Abstract
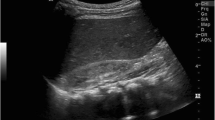
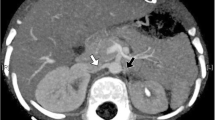
We report a case of severe hypertension in the newborn period due to obstruction of the right renal artery. The baby presented with polyuria leading to dehydration and was found to have hyponatraemia and severe renal salt loss. When sudden malignant hypertension is induced in experimental conditions, a high pressure diuresis and increased angiotensin II production are found. These findings could explain the renal salt loss, notwithstanding the effects of secondary hyperaldosteronism and hyper-reninaemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosendahl W, Ranke M, Mentzel H (1980) Sodium loss of leading symptom of renovascular hypertension in the newborn. Klin Wochenschr 58:953–954
Guignard JP, Gouyon JB, Adelman RD (1989) Arterial hypertension in the newborn infant. Biol Neonate 55:77–83
Caplan MS, Cohn RA, Langman CB, Conway JA, Shkolnik A, Brouillette RT (1989) Favorable outcome of neonatal aortic thrombosis and renovascular hypertension. J Pediatr 115:291–295
Payne RM, Martin TC, Bower RJ, Canter CE (1989) Management and follow-up of arterial thrombosis in the neonatal period. Pediatr 114:853–858
Blair-West JR, Coghlan JP, Denton DA, Orchard E, Scoggins BA, Wright RD (1968) Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and sodium balance in experimental hypertension. Endocrinology 83: 1199–1209
Mohring J, Petri M, Szokol M, Haack D, Mohring B (1976) Effects of saline drinking on malignant course of renal hypertension in rats. Am J Physiol 230:849–857
Barraclough MA (1966) Sodium and water depletion with the acute malignant hypertension. Am J Med 40:265–272
Kotchen TA, Roy MW (1983) Renin angiotensin. In: Dunn M (eds) Renal endocrinology. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 181–204
Garcia R, Thibault G, Gutkowska J, Hamet P, Cantin M, Genest J (1985) Effect of chronic infusion of synthetic atrial natriuretic factor (ANF 8-33) in conscious two-kidney, one clip hypertensive rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 178:155–159
Kramer P, Kokthe E, Scheler F (1974) Hyponatriämisch — hypertone Krise. Klin Wochenschr 52:787–791
Sheth KJ, Tang TT, Blaedel ME, Good TA (1978) Polydipsia, polyuria and hypertension associated with renin secreting Wilms' tumor. J Pediatr 92:921–924
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blanc, F., Bensman, A. & Baudon, J.J. Renovascular hypertension: a rare cause of neonatal salt loss. Pediatr Nephrol 5, 304–306 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00867486
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00867486