Conclusions
-
1.
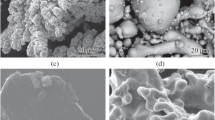
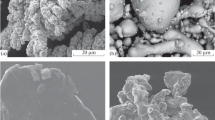
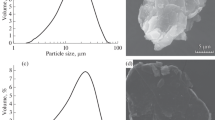
A study was made of the structure, physicomechanical properties, and service behavior of powder metallurgy friction disks sintered under various temperature, time, and pressure conditions.
-
2.
It was established that disks sintered at lower temperatures exhibit wear resistance and coefficients of friction comparable to those of standard disks.
-
3.
To improve the properties of the steel carrier plate and stabilize the properties of the powder metallurgy layer, it is recommended that the sintering of disks should be performed at a temperature of 560–580°C and a pressure of 50–75 kg/cm2 for a period of 4–6 h.
-
4.
It is also recommended that a high-strength steel (such as 30KhGSA), whose tempering temperature exceeds the sintering temperature of disks, should be employed for the casing of friction disks.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Poroshkovaya Metallurgiya, No. 10 (118), pp. 71–76, October, 1972.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aleksandrova, A.B., Kryachek, V.M., Levit, G.B. et al. Effect of technological factors on the properties of friction materials II. Effect of sintering conditions on the structure and frictional and wear properties of powder metallurgy friction disks. Powder Metall Met Ceram 11, 831–834 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00844710
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00844710