Abstract
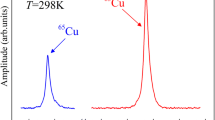
Results of cw63Cu NMR measurements in dilute CuFe alloys containing from 0.01 up to 0.2 at.-% Fe are presented. The temperature was well above the Kondo temperature of this specimen. The broadening of the NMR line width is caused by the localized magnetic moment of the Fe impurities. The decreasing signal amplitude with increasing iron content is due to the quadrupolar interactions appearing simultaneously. The line broadening correspond strongly to that of the impurity susceptibility behaviour in CuFe. The quadrupolar disturbances are temperature independent. The influence of the simultaneously appearing magnetic and electric interactions on the spin lattice nuclear relaxation time is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
R. E. Watson: In:Hyperfine Interactions, hrsg. v. A. J. Freeman u. R. B. Frankel (Academic Press, New York 1967) S. 413
A. J. Heeger: In:Solid State Physics, Vol. 23, hrsg. v. F. Seitz, D. Turnbull, H. Ehrenreich (Academic Press, New York 1969) S. 283
K. Tompa: J. Phys. Chem. Sol.33, 163 (1972)
T. Sugawara: J. Phys. Soc. Japan,14, 643 (1959)
R. Behringer: J. Phys. Chem. Sol.2, 209 (1957)
J. E. Potts, L. B. Welsh: Phys. Rev. B5, 3421 (1972)
E. R. Andrew, J. L. Carolan, P. J. Randall: Phys. Letters37A, 125 (1971)
I. Ebert, G. Seifert:Kernresonanz im Festkörper(Akademische Verlagsgesellschaft, Leipzig 1966) S. 192
B. B. Schwartz: In:Hyperfine Interactions in Excited Nuclei, Vol. 1, hrsg. v. G. Goldwing, R. Kalisch (Gordon and Breach, New York, 1971)
K. Tompa, G. Grüner, A. Janossy, F. Toth: Sol. Stat. Commun.7, 697 (1969)
K. Tompa: Proc. Low Temp. Physics LT-12, Kyoto (Academic Press, New York 1970) S. 783
F. N. Robinson: J. Sci. Instr.40, 481 (1959)
J. Kopp: J. Phys. F (Metal Phys.)3, 1994 (1973)
R. E. Walstedt, L. R. Walker: Phys. Rev. B9, 4857 (1974)
D. W. Posener: Australian J. Phys.,12, 184 (1959)
C. M. Hurd: Phys. Rev. Letters18, 1127 (1967)
J. M. Franz, D. J. Sellmeyer: Phys. Rev. B8, 2083 (1973)
N. Bloembergen, T. J. Rowland: Acta Met.1, 731 (1953)
K. Tompa, A. Lovas, L. Zambo: Phys. Stat. Sol. (b)54, K 17 (1972)
B. Giovannini, P. Pincus, G. Gladstone, A. J. Heeger: J. Physique32, C1, 163 (1971)
P. Bernier, H. Alloul: J. Phys. F (Met. Phys.)3, 869 (1973)
W. W. Simmons, W. J. O'Sullivan, W. A. Robinson: Phys. Rev.127, 1168 (1962)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hesse, J., Szücs, Z. Einfluß der Ladungs- und Spindichteoszillationen auf das63Cu-Kernresonanzsignal in CuFe. Appl. Phys. 6, 55–60 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00883549
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00883549