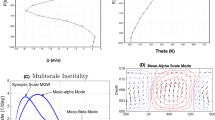
Abstract
Data from the SESAME storm-scale network are used in computing the momentum budget of the prestorm, storm, and poststorm environment of a severe storm complex. In the prestorm period geostrophic flow dominates the environment. With progression into the storm period all terms in the momentum equation become important, as a significant ageostrophic component in the momentum field develops. Turbulent effects are estimated as a residual, and the results indicate that they are comparable in magnitude to the other terms. Their effect is to decrease the positive momentum, particularly at levels above 500 mbar, where the vertical motion is the strongest. Vertical profiles of area means ofu andv indicate that the storm is apparently redistributing momentum downwards, thus reducing the mean shear. In the poststorm period the flow once again becomes largely geostrophic, and a maximum in wind speed reappears at upper levels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Danielsen, E. J. (1974),The relationship between severe weather, major dust storms and rapid large scale cyclogenesis: Subsynoptic extratropical weather systems. NCAR PB-247 285, 215–241.
Fritsch, J. M., andMaddox, R. A. (1981),Convectively driven mesoscale weather systems aloft. Part I: Observations, Jour. Appl. Met.,20, 9–19.
Fuelberg, H. E. (1974),Reduction and error analysis of AVE II pilot experiment data. NASA CR-120496, NASA Marshall Space Flight Center, Huntsville, Alabama, 131 pp.
Maddox, R. A., Hoxit, L. R., andChappel C. F. (1980),A study of tornadic thunderstorm interactions with thermal boundaries, Mon. Wea. Rev.108, 322–336.
Maddox, R. A. (1983),Large scale meteorological conditions associated with midlatitude mesoscale convective complexes, Mon. Wea. Rev.111, 1475–1493.
Moncrieff, M. W., andMiller, M. J. (1976),The dynamics and simulation of tropical squall lines. Q. J. Roy. Met. Soc.102, 373–395.
Newton, C. W. (1963),Dynamics of severe convective storms, Meteorological Monographs,5, 33–58.
Newton, C. W., andNewton, H. R. (1959),Dynamical interactions between large convective clouds and environments with vertical shear, J. Meteor.,16, 483–496.
Ninomiya, K. (1971),Mesoscale modification of synoptic situations from thunderstorms as revealed by ATS III pictures, J. App. Meteor.10, 275–294.
Sanders, F., andEmanuel, K. A. (1977),The momentum budget and temporal evolution of a mesoscale convection system. J. Atmos. Sci.34, 322–330.
Sasaki, Y. (1974),Variational method aiming at operational application to analysis and short range prediction of local severe weather. Norman, OK, Jan. 1974 Office of Research Administration Final Report, 17 pp.
Schneider, E. K., andLindzen, R. S. (1976),A discussion of the parameterization of momentum exchange by cumulus convection, J. Geophys. Res.81, 3158–3160.
Sikdar, D., and Fox, D. F. (1984),Meso-α and meso-β network analyses of a severe storm complex during SESAME-AVE V. Accepted for publication in Pure Appl. Geophys.
Zipser, E. J., Meitin, R. J., andLemone, M. A. (1981),Mesoscale motion fields associated with a slowly moving GATE convective band. J. Atmos. Sci.38, 1725–1750.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fox, D.J., Sikdar, D.N. Meso-β-scale momentum budget of an evolving severe storm complex during SESAME AVE-V. PAGEOPH 122, 110–123 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00879652
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00879652