Abstract
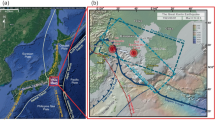
Relationships between the locations of mining-induced seismic events, local fault structure, and mine geometry were examined in a deep hard-rock mine in northern Idaho. Stopes experiencing rock bursts and other large seismic events were found to fall into two structural regimes: the “Silver Vein”, and the “N48°W Trend,” a steeply dipping plane of seismic activity that is subparallel to major local steeply dipping faults which bound blocky structures. The N48°W Trend also intersects a shaft that was seriously damaged when fault gouge was expelled into the opening during a 3-month period of high seismic energy release. Models of stress interaction are used to support the hypothesis that mining-induced deformation was mobilized along a 1.5 km length of the N48°W Trend. Specifically, numerical models are used to simulate rupture of seismic events and estimate induced changes in the quasi-static stress field. A Coulomb failure criterion is used with these results to estimate the spatial variation in potential for slip on planes parallel to local faulting. Increases in the potential for slip on fault planes subparallel to the N48°W Trend are consistent with activation of deformation along its 1.5 km length. For events with constant seismic moment, stress drop is shown to be far more important than source dimension in elevating slip potential along the observed plane of seismic activity
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakun, W. H. (1984),Seismic Moments, Local Magnitudes, and Coda-duration Magnitudes for Earthquakes in Central California, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am.74, 439–458.
Blake, W. (1972),Rock Burst Mechanics, Quart. Colo. School of Mines67, 1–64.
Board, M., andBeus, M.,Instrumentation and Preliminary Analysis of a 6,200-ft Deep Circular Shaft in Northern Idaho, Geomechanics Applications in Underground Hardrock Mining (Proc. Soc. Mining Engineers, Denver, 1984), AIME, 127–140.
Brummer, R. K., andRorke, A. J.,Case studies on large rockbursts in South African gold mines. InRockbursts and Seismicity in Mines (Proc. 2nd Int. Symp. Rockbursts and Seismicity in Mines, Minneapolis, MN, June 8–10, 1988) (Balkema, Rotterdam 1990) pp. 323–329.
Brune, J. N. (1970),Tectonic Stress and the Spectra of Seismic Shear Waves from Earthquakes, J. Geophys. Res.75, 4997–5009.
Cook, N. G. W. (1963),The seismic location of rockbursts. In Proc. 5th U.S. Nat. Symp. onRock Mechanics, pp. 493–516.
Cook, N. G. W., Hoek, E., Pretorius, J. P. G., Ortlepp, W. D., andSalamon, M. D. G. (1966),Rock Mechanics Applied to the Study of Rockbursts, J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall.66, 436–528.
Crouch, S. L., andStarfield, A. M.,Boundary Elements in Solid Mechanics (Allen and Unwin, London 1983) 322 pp.
Estey, L. H., Swanson, P. L., Boler, F. M., andBillington, S.,Microseismic source locations: A test of faith. InRock Mechanics Contributions and Challenges (Proc. 31st U.S. Nat. Symp. on Rock Mechanics, Golden, CO, June 1990) (Balkema, Rotterdam 1990) pp. 939–946.
Gay, N. C., Spencer, D., Van Wyk, J. J., andVan der Heever, P. K.,The control of geological and mining parameters on seismicity in the Klerksdorp gold mining district. In Proc.1st. Int. Congr. on Rockbursts and Seismicity in Mines, 1984 (SAIMM, Johannesburg 1984) pp. 107–120.
Gibowicz, S. J. (1990),The mechanism of seismic events induced by mining: A review. InRockbursts and Seismicity in Mines (Proc. 2nd Int. Symp. Rockbursts and Seismicity in Mines, Minneapolis, MN, June 8–10, 1988) (Balkema, Rotterdam 1990) pp. 3–27.
Grasso, J. R. (1993),Mechanics of Seismic Instabilities Induced by the Recovery of Hydrocarbons, Pure Appl. Geophys.139, 507–534.
Gutenberg, B., andRichter, C. F. (1956),Magnitude and Energy of Earthquakes, Ann. Geofis.9, 1–15.
Hobbs, S. W., Griggs, A. B., Wallace, R. E., andCampbell, A. B. (1965),Geology of the Coeur d'Alene District, Shoshone County, Idaho, U.S. Geol. Surv. Prof. Paper478, 139 pp.
Jaeger, J. C., andCook, N. G. W.,Fundamentals of Rock Mechanics (Chapman and Hall, NY 1976) 585 pp.
McGarr, A., Bicknell, J., Churcher, J., andSpottiswoode, S. (1990),Comparison of Ground Motion from Tremors and Explosions in Deep Gold Mines, J. Geophys. Res.95, 21,777–21,792.
McGarr, A., Green, R. W. E., andSpottiswoode, S. M. (1981),Strong Motion of Mine Tremors: Some Implications for Near-source Ground Motion Parameters, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am.71, 295–320.
Oppenheimer, D. H., Reasenberg, P. A., andSimpson, R. W. (1988),Fault Plane Solutions for the 1984 Morgan Hill, California, Earthquake Sequence: Evidence for the State of Stress on the Calaveras Fault, J. Geophys. Res.93, (B8), 9007–9026.
Reasenberg, P. A., andSimpson, R. W. (1992),Response of Regional Seismicity to the Static Stress Change Produced by the Loma Prieta Earthquake, Science255, 1687–1690.
Roeloffs, E. (1993),Can Poroelastic Models Explain the Focal Mechanisms of Reservoir-induced Seismicity? Pure Appl. Geophys., in preparation.
Ryder, J. A. (1988),Excess Shear Stress in the Assessment of Geologically Hazardous Situations, J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall.88 (1), 27–39.
Simpson, R. W., Schulz, S. S., Dietz, L. D., andBurford, R. O. (1988),The Response of Creeping Parts of the San Andreas Fault to Earthquakes on Nearby Faults:Two Examples, Pure Appl. Geophys.126, 665–685.
Spottiswoode, S. M.,Source mechanisms of mine tremors at Blyvooruitzicht gold mine. In Proc.1st Int. Congr. on Rockbursts and Seismicity in Mines, 1984 (SAIMM, Johannesburg 1984) pp. 107–120.
Spottiswoode, S. M., andMcGarr, A. (1975),Source Parameters of Tremors in a Deep-level Gold Mine, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am.65, 93–112.
Sprenke, K. F., Stickney, M. C., Dodge, D. A., andHammond, W. R. (1991),Seismicity and Tectonic Stress in the Coeur d'Alene Mining District, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am.81, 1145–1156.
Steblay, B. J., Swendseid, J., andBrady, B.,Innovative microseismic rock burst monitoring system InRockbursts and Seismicity in Mines (Proc. 2nd Int. Symp. Rockbursts and Seismicity in Mines, Minneapolis, MN, June 8–10, 1988) (Balkema, Rotterdam 1990) pp. 259–262.
Stein, R. S., King, G. C. P., andLin, J. (1992),Change in Failure Stress on the Southern San Andreas Fault System Caused by the 1992 Magnitude =7.4 Landers Earthquake, Nature258, 1328–1332.
Stein, R. S., andLisowski, M. (1983),The 1979 Homestead Valley Earthquake Sequence, California: Control of Aftershocks and Postseismic Deformation, J. Geophys. Res.88, (B8), 6477–6490.
Swanson, P. L., Estey, L. H., Boler, F. M., andBillington, S. (1993),Mining-induced Microseismic Event Location Errors: Accuracy and Precision of Two Location Systems, Pure Appl. Geophys.139, 375–404.
Swanson, P. L., andSines, C. D. (1990),Repetitive Seismicity and Rock Bursting along a Plane Parallel to Known Faulting in the Coeur d'Alene District, ID, Trans. Am. Geophys. Un., EOS,71, 1453 pp.
Swanson, P. L., andSines, C. D. (1991),Characteristics of Mining-induced Seismicity and Rock Bursting in a Deep Hard-rock Mine. Bur. of Mines Report of Invest. 9393, 12 pp.
Toksöz, M. N., Goins, N. R., andCheng, C. H. (1977),Moonquakes: Mechanisms and Relation to Tidal Stresses, Science196, 979–981.
Wallace, C. A., Lidke, D. J., andSchmidt, R. G. (1990),Faults of the Central Part of the Lewis and Clark Line and Fragmentation of the Late Cretaceous Foreland Basin in West-central Montana, Geolog. Soc. Am. Bull.102, 1021–1037.
Wallace, R. E., andMorris, H. T. (1986),Characteristics of Faults and Shear Zones in Deep Mines, Pure Appl. Geophys.124, 107–125.
Whyatt, J. K. (1986),Geomechanics of the Caladay Shaft, M.S. Thesis, Univ. of Idaho, Moscow, ID.
Williams, T. J., andCuvelier, D. J.,Report on a field trial of an underhand longwall mining-method to alleviate rockburst hazards. InRockbursts and Seismicity in Mines (Proc. 2nd Int. Symp. Rockbursts and Seismicity in Mines, Minneapolis, MN, June 8–10, 1988) (Balkema, Rotterdam 1990) pp. 349–353.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swanson, P.L. Mining-induced seismicity in faulted geologic structures: An analysis of seismicity-induced slip potential. PAGEOPH 139, 657–676 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00879957
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00879957