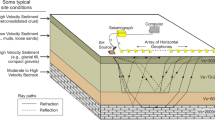
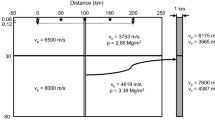
Abstract
The necessary condition for the seismic refraction method to succeed is that the refracted first arrivals from each layer in a multilayered earth system should be detected on a seismogram as first arrivals, and this is possible only when velocities of all underlying layers are successively greater. The usual procedure to interpret the refraction travel times is to fit such a data set with several intersecting straight lines by employing a visual technique which may lead to errors of subjective judgment, as the velocity model depends on the selection of various line segments through the data. To remove the visual fit we propose here a layer stripping method based on minimum intercept time, apparent velocity, rms residual, and maximum data points by least-squares fitting to yield several intersecting straight lines. Once data are segmented out, the conventional equations can be used to determine the velocity structure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi, R. (1954),On a Proof of a Fundamental Formula Concerning Refraction Method of Geophysical Prospecting and Some Remarks, Kumamoto J. Sci.2, 18–23.
Dobrin, M. B.,Introduction to Geophysical Prospecting (McGraw-Hill, New York 1976).
Green, R. (1974),The Seismic Refraction Method, a Review, Geoexploration12, 259–284.
Hobson, G. D. (1970),Seismic Methods in Mining and Ground Water Exploration, Mining and Ground Water Geophysics, Geol. Surv. Canada, Econ. Geol. Report26, 148–176.
Iyer, H. M., Pakiser, L. C., Stuart, D. J., andWarren, D. H. (1969),Project Early Rise: Seismic Probing of the Upper Mantle, J. Geophys. Res.74, 4409–4441.
Johnson, J. H. (1976),Interpretation of Split Spread Refraction Data in Terms of Plane Dipping Layers, Geophysics41, 418–424.
Kaila, K. L., andNarain, H. (1970),Interpretation of Seismic Refraction Data and the Solution of the Hidden Layer Problem, Geophysics35, 613–623.
Kaila, K. L., Reddy, P. R., Mall, D. M., Venkateswarlu, N., Krishna, V. G., andPrasad, A. S. S. S. (1992),Crustal Structure of the West Bengal Basin, India, from Deep Seismic Sounding Investigations, Geophys. J. Int.111, 45–66.
Kaila, K. L., Murty, P. R. K., Rao, N. M., Rao, I. B. P., Rao, P. K., Sridhar, A. R., Murthy, A. S. N., Rao, V. V., andPrasad, B. R. (1996),Structure of the Crystalline Basement in the West Bengal Basin, India, as Determined from DSS Studies, Geophys. J. Int.124, 175–188.
Mitchell, B. J., andHashim, B. M. (1977),Seismic Velocity Determinations in the New Madrid Seismic Zone, Seis. Bull. Soc. Am.67, 413–424.
Mooney, H. M.,Handbook of Engineering Geophysics (Bison Instruments Inc., Minneapolis 1976).
Musgrave, A. W.,Seismic Refraction Prospecting (Soc. Expl. Geophysicists, Tulsa 1967).
Palmer, D.,Refraction Seismics (Geophysical Press, London 1986).
Smith, T. A., andSendlein, L. V. A. (1973),An Algorithm for Best Fit Solution of a System of Linear Regression Equations for Seismic Refraction Data, Geophysics38, 1062–1069.
Steinhert, J. S., andMeyer, P. R. (1961),Minimum Statistical Uncertainty of the Seismic Refraction Profile, Geophysics26, 574–589.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sain, K., Kaila, K.L. Interpretation of first arrival travel times in seismic refraction work. PAGEOPH 147, 181–194 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00876443
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00876443