Abstract
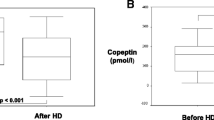
Plasma atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) and cyclic 3′5′-guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) were investigated as indicators of fluid volume overload in children and adolescents with chronic renal failure. Plasma ANP and cGMP were measured in both paediatric patients with chronic renal failure (n=17, mean serum creatinine 371±242 μmol/l) and those with end-stage renal disease on haemodialysis (n=18). cGMP was higher in children with chronic renal failure than in 45 healthy controls (1.0±0.4 vs 2.1±0.8 nmol/l,P<0.01), whereas plasma ANP was similar (26.9±9.7 vs 34.0±12.3 pmol/l). Both ANP and cGMP were markedly elevated in children with end-stage renal disease before haemodialysis and fell significantly during dialysis. During dialysis body weight decreased by 1.6±0.7 kg, corresponding to 4.5±2.1% of body weight. Plasma ANP correlated positively with plasma cGMP in haemodialysed patients (r=0.43,P<0.05). Reduction in body weight and in mean arterial pressure correlated more closely with plasma ANP than with cGMP. Therefore, elevation of plasma ANP appears to indicate volume overload in children undergoing haemodialysis, but whether it can be used also in children with chronic renal failure requires further investigation
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chung HM, Kluge R, Schrier RW, Anderson RJ (1987) Clinical assessment of extracellular fluid volume in hyponatremia. Am J Med 83: 905–908
Rascher W, Tulassay T, Lang RE (1985) Atrial natriuretic peptide in plasma of volume-overloaded children with chronic renal failure. Lancet II: 303–305
Czekalski S, Michel C, Dussaule JC, Touraine P, Mignon F, Ardaillou R (1988) Atrial natriuretic peptide and adaptation of sodium urinary excretion in patients with chronic renal failure. Clin Sci 75: 243–249
Hasegawa K, Matsushita Y, Inoue T, Morii H, Ishibashi M, Yamaji T (1986) Plasma levels of atrial natriuretic peptide in patients with chronic renal failure. J Clin Endocrinol Metal 63: 819–822
Eisenhauer T, Talartschik J, Scheler F (1986) Detection of fluid overload by plasma concentration of human atrial natriuretic peptide in patients with renal failure. Klin Wochenschr 64 [Suppl VI]: 68–72
Hartter E, Pacher R, Frass M, Woloszczuk W, Leither C (1986) Plasma levels of atrial natriuretic peptide in volume expanded patients: response to fluid removal by continuous pump driven haemofiltration. Klin Wochenschr 64 [Suppl VI]: 112–114
Gerzer R, Heim JM, Schutte B, Weil J (1987) Cellular mechanisms of action of atrial natriuretic factor. Klin Wochenschr 65 [Suppl VIII]: 109–114
Hamet P, Tremblay J, Pang SC, Skuhherska R, Schiffin L, Garcia R, Chantin M, Genest J, Palmour R, Ervin FR, Martin S, Goldwater R (1986) Cyclic GMP as mediator and biological marker of atrial natriuretic factor. J Hypertens 4 [Suppl 2]: 49–56
Rascher W, Bald M, Kreis J, Tulassay T, Heinrich V, Schärer K (1987) Atrial natriuretic peptide in infants and children. Horm Res 28: 58–63
Heim J-M, Gottmann K, Weil J, Haufe MC, Gerzer R (1988) Is cyclic GMP a clinically useful marker of ANF action? Z Kardiol 77 [Suppl 2]: 41–46
Hodsman GP, Jackson B, Debrevi LM, Ogawa K, Johnston CI (1987) Atrial natriuretic factor in chronic renal failure: studies in man and the rat. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 14: 247–251
Rascher W, Bald M (1989) Atrial natriuretic peptide and chronic renal failure. In: Kaufmann W, Wambach G (eds) Endocrinology of the heart. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, New York, pp 112–117
Genest J (1986) The atrial natriuretic factor. Br Heart J 56: 302–316
Gerbers AL, Arendt RM, Gerzer R, Schnitzer W, Jüngst D, Paumgartner G, Wernze H (1988) Role of atrial natriuretic factor, cyclic GMP and the renin-aldosterone system in acute volume regulation of healthy human subjects. Eur J Clin Invest 18: 425–429
Yamamoto Y, Higa T, Kitamura K, Tanaka K, Kawangu K, Matsuo H (1987) Plasma concentration of human atrial natriuretic peptide in patients with impaired renal function. Clin Nephrol27: 84–86
Tulassay T, Rascher W, Schärer K (1989) Atrial natriuretic peptide and sodium homeostasis in chronic renal failure. Pediatr Nephrol 3: 397–400
Luft FC, Sterzel RB, Lang RE, Trabold EM, Veelken R, Ruskoaho H, Gao Y, Ganten D, Unger T (1986) Atrial natriuretic factor determinations and chronic sodium homeostasis. Kidney Int 29: 1004–1010
Eisenhauer T, Talartschik J, Quentin E, Kreutzfeld W, Scheler F (1988) Beeinflussung von atrialem natriuretischem Peptid (ANP) and zyklischem GMP durch Hämofiltration and Hämodialyse. Klin Wochenschr 66: 940–945
Luft FC, Lang RE, Aronoff GR, Ruskoaho H, Toth M, Ganten D, Sterzel RB, Unger Th (1986) Atriopeptin III kinetics and pharmacodynamics in normal and anephric rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 236: 416–418
Espiner EA, Nicholls MG, Yandle TG, Crozier IG, Cuneo RC, McCormick D, Ikram H (1986) Studies on the secretion, metabolism and action of atrial natriuretic peptide in man. J Hypertens, 4 [Suppl 2]: S85-S91
Waldman SA, Rapoport RN, Murad F (1984) Atrial natriuretic factor selectively activates particulate guanylate cyclase and elevates cGMP in rat tissues. J Biol Chem 259: 14332–14334
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lettgen, B., Bald, M., Valleé, H. et al. Atrial natriuretic peptide and cyclic 3′5′-guanosine monophosphate as indicators of fluid volume overload in children with chronic renal failure. Pediatr Nephrol 6, 60–64 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00856837
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00856837