Abstract
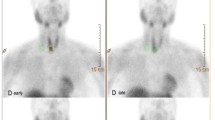
Seventy-six patients with thyroid nodules were studied. Initially, 74 MBq of thallium-201 was injected. The thyroid gland was imaged 15 min (early) and 3 h (delayed) after the injection. Thereafter, 185 MBq technetium-99m pertechnetate was injected. Immediately after the injection, a 1-min perfusion image was acquired, followed by an image at 20 min. Increased early and delayed201Tl uptake compared with the contralateral thyroid tissue was adopted as the criterion for malignancy. Sensitivity, specificity and negative predictive values were found to be 85%, 64% and 78%, respectively, in operated patients, but these values were 86%, 87% and 95%, respectively, in the whole group, including patients followed with fine-needle aspiration biopsy. With the purpose of investigating the relationship between perfusion and early201Tl uptake, both perfusion and early images were graded comparing nodular activity with contralateral thyroid activity. There was a poor correlation between perfusion and201Tl uptake. The correlation was even worse in hyperactive nodules. It is concluded that early and delayed201Tl imaging should not be used in the differential diagnosis of cold nodules and that early201Tl uptake seems to be more closely related to factors other than perfusion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vander JB, Gaston EA, Dawber TR. The significance of nontoxic thyroid nodules: final report of a 15-year study of the incidence of thyroid malignancy.Ann Intern Med 1968; 69: 537–540.
Solomon D. Fine needle aspiration of the thyroid: an update.Thyroid Today 1993; 16:1–9.
Barry LS, Brahm S. The role of imaging test in the diagnosis of thyroid nodules.Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 1990; 19:523–542.
Senga O, Miyakawa M, Shirota H, et al. Comparison of Tl-201 chloride and Ga-67 citrate scintigraphy in the diagnosis of thyroid tumors.J Nucl Med 1982; 23: 225–228.
Foldes I, Levay A, Stotz G. Comparative scanning of thyroid nodules with technetium-99m pertechnetate and technetium-99m methoxyisobutylisonitrile.Eur J Nucl Med 1993; 20: 330–333.
Klain M, Maurea S, Lastoria S, et al. Tc-99m terrofosmin scintigraphy in the evaluation of patients with thyroid nodules: comparison with Tc-99m pertechnetate and thallium-201 studies [abstract].Eur J Nucl Med 1995; 22: 749.
Hisada K, Tonami K, Miyamae T, et al. Clinical evaluation of tumor imaging with Tl-201 chloride.Radiology 1978; 129: 497–500.
Tonami N, Bunko H, Michigishi T, et al. Clinical application of T1-201 in patients with cold thyroid nodules. Clin Nucl Med 1978; 3: 217–221.
Harada T, Ito Y, Shimaokak K, et al. Clinical evaluation of Tl-201 scan for thyroid nodules.Eur J Nucl Med 1980; 5: 125–130.
Tennvall J, Palmer J, Cederquist E, et al. Scintigraphic evaluation and dynamic studies with thallium-201 in thyroid lesion suspected cancer.Eur J Nucl Med 1981; 6: 295–300.
Pavoni P, Mango L. Clinical evaluation of thallium chloride scan for thyroid nodules.Eur J Nucl Med 1981; 6: 47–50.
Ochi H, Sawa H, Fukada T, et al. Thallium 201 chloride thyroid scintigraphy to evaluate benign and/or malignant nodules.Cancer 1982; 50: 236–240.
Senga O, Miyakawa M, Shirota H. Comparison of Tl-201 chloride and Ga-67 citrate scintigraphy in the diagnosis of thyroid tumor.J Nucl Med 1982; 23: 225–228.
Makimoto K, Ohmura M, Tammada A, et al. Combined scintigrams in the diagnosis of thyroid carcinomas.Acta Otolaryngol Suppl (Stockh) 1984; 419: 189–194.
Hoschl R, Murray IPC, Lean RG. Radiothallium scintigraphy in solitary nonfonctioning thyroid nodules.World J Surg 1984; 8: 956–962.
Simonin R, Bernard PJ, Barnouin M. et al. Les explorations isotopiques des nodules thyroidiens.Rev Fr Endocrinol 1984; 25: 303–319.
Hermans J, Beauduin M, Gigot JF, et al. Detecting thyroid cancer: utopia or reality? Possibilities for thallium 201.Ann Endocrinol (Paris) 1986; 47: 409–414.
Bleichrodh RP, Vermey A, Piers A. Early and delayed thallium 201 imaging.Cancer 1987; 60: 2621–2623.
Hermans J, Schimitz A, Therasse G, et al. Thyroid scintigraphy with thallium 201: non-traumatic method for early detection of tumors and a better assessment patients suitable for operation.Acta Oto-Rhino-Laryngol (Belg) 1987; 41: 649–655.
Palermo F. Diagnostic efficacy of radiothallium uptake in thyroid nodules determined by computer assisted scintigraphy: reevaluation of radioisotope procedure.Nucl Med 1989; 28: 114–119.
Katagiri M, Harada T, Arita S. The thallium 201 curve in thyroid cancer: a role for the detection of metastases.Thyroidal Clin Exp 1989; 1: 11–15.
Binter G, Lind P, Langsteger G, et al. Clinical value of Tl-201/Tc-99m subtraction scintiscan as a criterion for surgery of cold goiter nodules.AMA 1990; 17: 2–3.
El-Desouki M. Tl 201 imaging differentiating benign from malign thyroid nodules. Clin Nucl Med 1991; 16: 425–430.
Hardorff R, Baron E, Scheinfeld M. Early and late lesion to non-lesion ratio of thallium 201 chloride uptake in the evaluation of cold thyroid nodules.J Nucl Med 1991; 32: 1873–1876.
Helal BO, Frounin F, Schaison G, et al. Diagnosis of malignancy in thyroid nodules by factor analysis of spectral and dynamic structures: a simultaneous dual-isotope studies with Tl-201 and I-131.Eur J Nucl Med 1992; 19: 517–521.
Hermans J, Schmitz A, Merlo P. Can benign and malignant thyroid nodules be differentiated with T1-201?Ann Endocrinol (Paris) 1993; 54: 248–254.
Henze E, Roth C, Boerer H, et al. Diagnostic value of early and delayed201Tl throid scintigraphy in the evaluation of thyroid nodules for malignancy.J Nucl Med 1986; 11: 413–416.
Menendez LR, Lucero EM, Swanson L, et al. Clinical evaluation of musculoskeletal tumors with thallium 201 scintigraphy. In: Brown KLB, ed. 6th International Symposium of Complications of Limb Salvage (Prevention, Management and Outcome). Montreal: Publisher ISOLS; 1991: 637–640.
Waxman AD. T1-201 in nuclear oncology. In: Freeman LM, ed.Nuclear medicine annual. New York: Raven Press; 1991: 193–209.
Waxman AD, Ramanna L, Memsic LD, et al. Thallium scintigraphy in the evaluation of mass abnormalities of the breast.J Nucl Med 1993; 34: 18–23.
Tonami N, Shuke N, Kunihiko Y, et al. T1-201 single photon computed tomography in the evaluation of suspected lung cancer.J Nucl Med 1989; 30: 997–1004.
Khalkhali I, Cutrone JA, Mena IG, et al. Scintimammography: the complementary role of Tc-99m sestamibi prone breast imaging for the diagnosis of breast carcinoma.Radiology 1995; 196: 421–426.
Tennvall J, Palmer J, Biorklund A, et al. Kinetics of T1-201 in adenomas and well-differentiated carcinomas of the thyroid: double isotope investigation with Tc-99m and Tl-201.Acta Radiol Oncol 1984; 23: 55–59.
Gharib H, Goellner JR. Fine-needle aspiration biopsy of the thyroid: an appraisal.Ann Intern Med 1993; 118: 282–289.
Schweil A, McKillop JH, Milroy R, et al. Mechanism of Tl-201 uptake in tumors.Eur J Nucl Med 1989; 15: 376–378.
Caluser C, Macapinlac H, Healey J, et al. The relationship between Tl-201 uptake, blood flow and blood pool in bone and soft tissue tumors.Clin Nucl Med 1992; 17: 565–572.
Waxman AD, Ramanna L, Said J. Thallium scintigraphy in lymphoma: relationship to gallium 67 [abstract].J Nucl Med 1989; 30: 915.
Schwaighofer B, Kurtaran A, Hubsch P, et al. Color-coded Doppler sonography in thyroid disease: initial experiences.ROFO 1988; 149: 310–313.
Woodcock JP, Owen GM, Shedden EJ, et al. Duplex scanning of the thyroid.Ultrasound Med Biol 1985; 11: 659–663.
Hubsch P, Niederle B, Barton P, et al. Color-coded sonography of the thyroid: an advance in carcinoma diagnosis.ROFO 1992; 156: 125–129.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Derebek, E., Biberoglu, S., Kut, O. et al. Early and delayed thallium-201 scintigraphy in thyroid nodules: the relationship between early thallium-201 uptake and perfusion. Eur J Nucl Med 23, 504–510 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00833383
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00833383