Abstract
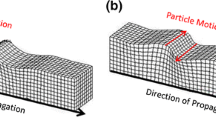
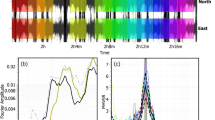
Characterization of the microseismic activity (M L <2.0) has been performed at Mt. Melbourne since 1990. We recorded a group of low frequency events with common morphological characteristics, i.e., an emerging onset, an unclear second phase and a sharply dropping coda. Spectral analysis of events recorded at more than one station indicates that the seismogram characteristics and spectral content are largely due to source effects. A polarization filter applied to a set of three component data revealed a first phase made up ofP waves followed (after about 0.9–1.4 sec.) by a second phase probably composed ofSH-type waves. Particle motion analysis detected a seismic ray angle direction mainly between N70°E and N110°E and apparent angle of incidence between 35° and 48° for the first phase. The studied seismicity was localized in an area on the eastern slope of Mt. Melbourne Volcano which presents a surface temperature anomaly (Mazzarini andSalvini, 1994).
We formulate two hypotheses for the type of earthquakes recorded: 1) long-period events involving active presence of magmatic fluids in the source processes; 2) or the result of fracturing processes (shear?) in a medium characterized by transition between brittle and plastic behaviors. In the latter hypothesis the superficial thermal anomaly may be a symptom of this behavior at depth and is confirmed by the lown values observed for the exponential fit in the codaQ analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aki, K. (1980),Scattering and Attenuation of Shear Waves in the Lithosphere, J. Geophys. Res.85, 6496–6504.
Aki, K., andChouet, B. (1975),Origin of Coda Waves: Source, Attenuation, and Scattering Effect, J. Geophys. Res.80, 3322–3342.
Armienti, P., Ghezzo, C., Innocenti, F., Manetti, P., Rocchi, S., andTonarini, S. (1988),Paleozoic and Cainozoic Instrusives of Wilson Terrane: Geochemical and Isotopic Data, Mem. Soc. Geol. It.43, 67–75.
Armstrong, R. L. (1978),Late Cenozoic McMurdo Volcanic Group and Dry Valley Glacial History, Victoria Land, Antarctica, New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics21, 685–698.
Behrendt, J. C., LeMasurier, W. E., Cooper, A. K., Tessensohn, F., Trehu, A., andDamaske, D. (1991),Geophysical Studies of the West Antarctic Rift System, Tectonics10 (6), 1257–1273.
Bonaccorso, A., Falzone, G., Privitera, E., andVillari, L. Seismic and ground tilt monitoring at Mt. Melbourne Volcano (Northern Victoria Land, Antarctica). InSixth International Symposium on Antarctic Earth Sciences (National Institute of Polar Research, Tokyo 1991) pp. 72–75.
Bonaccorso, A., Falzone, G., Gambino, S., andVillari, L. (1995),Tilt Signals Recorded at Mt. Melbourne Volcano (Northern Victoria Land, Antarctica) between 1989–94, Terra Antarctica (in print).
Both, D. C., Crampin, S., Evans, R., andRoberts, G. (1985),Shear-wave Polarization near the North Anatolian Fault. I. Evidence for Anisotropy-induced Shear-wave Splitting, Geophys. J. R. Astr. Soc.83, 61–73.
Both, D. C., Crampin, S., Lovell, J. H., andChiu, J-M. (1990),Temporal Changes in Shear-wave Splitting during an Earthquake Swarm in Arkansas, J. Geophys. Res.95, 11151–11164.
Chouet, B. (1976),Source, Scattering, and Attenuation Effects on High Frequency Seismic Waves, Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts.
Chouet, B. (1988),Resonance of a Fluid-driven Crack: Radiation Properties and Implications for the Source of Long-period Events and Harmonic Tremor, J. Geophys. Res.93, 4375–4400.
Chouet, B.,A seismic model for the source of long-period events and harmonic tremor. InVolcanic Seismology IAVCEI Proceeding in Volcanology 3 (Gasparini, P., Scarpa, R., and Aki, K., eds.) (Springer-Verlag, Berlin 1992) pp. 133–156.
Della Vedova, B., Pellis, G., Lawver, L. A., andBrancolini, G.,Hear flow and tectonics Western Ross Sea. InRecent Progress in Antartic Earth Sciences (Yoshida, Y., Kaminuma, K., and Shiraishi, K., eds.) (TERRAPUB, Tokio 1992) pp. 627–637.
Del Pezzo, E., Ferulano, F., Giarrusso, A., andMartini, M. (1983),Seismic Coda Q and Scaling Law of the Source Spectra at the Aeolian Islands, Southern Italy, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am.73, 97–108.
Del Pezzo, E., De Natale, G., Scarcella, G., andZollo, A. (1985),Qc of Three-component Seismograms of Volcanic Microearthquakes at Campi Flegrei Volcanic Area, Southern Italy, Pure and Appl. Geophys.123, 683–696.
Fehler, M., Roberts, P., andFairbanks, T. (1988),A Temporal Change in Coda Wave Attenuation Observed During an Eruption of Mount St. Helens, J. Geophys. Res.93, 4367–4373.
Fehler, M., andChouet, B. (1982),Operation of a Digital Seismic Network on Mount St. Helens Volcano and Observation of Long-period Seismic Events that Originate under the Volcano, Geophys. Res. Lett.9, 1017–1020.
Flinn, E. A. (1965),Signal Analysis Using Rectilinearity and Direction of Particle Motion, Proc. IEEE53, 1974–1976.
Cambino, S., andPrivitera, E. (1994),Characterization of Earthquakes Recorded by Mt. Melbourne Volcano Seismic Network (Northern Victoria Land, Antarctica), Terra Antarctica1, 167–172.
Harrington, H. J. (1958).Nomenclature of Rock Units in the Ross Sea Region, Antarctica, Nature82 (4361), 290–291.
Jin, A., andAki, K. (1988),Spatial and Temporal Correlation between Coda Q and Seismicity in China, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am.79, 1575–1588.
Jurkevics, A. (1988),Polarization Analysis of Three-component Array Data, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am.78, 1725–1743.
Kyle, P. R.,McMurdo Volcanic Group, western Ross Embayment. InVolcanoes of the Antarctic Plate and Southern Oceans (LeMasurier, W. E., and Thomson, J. W., eds.) (AGU Antarctic Research Series48, 1989) pp. 19–145.
Lanzafame, G., andVillari, L. (1991),Structural Evolution and Volcanism in Northern Victoria Land (Antarctica): Data from Mt. Melbourne. Mt. Overlord. Malta Plateau Region, Mem. Soc. Geol. It.46, 371–381.
Lee, W. H. K., andLahr, J. C. (1975), HYPO71 (Revised):A Computer Program for Determining Hypocenter, Magnitude and First Motion Pattern of Local Earthquakes, U.S. Geol. Surv. Open-File Report75-311, 144 pp.
Lyon, G. L. (1986),Stable Isotope Stratigraphy of Ice Cores and the Age of the Last Eruption at Mount Melbourne, Antarctica, New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics29, 135–138.
Magotra, N., Ahmed, N., andChael, E. (1987),Seismic Event Detection and Source Location Using Single Station (Three-component) Data, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am.77, 958–971.
Mazzarini, F., andSalvini, F. (1994),Contribution to Geothermal Survey by Spectral Analysis of TM Landsat Satellite Data in Mt. Melbourne Area, Northern Victoria Land (Antarctica), Terra Antarctica1, 104–106.
Privitera, E., Villari, L., andGambino, S.,An Approach to the Seismicity of Mt. Melbourne Volcano (Northern Victoria Land, Antarctica). InRecent Progress in Antarctic Earth Sciences (Yoshida, Y., Kaminuma, K., and Shiraishi, K., eds.) (TERRAPUB, Tokio 1992) pp. 499–505.
Riviere-Barbier, F., Suteau-Henson, A., Ryaboy, V. Z., andCarter, J. A. (1992),Analysis of Three-component Data from IRIS/IDA Stations in the USSR, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am.82, 192–220.
Roecker, S. W., Tucker, B., King, J., andHatzfeld, D. (1982),Estimates of Q in Central Asia as a Function of Frequency and Depth Using the Coda of Locally Recoded Earthquakes, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am.72, 129–149.
Suteau-Henson, A. (1991),Three-component Analysis of Regional Phases at NORESS and ARCESS: Polarization and Phase Identification, Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am.81, 2419–2440.
Von Frese, R. R. B., Alsdorf, D. E., Kim, J-H., Stepp, T. M., O'Connell, D. R. H., Hayden, K. J., andLi, W. S.,Regional geophysical imaging of the Antarctic Lithosphere. InRecent Progress in Antarctic Earth Sciences (Yoshida, Y., Kaminuma, K., and Shiraishi, K., eds.) (TERRAPUB, Tokio 1992) pp. 465–474.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gambino, S., Privitera, E. Mt. Melbourne volcano, antarctica: Evidence of seismicity related to volcanic activity. PAGEOPH 146, 305–318 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00876495
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00876495