Abstract
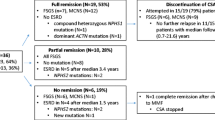
Eighteen children with steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome received cyclosporine A (CsA), including 7 patients with minimal change disease, 4 with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis and 7 with mesangial hypercellurarity. Doses were adjusted to maintain whole blood trough levels at 80–200 ng/ml and ranged from 5 to 10 mg/kg (mean 7 mg/kg). Fourteen patients responded after 2 months of therapy with either a complete or partial remission, and received a total of 12 months of CsA with low-dose corticosteroids. Remission rates were similar among the three histological types, although complete remissions occurred more commonly in minimal change disease, while the other two histological types tended to have partial responses. Serum creatinine values ranged from 0.3 to 1.2 mg/dl at the start of treatment and were stable in 17 of 18 patients during CsA therapy. CsA was discontinued after 12 months in 11 responders. Relapses were a significant problem. Nine patients had 16 relapses, all occurring within 6 months after discontinuing CsA; 13 of 16 relapses responded to CsA and corticosteroids. Five children had multiple relapses. Three patients who initially responded to treatment had CsA-resistant relapses. There were no differences among the histological types with respect to the occurrence of relapses or response to CsA after relapsing. Four patients developed chronic renal failure, including 2 of 4 who failed initial therapy and 2 of 3 who developed CsA-resistant relapses. In conclusion, initial therapy with CsA was effective in resolving nephrotic syndrome in steroid-resistant patients. However, CsA dependency, frequent relapses and the development of chronic renal failure presented significant problems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borel JF, Feurer C, Gubler HU, Stahelin H (1976) Biological effects of cyclosporine A: a new antilymphocytic agent. Agents Actions 6: 468–475
Tejani A, Butt K, Trachtman H, Suthanthiran M, Rosenthal CJ, Khawar MR (1988) Cyclosporine A induced remission of relapsnephrotic syndrome in children. Kidney Int 33: 729–734
Tanaka R, Yoshikawa N, Kitano Y, Ito H, Nakamura H (1993) Long-term ciclosporin treatment in children with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 7: 249–252
Neuhaus TJ, Burger HR, Klingler M, Fanconi A, Leumann EP (1992) Long-term low cyclosporin A in steroid dependent nephrotic syndrome of childhood. Eur J Pediatr 151: 775–778
Hoyer P-F, Brodehl J, Ehrich J-H, Offner G (1991) Practical aspects in the use of cyclosporin in paediatric nephrology. Pediatr Nephrol 5: 630–638
Brodehl J, Hoyer FF, Oemar BS, Helmchen U, Wonigeit K (1988) Cyclosporine treatment of nephrotic syndrome in children. Transplant Proc 20 [Suppl 4]: 269–274
Niaudet P (1992) Comparison of cyclosporine and chlorambucil in the treatment of steroid-dependent idiopathic nephrotic syndrome: a multicentre randomized controlled trial. The French Society of Paediatric Nephrology. Pediatr Nephrol 6: 1–3
Meyrier A and Collaborative Group of the Societe de Nephrologie (1989) Cyclosporine in the treatment of nephrosis. Am J Nephrol 9 [Suppl 1]: 65–71
Menster M, Shannon B, Mahan JD (1988) Cyclosporine treatment in children. Response to therapy and evidence for a T-cell abnormality. Kidney Int 33: 329
Ponticelli C, Rizzoni G, Edefonti A, Altieri P, Rivolta E, Rinaldi S, Ghio L, Lusvarghi E, Gusmano R, Locatelli F (1993) A randomized trial of cyclosporine in steroid-resistant idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int 43: 1377–1384
Donckerwolcke RA, Vande-Walle J (1992) Treatment of children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome using ciclosporine A. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 136: 1770–1774
Ingulli E, Tejani A (1992) Severe hypercholesterolemia inhibits cyclosporine A efficacy in a dose-dependent manner in children with nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 3: 254–259
Brodehl J, Brandis M, Helmchen U, Hoyer PF, Burghard R, Ehrich JH, Zimmerhackl RB, Klein W, Wonigeit K (1988) Cyclosporine A treatment in children with minimal change nephrotic syndrome and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Klin Wochenschr 66: 1126–1137
James RW, Burke JR, Petrie JJ, Rigby RJ, Williams M (1989) Cyclosporine A in the treatment of childhood glomerulonephritis. Aust N Z J Med 19: 198–201
Meyrier A (1989) Treatment of glomerular disease with cyporine A. Nephrol Dial Transplant 4: 923–931
Tejani A, Butt K, Trachtman H, Suthanthiran M, Rosenthal CJ, Khawar MR (1987) Cyclosporine A induced remission of relaps-nephrotic syndrome in children. J Pediatr 111: 1056–1062
Niaudet P, Habib R, Tete MJ, Hinglais N, Broyer M (1987) Cyclosporine in the treatment of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 1: 566–573
Capodicasa G, De-Santo NG, Nuzzi F, Giordano C (1986) Cyclosporine A in nephrotic syndrome of childhood — a 14 month experience. Int J Pediatr Nephrol 2: 69–72
Garin EH, Orak JK, Hiott KL, Sutherland SE (1988) Cyclosporine therapy for steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. A controlled study. Am J Dis Child 142: 985–988
Waldo FB, Kohaut EC (1987) Therapy of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis with cyclosporine A. Pediatr Nephrol 1: 180–182
Melocoton TL, Kamil ES, Cohen AH, Fine RN (1991) Long-term cyclosporine A treatment of steroid-resistant and steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Am J Kidney Dis 18: 583–588
Niaduet P, Broyer M, Habib R (1990) Evaluation of nephrotoxicity by sequential biopsies in 38 children with idiopathic nephrosis treated with cyclosporine (abstract). Kidney Int 37: 260
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hymes, L.C. Steroid-resistant, cyclosporine-responsive, relapsing nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 9, 137–139 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00860726
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00860726