Abstract
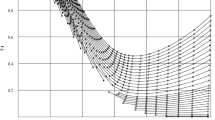
The thermodynamic similarity of nitrogen, oxygen, and air is established. The data for nitrogen are used to calculate the thermodynamic properties of oxygen at pressures of (1–1500)·105 N/m2 and temperatures of 170–1000 deg K. Tables of specific volume, enthalpy, entropy, and heat capacity of oxygen are given.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. M. Kessel'man, P. A. Kotlyarevskii, and A. P. Voloshin, IFZh, no. 1, 1965.
A. A. Vasserman and Ya. Z. Kazavchinskii, IFZh, no. 4, 1960.
A. A. Vasserman, Teploenergetika, no. 11, 1963.
H. Baehr and K. Schwier, “Die thermodynamischen Eigenschaften der Luft,” 1961.
Tables of Thermal Properties of Gases, National Bureau of Standards, Circular S64, 1955.
P. M. Kessel'man, IFZh, no. 6, 1963.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kessel'man, P.M., Gorykin, S.F. The thermodynamic similarity of nitrogen, oxygen, and air. Journal of Engineering Physics 8, 279–282 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00829632
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00829632