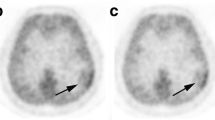
Abstract
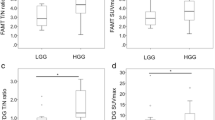
Use of iodine-123-α-methyl tyrosine (123I-IMT) allows investigation of the amino acid transport rate in gliomas. It was the aim of this study to compare the value of measurement of glucose metabolism with that of measurement of123I-IMT uptake for the non-invasive grading of brain tumours. The study population comprised 23 patients with histopathologically proven primary brain tumours; 14 had high-grade gliomas, and nine low-grade brain neoplasms. Glucose metabolism was studied using an ECAT EXACT 47 positron emission tomography (PET) camera and fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG);123I-IMT uptake was measured with the triple-headed single-photon emission tomography (SPET) camera, MULTISPECT 3.18F-FDG and123I-IMT uptake was quantified as ratios between the uptake by the tumour and contralateral regions of reference. Glucose metabolism and amino acid uptake of the brain tumours correlated significantly (r=0.71,P <0.001). Assuming discrimination thresholds between high-grade and low-grade tumours of 0.8 for18F-FDG uptake and 1.8 for123I-IMT uptake, the accuracy values of18F-FDG PET and123I-IMT SPET for differentiating between high-grade and low-grade tumours were 21/23 (91%) and 19/23 (83%), respectively. The difference in diagnostic performance was not significant on receiver operating characteristic analysis (P >0.4). It is concluded that there is no major difference between the PET investigation of glucose metabolism and the less expensive SPET measurement of amino acid uptake in terms of their accuracy in evaluating the malignancy grade of primary brain tumours. This encourages the performance of further studies to analyse the potential impact of123I-IMT SPET on the therapeutic management of patients with brain tumours.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schmidek HH. Surgical management of supratentorial gliomas. In: Schmidek HH, Sweet WH, eds.Operative neurosurgical techniques, 3rd edn. Philadelphia: Saunders; 1995: 517–534.
Glantz MJ, Burger PC, Herndon JE, Friedman AH, Cairncross JG, Vick NA, Schold SC. Influence of the type of surgery on the histologic diagnosis in patients with anaplastic gliomas.Neurology 1991; 41: 1741–1744.
Di Chiro G. Positron emission tomography using [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose in brain tumours: a powerful diagnostic and prognostic tool.Invest Radiol 1986; 22: 360–371.
Patronas NJ, Di Chiro G, Kufta C, Bairamian D, Kornblith PL, Simon R, Larson SM. Prediction of survival in glioma patients by means of positron emission tomography.J Neurosurg 1985; 62: 816–822.
Hölzer T, Herholz K, Jeske J, Heiss WD. FDG-PET as a prognostic indicator in radiochemotherapy of glioblastoma.J Comput Assist Tomogr 1993; 17: 681–687.
Alavi JB, Alavi A, Chawluk J, Kushner M, Powe J, Hickey W, Reivich M. Positron emission tomography in patients with glioma — a predictor of prognosis.Cancer 1988; 62: 1074–1078.
Kim CK, Alavi JB, Alavi A, Reivich M. New grading system of cerebral gliomas using positron emission tomography with F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose.J Neurooncol 1991; 10: 85–91.
Mineura K, Sasajima T, Kowada M, Ogawa T, Hatazawa J, Shishido F, Uemura K. Perfusion and metabolism in predicting the survival of patients with cerebral gliomas.Cancer 1994; 73: 2386–2394.
Schifter T, Hoffman JM, Hanson MW, Boyko OB, Beam C, Paine S, Schold SC, Burger PC, Coleman RE. Serial FDG-PET studies in the prediction of survival in patients with primary brain tumours.J Comput Assist Tomogr 1993; 17: 509–516.
Kuwert T, Morgenroth C, Woesler B, Matheja P, Palkovic S, Vollet B, Samnick S, Maasjosthusmann U, Lerch H, Gildehaus F-J, Wassmann H, Schober O. Uptake of iodine-123-α-methyl tyrosine by primary brain tumours and non-neoplastic brain lesions.Eur J Nucl Med 1996; 23: 1345–1353.
Kleihues P, Burger PC, Scheithauer BW.Histological typing of tumours of the central nervous system. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer, 1993.
Kuwert T, Morgenroth C, Woesler B, Matheja P, Palkovic S, Vollet B, Schäfers M, Wassmann H, Schober O. Influence of size of regions of interest on the measurement of uptake of iodine-123-α-methyl tyrosine by brain tumours.Nucl Med Commun 1996; 17: 609–615.
Machulla HJ, Skansdal A, Stöcklin G.123(125)Xe-exposed KIO3, a reagent for iodination with high specific activity.Radioclin Acta 1977; 24: 42–46.
Fischer S, Wolf H, Brandau W, Clausen M, Henze E, Schober O. Iodierung von α-Methyltyrosin (AMT): Optimierung der Methode für die Routinepräparationz.Nucl Med 1993; 32: A113.
Kuikka JT, Tenhunen-Eskelinen M, Jurvelin J, Kiliänen H. Physical performance of the Siemens Multi SPECT 3 gamma camera.Nucl Med Commun 1993; 14: 490–497.
Chang LT. A method for attenuation correction in radionuclide computed tomography.IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 1978; NS-26/2: 2780–2789.
Wienhard K, Eriksson L, Grootoonk S, Casey M, Pietrzyk U, Heiss WD. Performance evaluation of the positron scanner ECAT EXACT.J Comput Assist Tomogr 1992; 16: 804–813.
Talairach J, Tournoux P.Co-planar stereotactic atlas of the human brain. Stuttgart, New York: Thieme; 1988; 37–110.
Ogawa T, Kanno I, Shishido F, Inugami A, Higano S, Fujita H, Murakami M, Uemura K, Yasui N, Mineura K, Kowada M. Clinical value of PET with18F-fluorodeoxyglucose andl-methyl-11C-methionine for diagnosis of recurrent brain tumors and radiation injury.Acta Radiol 1991; 32: 197–202.
Bortz J.Lehrbuch der Statistik, 2nd edn. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer, 1985.
Delbeke D, Meyerowitz C, Lapidus RL, Maciunas RJ, Jennings MT, Moots PL, Kessler RM. Optimal cutoff levels of F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in the differentiation of low-grade from high-grade brain tumors with PET.Radiology 1995; 195: 47–52.
Metz CE. ROC methodology in radiologic imaging.Invest Radiol 1986; 21: 720–733.
Metz CE. Quantification of failure to demonstrate statistical significance.Invest Radiol 1993; 28: 59–63.
Müller SP, Reiners C. Untersuchungen und Empfehlungen zum Design von ROC-Studien in der Nuklearmedizin.Nucl Med 1995; 34: 24–31.
Herholz K, Friedrichs B, Jeske J, Heiss WD. Prognostic significance of positron emission tomography with F-18-fluorodeoxyglucose in gliomas.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol (Suppl) 1992; R119.
Patronas NJ, Di Chiro G, Brooks RA, DeLaPaz RL, Kornblith PL, Smith BH, Rizzoli HV, Kessler RM, Manning RG, Channing M, Wolf AP, O'Connor CM. 18-Fluorodeoxyglucose and positron emission tomography in the evaluation of radiation necrosis of the brain.Radiology 1982; 144: 885–889.
Glantz MJ, Hoffman JM, Coleman RE, Friedman AH, Hanson MW, Burger PC, Herndon JE, Meisler WJ, Schold SC. Identification of early recurrence of primary central nervous system tumors by [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography.Ann Neurol 1991; 29: 347–355.
Di Chiro G, DeLaPaz RL, Brooks RA, Sokoloff L, Kornblith PL, Smith BH, Patronas NJ, Kufta CV, Kessler RM, Johnston GS, Manning RG, Wolf AP. Glucose utilization of cerebral gliomas measured by 18-F-fluorodeoxyglucose and positron emission tomography.Neurology 1982; 32: 1323–1329.
Patronas NJ, Brooks RA, DeLaPaz RL, Smith BH, Kornblith PI, Di Chiro G. Glycolytic rate (PET) and contrast enhancement (CT) in human cerebral gliomas.AJNR 1983; 4: 533–535.
Derlon JM, Bourdet C, Bustany P; Chatel M, Theron J, Darcel F, Syrota A. [11C]l-methionine uptake in gliomas.Neursurgery 1989; 25: 720–728.
Wienhard K, Herholz K, Coenen HH, Rudolf J, Kling P, Stöcklin G, Heiss WD. Increased amino acid transport into brain tumors measured by PET ofl-(2-18F)fluorotyrosine.J Nucl Med 1991; 32: 1338–1346.
Schober O, Meyer GJ, Stolke D, Hundeshagen H. Brain tumor imaging using C-11-labelledl-methionine andd-methionine.J Nucl Med 1985; 26: 98–99.
Bergström M, Lundqvist H, Ericson K, Lilja A, Johnstrom P, Langstrom B, von Holst H, Eriksson L, Blomqvist G. Comparison of the accumulation kinetics ofl-(methyl-11C)-methionine andd-(methyl-11C)-methionine in brain tumors studied with positron emission tomography.Acta Radiol 1987; 28: 225–229.
Ishiwata K, Kubota K, Murakami M, Kubota R, Sasaki T, Ishii S, Senda M. Re-evaluation of amino acid PET studies: Can the protein synthesis rates in brain and tumor tissues be measured in vivo?J Nucl Med 1993; 34: 1936–1943.
Ogawa T, Shishido F, Kanno I, Inugami A, Fujita H, Murakami M, Shimosegawa E, Ito H, Hatazawa J, Okudera T, Uemura K, Yasui N, Mineura K. Cerebral glioma: evaluation with methionine PET.Radiology 1993; 186: 45–53.
Ogawa T, Inugami A, Hatazawa J, Kanno I, Murakami M, Yasui N, Mineura K, Uemura K. Clinical positron emission tomography for brain tumors: comparison of fludeoxyglucose F-18 andl-methyl-11C-methionine.AJNR 1996; 17: 345–353.
Drane WE, Abbott FD, Nicole MW, Mastin ST, Kuperus JH. Technology for FDG SPECT with a relatively inexpensive gamma camera. Work in progress.Radiology 1994; 191: 461–465.
Langen KJ, Roosen N, Coenen HH, Kuikka JT, Kuwert T, Herzog H, Stöcklin G, Feinendegen LE. Brain and brain tumor uptake ofl-3-[123I]iodomethyl tyrosine: competition with naturall-amino acids.J Nucl Med 1991; 32 1225–1228.
Langen KJ, Coenen HH, Roosen N, Kling P, Muzik O, Herzog H, Kuwert T, Stöcklin G, Feinendegen LE. SPECT studies of brain tumors withl-3-[123I]iodo-α-methyl tyrosine: comparison with PET,124IMT and first clinical results.J Nucl Med 1990; 31: 281–286.
Kawai K, Fujibayashi Y, Saji H, Konishi J, Yokoyama A. New radioiodinated radiopharmaceutical for cerebral amino acid transport studies: 3-iodo-alpha-methyl-l-tyrosine [abstract].J Nucl Med 1988; 29: 778.
Guth-Tougelidis B, Müller S, Mehdorn MM, Knust EJ, Dutschka K, Reiners C.dl3-123I-iodo-α-methyltyrosine uptake in brain tumor recurrences.Nucl Med 1995; 34: 71–75.
Biersack HJ, Coenen HH, Stöcklin G, Reichmann K, Bockisch A, Oehr P, Kashab M, Rollmann O. Imaging of brain tumors withl-3-[123I]iodo-α-methyl tyrosine and SPECT.J Nucl Med 1989; 30: 110–112.
Kuwert T, Sures T, Herzog H, Loken M, Hennerici M, Langen KJ, Feinendegen LE. On the influence of spatial resolution and of the size and form of regions of interest on the measurement of regional cerebral metabolic rates by positron emission tomography.J Neural Transm (Suppl) 1992; 37: 53–66.
Leskinen-Kallio S, Ruotsalainen U, Nagren K, Teräs M, Joensuu H. Uptake of caron-11-methionine and fluorodeoxyglucose in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: a PET study.J Nucl Med 1991; 32: 1211–1218.
Black KL, Hawkins RA, Kim KT, Becker DP, Lerner C, Marciano D. Use of thallium-301 SPECT to quantitative malignancy grade of gliomas.J Neurosurg 1989; 71: 342–346.
Oriuchi N, Tomiyoshi K, Inoue T, Ahmad K, Sarwar M, Tokunaga M, Suzuki H, Watanabe N, Hirano T, Horikoshi S, Shibasaki T, Tamura M, Endo K. Independent thallium-201 accumulation and fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose metabolism in glioma.J Nucl Med 1996; 37: 457–462.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Woesler, B., Kuwert, T., Morgenroth, C. et al. Non-invasive grading of primary brain tumours: Results of a comparative study between SPET with123I-α-methyl tyrosine and PET with18F-deoxyglucose. Eur J Nucl Med 24, 428–434 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00881816
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00881816