems. J. cell. comp. Physiol. Suppl.1, 13 (1961).
Serres, F. J. de, H. G. Kølmark, andH. E. Brockman: Factors influencing the survival ofNeurospora crassa conidia in sorbose-sucrose media. Nature (Lond.)193, 556 (1962).
Somers, C. E., R. P. Wagner, andT. C. Hsu: Mitosis in vegetative nuclei ofNeurospora crassa. Genetics45, 801 (1960).
Sparrman, B., L. Ehrenberg, andA. Ehrenberg: Scavenging of free radicals and radiation protection by nitric oxide in plant seeds. Acta chem. scand.13, 199 (1959).
Stapelton, G. E., andA. Hollaender: Mechanism of lethal and mutagenic action of ionizing radiations onAspergillus terreus. II. Use of modifying agents and conditions. J. cell. comp. Physiol., Suppl. 1,101 (1952).
Tallentire, A., andE. L. Powers: Modification of sensitivity to X-irradiation by water in bacillus megaterium. Radiat. Res.20, 270 (1963).
Woodward, V. W., andV. Swarup: The influence of water on the UV-sensitivity ofNeurospora conidia. Microbial Genetics Bull. No 13 (1956).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Mit 12 Textabbildungen
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klingmüller, W. Der Einfluss des Wassergehaltes auf Inaktivierung und Mutationsrate von röntgen- und gammabestrahltenNeurospora Crassa-Conidien. Zeitschrift für Vererbungslehre 96, 116–127 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00888783
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00888783