Summary
The present investigation analyzes intercellular junctions in tissues with different developmental capacities. The distribution of junctions was studied inDrosophila embryos, in imaginal disks, and in cultures of disk cells that were no longer able to differentiate any specific pattern of the adult epidermis.
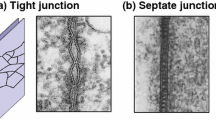
The first junctions —primitive desmosomes andclose membrane appositions — already appear in blastoderm.Gap junctions are first detected in early gastrulae and later become more and more frequent.Zonulae adhaerentes are formed around 6 h after fertilization, whileseptate junctions appear in the ectoderm of 10-h-old embryos.
Inwing disks of all stages studied (22–120 h), three types of junctions are found: zonulae adhaereentes, gap junctions, and septate junctions. Gap junctions, which are rare and small at 22 h, increase in number and size during larval development. The other types of junctions are found between all cells of a wing disk throughout development.
All types of junctions that are found in normal wing disks are also present in theimaginal disk tissues cultured in vivo for some 15 years and in thevesicles of imaginal disk cells grown in embryonic primary cultures in vitro. However, gap junctions are smaller and in the vesicles less frequent than in wing disks of mature larvae.
Thus gap junctions, which allow small molecules to pass between the cells they connect, are present in the early embryo, when the first developmental decisions take place, and in all imaginal disk tissues studied, irrespective of whether or not these are capable of forming normal patterns.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, M.V.L., Spira, M.E., Pappas, G.D.: Properties of electrotonic junctions between embryonic cells ofFundulus. Dev. Biol.29, 419–435 (1972)
Bodenstein, D.: Investigations on the problem of metamorphosis. VI. Developmental relations of interspecific organ transplants inDrosophila. J. Exp. Zool.82, 1–30 (1939)
Bryant, P.J.: Pattern formation in imaginal discs. In: The genetics and biology ofDrosophila (M. Ashburner and T.R.F. Wright, eds.), vol. 2c, pp. 229–335, London, New York, San Francisco: Academic Press 1978
Decker, R.S., Friend, D.S.: Assembly of gap junctions during amphibian neurulation. J. Cell Biol.62, 32–47 (1974)
De Haan, R.L., Hirakow, R.: Synchronization of pulsation rates in isolated cardiac myocytes. Exp. Cell Res.70, 214–220 (1972).
Ducibella, T., Anderson, E.: Cell shape and membrane changes in the eight-cell mouse embryo: Prerequisites for morphogenesis of the blastocyst. Dev. Biol.47, 45–58 (1975)
Dübendorfer, A., Shields, G., Sang, J.H.: Development and differentiation in vitro ofDrosophila imaginal disc cells from dissociated early embryos. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol.33, 487–498 (1975)
Dübendorfer, A.: Metamorphosis of imaginal disc tissue grown in vitro from dissociated embryos ofDrosophila. In: Invertebrate tissue culture, pp. 151–159. New York: Academic Press 1976
Fristrom, D.: Cellular degeneration in the production of some mutant phenotypes inDrosophila melanogaster. Mol. Gen. Genet.103, 363–379 (1969)
Fristrom, D., Fristrom, J.W.: The mechanism of evagination of imaginal discs ofDrosophila melanogaster. I. General considerations. Dev. Biol.43, 1–23 (1975)
Gateff, E.: Malignant neoplasms of genetic origin inDrosophila melanogaster. Science200, 1448–1459 (1978)
Gateff, E.A., Schneiderman, H.A.: Developmental capacities of immature eye-antennal imaginal discs ofDrosophila melanogaster. Wilhelm Roux' Archiv176, 171–189 (1975)
Gilula, N.B.: Junctions between cells. In: Cell communication (R.P. Cox, ed.), pp. 1–29. New York: Wiley and Sons 1974
Hadorn, E.: Konstanz, Wechsel und Typus der Determination und Differenzierung in Zellen aus männlichen Genitalanlagen vonDrosophila melanogaster nach Dauerkultur in vivo. Dev. Biol.13, 424–509 (1966)
Lentz, T.L., Trinkaus, J.P.: Differentiation of the junctional complex of surface cells in the developingFundulus blastoderm. J. Cell Biol.48, 455–472 (1971)
Loewenstein, W.R.: Intercellular communication. Sci. Am.222, 79–86 (1970)
Luft, J.H.: Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol.9, 409–414 (1961)
Madhavan, M.M., Schneiderman, H.A.: Histological analysis of the dynamics of growth of imaginal discs and histoblast nests during the larval development ofDrosophila melanogaster. Wilhelm Roux's Archives183, 269–305 (1977)
Magnuson, T., Demsey, Y., Stackpole, C.W.: Characterization of intercellular junctions in the preimplantation mouse embryo by freeze-fracture and thin-section electron microscopy. Dev. Biol.61, 252–261 (1977)
Mahowald, A.P.: Electron microscopy of the formation of the cellular blastoderm inDrosophila melanogaster. Exp. Cell Res.32, 457–468 (1963a)
Mahowald, A.P.: Ultrastructural differentiations during formation of the blastoderm in theDrosophila melanogaster embryo. Dev. Biol.8, 186–204 (1963b)
Mindek, G.: Metamorphosis of imaginal discs ofDrosophila malanogaster. Wilhelm Roux' Archiv169, 353–356 (1972)
Mindek, G., Nöthiger, R.: Parameters influencing the acquisition of competence for metamorphosis in imaginal disks ofDrosophila. J. Insect Physiol.19, 1711–1720 (1973)
Poodry, C.A., Schneiderman, H.A.: The ultrastructure of the developing leg ofDrosophila malanogaster. Wilhelm Roux' Archiv166, 1–44 (1970)
Quick, D.C., Johnson, R.G.: Gap junctions and rhombic particle arrays inPlanaria. J. Ultrastruct. Res.60, 348–361 (1977)
Revel, J.P., Karnovsky, M.J.: Hexagonal array of subunits in intercellular junctions of the mouse heart and liver. J. Cell Biol.33, C7-C12 (1967)
Reynolds, E.S.: The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol.17, 208–212 (1963)
Rickoll, W.L.: Cytoplasmic continuity beteen embryonic cells and the primitive yolk sac during early gastrulation inDrosophila melanogaster. Dev. Biol.49, 304–310 (1976)
Sanders, E.J.: Intercellular contact in the unincubated chick embryo. Z. Zellforsch. Mikrosk. Anat.141, 459–468 (1973)
Sanders, E.J.: Aspects of furrow membrane formation in the cleavingDrosophila embryo. Cell Tissue Res.156, 463–474 (1975)
Sanders, E.J., Zalik, S.E.: The blastomere periphery ofXenopus laevis with special reference to intercellular relationships. Wilhelm Roux' Archiv171, 181–194 (1972)
Schubiger, G.: Acquisition of differentiative competence in the imaginal leg discs ofDrosophila. Wilhelm Roux' Archiv174, 303–311 (1974)
Sheridan, J.D.: Dye movement and low-resistance junctions between reaggregated embryonic cells. Dev. Biol.26, 627–636 (1971)
Sheridan, J.D.: Electrical coupling of cells and cell communication. In: Cell communication (R.P. Cox, ed.), pp. 31–42 New York, Wiley and Sons 1974
Shields, G., Dübendorfer, A., Sang, J.H.: Differentiation in vitro of larval cell types from early embryonic cells ofDrosophila melanogaster. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol.33, 159–175 (1975)
Slack, C., Palmer, J.F.: The permeability of intercellular junctions in the early embryo ofXenopus laevis, studied with a fluorescent tracer. Exp. Cell Res.55, 416–419 (1969)
Staehelin, L.A.: Three types of gap junctions interconnecting intestinal epithelial cells visualized by freeze-etching. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA60, 1318–1321 (1972)
Staehelin, L.A.: Structure and function of intercellular junctions. Int. Rev. Cytol.39, 191–283 (1974)
Weinstein, R.S., Merk, F.B., Alroy, J.: The structure and function of intercellular junctions in cancer. Adv. Cancer Res.23, 23–89 (1977)
Zalokar, M.: Fixation ofDrosophila eggs without pricking. Dros. Inf. Serv.47, 128–129 (1971)
Zalokar, M., Audit, C., Erk, J.: Developmental defects of female sterile mutants ofDrosophila melanogaster. Dev. Biol.47, 419–432 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eichenberger-Glinz, S. Intercellular junctions during development and in tissue cultures ofDrosophila melanogaster: An electron-microscopic study. Wilhelm Roux' Archiv 186, 333–349 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00848457
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00848457