Conclusions
-
1.
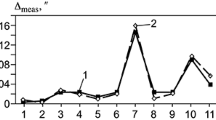
Any deviation from the parallel state on the part of the edges of the beam prisms leads to an error in the balance reading when the force is applied with a displacement relative to the longitudinal axis.
-
2.
The beam oscillation plane is determined by the position of the working edge of the reference prism, in view of which the requirements of [1] as to the perpendicular state of the working edges of the prisms require a certain refinement.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
All-Union State Standard 17159-71, “General-purpose balance having weight limits between 50 kg and 60 tons. Technical requirements” (1971).
V. A. Bocharov et al., Izmeritel. Tekh., No. 1 (1974).
V. A. Bocharov, Izmeritel. Tekh., No. 10 (1969).
V. V. Orlov, Dial-Type Balances [in Russian], Mashinostroenie, Moscow (1972).
M. N. Rudo, Laboratory Balances and Precision Weighing [in Russian], Standartgiz, Moscow (1963).
All-Union State Standard 9509-74, “Balances and gravimetric dosing systems. Steel prisms and bearings” (1974).
Gravimetric Instruments and Test Devices [in Russian], No. 1, Mashgiz, Moscow (1959).
Additional information
Translated from Izmeritel'naya Tekhnika, No. 12, pp. 23–24, December, 1976.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bocharov, V.A. Mutual disposition of working edges of the prisms in a beam balance. Meas Tech 19, 1714–1716 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00828212
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00828212