Summary
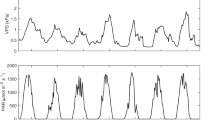
Simultaneous measurements of xylem sap flow and water vapour flux over a Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris) forest (Hartheim, Germany), were carried out during the Hartheim Experiment (HartX), an intensive observation campaign of the international programme REKLIP. Sap flow was measured every 30 min using both radial constant heating (Granier, 1985) and two types of Cermak sap flowmeters installed on 24 trees selected to cover a wide range of the diameter classes of the stand (min 8 cm; max 17.5 cm). Available energy was high during the observation period (5.5 to 6.9 mm.day−1), and daily cumulated sap flow on a ground area basis varied between 2.0 and 2.7 mm day−1 depending on climate conditions. Maximum hourly values of sap flow reached 0.33 mm h−1, i.e., 230 W m−2.
Comparisons of sap flow with water vapour flux as measured with two OPEC (One Propeller Eddy Correlation, University of Arizona) systems showed a time lag between the two methods, sap flow lagging about 90 min behind vapour flux. After taking into account this time lag in the sap flow data set, a good agreement was found between both methods: sap flow = 0.745* vapour flux,r 2 = 0.86. The difference between the two estimates was due to understory transpiration.
Canopy conductance (g c ) was calculated from sap flow measurements using the reverse form of Penman-Monteith equation and climatic data measured 4 m above the canopy. Variations ofg c were well correlated (r 2 = 0.85) with global radiation (R) and vapour pressure deficit (vpd). The quantitative expression forg c =f (R, vpd) was very similar to that previously found with maritime pine (Pinus pinaster) in the forest of Les Landes, South Western France.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blandford, J. H., Gay, L. W., 1992: Tests of a robust eddy correlation system for sensible heat flux.Theor. Appl. Climatol. 46, 53–60.
Bréda, N., Cochard, H., Dreyer, E., Granier, A., 1993: Water transfer in a mature oak stand (Quercus petraea): seasonal evolution and effects of a severe drought.Can. J. For. Res. 23, 1136–1143.
Cermak, J., Deml, M., Penka, M., 1973: A new method of sap-flow rate determination in trees.Biol. Plant. 15, 171–178.
Gash, J. H. C., Shuttleworth, W. J., Lloyd, C. R., André, J.-C., Goutorbe, J.-P., Gelpe, J., 1989: Micrometeorological measurements in Les Landes forest during HAPEXMOBILHYX.Agric. Forest. Meteor. 46, 131–147.
Gay, L. W., Vogt, R., Bernhofer, Ch., Blanford, J. H., 1996; Flud agreement above a Scots pine plantation.Theor. Appl. Climatol. 53, 33–48.
Gay, L. W., Vogt, R., Blanford, J. H., Kessel, A., 1996: The May–October energy budget of a Scots pine plantation at Hartheim, Germany.Theor. Appl. Climatol. 53, 79–94.
Granier, A., 1985: Une nouvelle méthode pour la mesure du flux de sève brute dans le tronc des arbres.Ann. Sci. For. 42(2), 193–200.
Granier, A., 1987: Evalution of transpiration in a Douglas-fir stand by means of sap flow measurements.Tree Physiol. 3, 309–320.
Granier, A., Bobay, V., Gash, J. H. C., Gelpe, J., Saugier, B., Shuttleworth, W. J., 1990: Vapour flux density and transpiration rate comparisons in a stand of Maritime Pine (Pinus pinaster Ait.) in Les Landes forest.Agric. Forest. Meteor. 51, 309–319.
Granier, A., Loustau, D., 1994: Measuring and modelling the transpiration of a maritime pine canopy from sap-flow data.Agric. Forest. Meteor. 71, 61–81.
Grier, C. C., Waring, R. H., 1974: Conifer foliage mass related to sapwood area.For. Sci. 20, 205–206.
Guehl, J. M., Aussenac, G., Bouachrine, J., Zimmermann, R., Pennes, J. M., Fehri, A., Grieu, P., 1991: Sensitivity of leaf gas exchange to atmospheric and soil drought and water use efficiency in some mediterraneanAbies species.Can. J. For. Res. 21, 1507–1515.
Jarvis, P. G., 1975: Water transfer in plants. In: de Vries, D. A., Afgan, N. G. (eds.)Heat and Mass Transfer in the Plant Environment. Part 1. Washington D. C.: Scripta Book Co., pp. 369–374.
Jarvis, P. G., 1976: The interpretation of the variations in leaf water potential and stomatal conductance found in canopies in the field.Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. London 273, 593–610.
Joss, U., Graber, W. K., 1996: Profiles and simulated exchange of H2O, O3, NO2 between the atmosphere and the Hartheim Scots pine plantation.Theor. Appl. Climatol. 53, 157–172.
Kelliher, F. M., Köstner, B. M. M., Hollinger, D. Y., Byers, J. N., Hunt, J. E., McSeveny, T. M., Meserth, R., Wier, P. L., Schulze, E.-D., 1992: Evaporation, xylem sap flow, and tree transpiration in a New Zealand broad-leaved forest.Agric. Forest. Meteor. 62, 53–73.
Köstner, B. M. M., Schulze, E.-D., Kelliher, F. M., Hollinger, D. Y., Byers, J. N., Hunt, J. E., McSeveny, T. M., Meserth, R., Weir, P. L., 1992: Transpiration and canopy conductance in a pristine broad-leaved forest of Nothofagus: an analysis of xylem sap flow and eddy correlation measurements.Oecologia 91, 350–359.
Köstner, B. M. M., Biron, P., Siegwolf, R., Granier, A., 1996: Estimates of water vapor flux and canopy conductance of Scots pine at tree level utilizing different xylem sap flow methods.Theor. Appl. Climatol. 53, 105–113.
Loustau, D., Granier, A., El Hadj Moussa, F., 1990: Evolution saisonnière du flux de sève dans un peuplement de Pins maritimes de 18 ans.Ann. Sci. For. 47, 599–618.
McNaughton, K. G., Black, T. A., 1973: A study of evapotranspiration from a Douglas-fir forest using the energy balance approach.Water Resour. Res. 9, 1579–1590.
McNaughton, K. G., Jarvis, P. G., 1973: Predicting effects of vegetation changes on transpiration and evaporation. In: Koslowski, T. T. (ed.)Water Deficits and Plant Growth, vol VII. New York, London: Academic Press, pp. 1–47.
Monteith, J. L., 1973:Principles of Environmental Physics. London: E. Arnold.
Schulze, E.-D., Cermak, J., Matyssek, R., Penka, M., Zimmermann, R., Vasicek, F., Gries, W., Kucera, J., 1985: Canopy transpiration and water fluxes in the xylem of the trunkLarix andPicea trees — A comparison of xylem flow, porometer and cuvette measurements.Oecologia 66, 475–483.
Shuttleworth, W. J., 1989: Micrometerology of temperate and tropical forest.Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. Lond. B 324, 299–334.
Stewart, J. B., 1988: Modelling surface conductance of pine forest.Agric. Forest. Meteor. 43, 19–35.
Tajchman, S., Hädrich, F., Lee, R., 1979: Energy budget evaluation of the transpiration-pF relationship in a young pine forest.Water Resour. Res. 15, 159–163.
Wedler, M., Heindl, B., Hahn, S., Köstner, B., Bernhofer, Ch., Tenhunen, J. D., 1996: Model-based estimates of water loss from “patches” of the understory mosaic of the Hartheim Scots pine plantation.Theor. Appl. Climatol. 53, 135–144.
Whitehead, D., Jarvis, P. G., Waring, R. H., 1983: Stomatal resistance, transpiration, and resistance to water uptake in a Pinus sylvestris spacing experiment.Can. J. For. Res. 14, 692–700.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With 6 Figures
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Granier, A., Biron, P., Köstner, B. et al. Comparisons of xylem sap flow and water vapour flux at the stand level and derivation of canopy conductance for Scots pine. Theor Appl Climatol 53, 115–122 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00866416
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00866416