Abstract
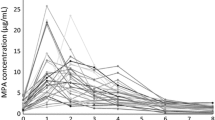
The aim of this study was to establish whether the criteria for the clinical effectiveness of steroids are correlated with the pharmacokinetics of prednisolone in children treated with prednisone during an attack of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome (INS). Thirteen patients with nephrosis were included. Prednisolone, prednisone and cortisol levels were measured using a specific high-performance liquid chromatography assay after an oral dose of 1 mg/kg body weight of prednisone taken at the onset of the disease. All the pharmacokinetic parameters, including the conversion of prednisone to prednisolone were similar to the data already published in children with INS. No correlation was found between the values of pharmacokinetic parameters and criteria of clinical effectiveness. Hypo-albuminaemia was significantly correlated with the area under the plasma-concentration curve but not with the elimination half-life of prednisolone. Moreover, the prednisolone elimination half-life correlated with the urinary exretion of 17-hydroxycorticosteroids achieved in the first 6h. The present study suggests that routine measurements of prednisolone kinetics do not help when assessing the treatment of children with INS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergrem H (1983) Pharmacokinetics and protein binding of prednisolone in patients with nephrotic syndrome and patients undergoing hemodialysis. Kidney Int 23: 876–881
Frey FJ, Frey BM (1982) Altered prednisolone kinetics in patients with the nephrotic syndrome. Nephron 32: 45–48
Green OC, Winter RJ, Kawahara FS, Phillips LS, Lewy PR, Hart RL, Pachman LM (1978) Pharmacokinetic studies of prednisolone in children. J Pediatr 93: 299–303
Rocci ML, Assael BM, Appiani AC, Edefonti A, Jusko WJ (1982) Effect of nephrotic syndrome on absorption and disposition of prednisolone in children. Int J Pediatr Nephrol 3: 161–166
Kleinknecht C, Gubler MC, Néphrose (1983) In: Royer P, Habib R, Mathieu H, Broyer M (eds) Néphrologie pédiatrique, 3rd edn Flammarion, Paris, pp 274–293
Alvinerie M, Toutain PL (1982) Simultaneous determination of corticosterone, hydrocortisone and dexamethasone in dog plasma using high performance liquid chromatography. J Pharm Sci 71: 816–818
Pickup ME (1979) Clinical pharmacokinetics of prednisone and prednisolone. Clin Pharmacokinet 4: 111–128
Rose JQ, Yurchak AM, Jusko WJ (1981) Dose-dependent pharmacokinetics of prednisone and prednisolone in man. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 9: 389–417
Baron S, Raux Demay MC, Vasman D, Bensman A (1988) Pharmacocinetique de la prednisolone chez l'enfant. Presse Med 17: 632–635
Demotes-Mainard F, Potaux L, Aparicio M, De Precigout V, Vinçon G, Albin H (1986) Pharmacocinétique de la prednisolone chez des malades transplantés rénaux avec ou sans syndrome de Cushing. Therapie 41: 449–454
Gambertoglio JG, Amend WJC, Benet LZ (1980) Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of prednisone and prednisolone in healthy volunteers and patients. a review. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 8: 1–52
Jusko WJ, Rose JQ (1980) Monitoring prednisone and prednisolone. Ther Drug Monit 2: 169–176
Gambertoglio JG, Frey FJ, Holford NHG, Birnbaum JL, Stanik Lizak P, Vincenti F, Feduska NJ, Salvatierra O, Amend WJC (1982) Prednisone and prednisolone bioavailability in renal transplant patients. Kidney Int 21: 621–626
Habet S, Rogers HJ (1980) Pharmacokinetics of intravenous and oral prednisolone. Br J Clin Pharmacol 10: 503–508
Perignon F, Pecquinot MA, Ged C, Antignac C, Guest G, Tete MJ, Broyer M, Lenoir G (1985) Pharmacocinétique de la prednisone après dose orale chez l'enfant greffé rénal. Arch Fr Pediatr 42: 639–644
Frey FJ, Amend WJC, Lozada JF, Frey BM, Benet LZ (1981) Endogenous hydrocortisone, a possible factor contributing to the genesis of cushingoid habitus in patients on prednisone. J Clin Endocrinal Metab 53: 1076–1080
Murnaghan K, Vasmant D, Bensman A (1984) Pulse methyl prednisolone therapy in severe idiopathic childhood nephrotic syndrome. Acta Paediatr Scand 73: 733–739
Lewis GP, Jusko WJ, Burke CW, Graves L (1971) Prednisone side effects and serum-protein levels. Lancet II: 778–781
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rostin, M., Barthe, P., Houin, G. et al. Pharmacokinetics of prednisolone in children with the nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 4, 470–473 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00869822
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00869822