Abstract
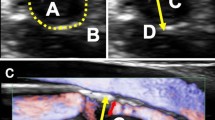
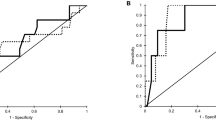
A transcranial colourcoded duplex sonography (TCCD) study was performed to establish reliable criteria for the assessment of collateral flow through the anterior (ACoA) and posterior (PCoA) communicating artery without using compression tests. We studied 86 patients with angiographically evaluated unilateral > 69% stenosis (n = 53) and occlusion (n = 33) of the carotid artery. The following TCCD criteria were evaluated: for diagnosis of cross-flow through the ACoA, detection of reversed flow in the anterior cerebral artery (ACA) on the obstructed (ipsilateral) side. For the diagnosis of cross-flow through the PCoA: (A) identification of the PCoA; (B) peak systolic velocity in P1 posterior cerebral artery (PCA) higher than the mean value + 2 SD of normals; (C) ratio of ipsilateral peak systolic P1 PCA velocity to peak systolic P2 PCA velocity higher than the mean ratio + 2 SD of normals; (D) ratio of ipsilateral peak systolic PI PCA velocity to contralateral peak systolic P1 PCA velocity higher than the mean ratio − 2 SD of normals; (E) peak systolic basilar artery velocity higher than the mean value + 2 SD of normals. Eight patients (9%) with inadequate temporal ultrasonic windows were excluded. The sensitivity and specificity for TCCD evaluation of ACoA crossflow were 100%. Using criteria A and B the corresponding values for the PCoA were 85 and 98%, respectively. Criteria C-E were not useful owing to lower sensitivity. In conclusion, we delineated TCCD criteria that make it possible to assess reliably the cross-flow through the circle of Willis in patients with adequate ultrasonic windows.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Battacharji SK, Hutchinson EC, McCall AJ (1967) The circle of Willis — the incidence of developmental abnormalities in normal and infarcted brains. Brain 90: 747–758
Schneider PA, Ringelstein EB, Rossmann ME, et al (1988) Importance of cerebral collateral pathways during carotid endarterectomy. Stroke 19: 1328–1334
Shomer DF, Marks MP, Steinberg GK, et al. (1994) The anatomy of the posterior communicating artery as a risk factor for ischemic cerebral infarction. N Engl J Med 330: 1565–1570
American Academy of Neurology, Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee (1990) Assessment: transcranial Doppler. Neurology 40: 680–681
Anzola GP, Gasparotti R, Magoni M, Prandini F (1995) Transcranial Doppler sonography and magnetic resonance angiography in the assessment of collateral hemispheric flow in patients with carotid artery disease. Stroke 26: 214–217
Grolimund P, Seiler RW, Aaslid R, Huber P, Zurbruegg H (1987) Evaluation of cerebrovascular disease by combined extracranial and transcranial Doppler sonography: experience in 1039 patients. Stroke 18: 1018–1024
Lindegaard KF, Bakke SJ, Grolimund P, Aaslid R, Huber P, Nornes H (1985) Assessment of intracranial hemodynamics in carotid artery disease by transcranial Doppler ultrasound. J Neurosurg 63: 890–898
Müller M, Hermes M, Brückmann H, Schimrigk K (1995) Transcranial Doppler ultrasound in the evaluation of collateral blood flow in patients with internal carotid artery occlusion: correlation with cerebral angiography. AJNR 16: 195–202
Fujioka KM, Douville CM (1992) Anatomy and freehand examination techniques. In: Newell DW, Aaslid R (eds) Transcranial Doppler. Raven Press, New York, pp 9–31
Friedman SG (1990) Transient ischemic attacks resulting from carotid duplex imaging. Surgery 107: 153–155
Khaffaf N, Karnik R, Winkler W-B, Valentin A, Slany J (1994) Embolic stroke by compression maneuver during transcranial Doppler sonography. Stroke 25: 1056–1057
Mast H, Ecker S, Marx P (1993) Cerebral ischaemia induced by compression tests during transcranial Doppler sonography. Clin Investig 71: 46–48
Nelson DA, Mahru MM (1963) Death following digital arterial occlusion. Arch Neurol 8: 640–643
Bogdahn U, Becker G, Winkler J, Greiner K, Perez J, Meurers B (1990) Transcranial colour-coded real-time sonography in adults. Stroke 21: 1680–1688
Baumgartner RW, Mathis J, Sturzenegger M, Mattle HP (1994) A validation study on the intraobserver reproducibility of transcranial colour-coded duplex sonography velocity measurements. Ultrasound Med Biol 20: 233–237
Baumgartner RW, Mattle HP, Aaslid R (1995) Intracranial duplex sonography, magnetic resonance angiography, and computed tomography angiography: methods, applications, advantages, and limitations. J Clin Ultrasound 23: 89–111
Martin PJ, Evans DH, Naylor AR (1994) Transcranial colour-coded sonography of the basal cerebral circulation. Reference data from 115 volunteers. Stroke 25: 390–396
Sitzer M, Fürst G, Fischer H, et al. (1993) Between-method correlation in quantifying internal carotid stenosis. Stroke 24: 1513–1518
Barnett HJM, Taylor DW, Haynes RB, et al (1991) Beneficial effect of carotid endarterectomy in symptomatic patients with high-grade carotid stenosis. N Engl J Med 325: 445–453
Von Reutern GM, Pourcelot L (1978) Cardiac cycle-dependent alternating flow in vertebral arteries with subclavian artery stenosis. Stroke 9: 229–236
Eikelboom BC, Welten RJTH, Ackerstaff RGA, Vermeulen F (1990) Recognizing stroke-prone patients with a poor collateral circulation. Eur J Vasc Surg 63: 890–898
Riggs HE, Rupp C (1963) Variation in the form of circle of Willis. The relation of the variations to collateral circulation. Arch Neurol 8: 8–14
Cormier JM, Fermand M, Massoni JM (1987) Appreciation préopératoire du risque de clampage dans la chirurgie carotidienne et adoptation de la technique opératoire. J Chir (Paris) 124: 585–592
Bass A, Krupski WC, Dilley RB, Bernstein EF, Otis SM (1990) Comparison of transcranial and cervical continuous-wave Doppler in the evaluation of intracranial collateral circulation. Stroke 21: 1584–1588
Fürst G, Steinmetz H, Fischer H, et al. (1993) Selective MR Angiography and intracranial collateral blood flow. J Comput Assist Tomogr 17: 178–183
Hu H-H, Luo C-L, Sheng W-Y, Teng M M-H, Wong W-J, Luk Y-O (1995) Transorbital colour Doppler flow imaging of the carotid siphon and major arteries at the base of the brain. AJNR 16: 591–598
Baker AB, Iannone A (1959) Cerebrovascular disease. I. The large arteries of the circle of Willis. Neurology 9: 321–333
Nakamura M, Yamamoto H, Kikuchi Y, Ishihara Y, Sata T, Yoshimura S (1971) Cerebral atherosclerosis in Japanese. I. Age related to atherosclerosis. Stroke 2: 400–408
Yasargil MG (1987) Pathological considerations. In: Yasargil MG (ed) Microneurosurgery, vol IIIA. AVM of the brain, history, embryology, pathological considerations, hemodynamics, diagnostic studies, microsurgical anatomy. Thieme, Stuttgart, pp 49–211
Schöning M, Walter J (1992) Evaluation of the vertebrobasilar-posterior system by transcranial colour duplex sonography in adults. Stroke 23: 1280–1286
Nomes H, Sorteberg W, Nakstad P, Bakke SJ, Aaslid R, Lindegaard KF (1990) Hemodynamic aspects of clinical cerebral angiography. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 105: 89–97
Eden A (1988) Transcranial Doppler ultrasonography and hyperostosis of the skull. Stroke 19: 1445–1446
Halsey JH (1990) Effect of emitted power on waveform intensity in transcranial Doppler. Stroke 21: 1573–1578
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baumgartner, R.W., Baumgartner, I. & Schroth, G. Diagnostic criteria for transcranial colour-coded duplex sonography evaluation of cross-flow through the circle of Willis in unilateral obstructive carotid artery disease. J Neurol 243, 516–521 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00886873
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00886873