Summary
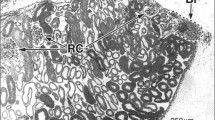
The structural organization of the kidney ofTyphlonectes compressicaudus (Amphibia, Gymnophiona) was studied by light microscopic (LM) examination of serial paraffin and semithin Epon sections. The kidney is slender and quite long and has a mesonephric segmental construction; the excretory duct (Wolffian duct), running along the lateral side of the kidney, segmentally receives the terminal trunks of the collecting duct system. The nephron has the following parts: renal corpuscle, neck segment, proximal tubule, intermediate segment, distal tubule and connecting tubule. The distal tubule is located in a ventromedial (central) zone of the kidney; all other tubular segments lie in a dorsolateral (peripheral) zone. The renal corpuscles are found at the border between these two zones.
The renal corpuscle is very large; its urinary pole faces the peripheral zone. A small proportion of neck segments receive either a nephrostomal duct or a blind branch. The proximal tubule is a thick, highly convoluted tubule. The intermediate segment is ciliated and makes a few coils. The distal tubule is composed of three portions: a highly convoluted part in the central zone, subsequently an attachment site with the renal corpuscle and a short postattachment-part. The connecting tubule and the collecting duct have a heterogeneous epithelium consisting of light and dark cells. The collecting duct is distinguished by dilated intercellular spaces. The Wolffian duct has a pseudostratified epithelium.
The present study correlates the course and segmentation of the renal tubule ofTyphlonectes. The tubule has three major convolutions. The first occurs in the proximal tubule in the peripheral zone; the second is established by the distal tubule and occurs in the central zone; the third is formed by the connecting tubule and is found in the peripheral zone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bargmann W, Knoop A, Schiebler TH (1955) Histologische, cytochemische und elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen am Nephron (mit Berücksichtigung der Mitochondrien). Z Zellforsch 42:386–422
Broek AJP van den, Oordt GJ van, Hirsch GC (1938) Harnorgane. In: Bolk L, Göppert E, Kallius E, Lubosch W (eds) Handbuch der vergleichenden Anatomie der Wirbeltiere. Bd 5. Urban & Schwarzenberg, Berlin, pp 683–854
Chase SW (1923) The mesonephros and urogenital ducts ofNecturus maculosus, Rafinesque. J Morphol 37:457–531
Clothier RH, Worley RTS, Balls M (1978a) A study of the renal tube of the urodele amphibianAmphiuma means. J Anat 126:405–406
Clothier RH, Worley RTS, Balls M (1978b) The structure and ultrastructure of the renal tubule of the urodele amphibian,Amphiuma means. J Anat 127:491–504
Crapon de Caprona D, Himstedt W (1985) Das aquatische Verhalten der BlindbühleIchthyophis kohtaoensis Taylor, 1960 (Gymnophiona: Ichthyophiidae). Salamandra 21:192–196
Gegenbaur C (1901) Vergleichende Anatomie der Wirbeltiere mit Berücksichtigung der Wirbellosen, vol 2. Engelmann, Leipzig
Geyer G, Linss W (1964) Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchung des Epithels im Verbindungsstück der Niere vonRana esculenta. Anat Anz 114:236–246
Herbert SC, Andreoli TE (1984) Control of NaCl transport in the thick ascending limb. Am J Physiol 246:F745-F756
Himmelhoch SR, Karnovsky MJ (1961) Oxidative and hydrolytic enzymes in the nephron ofNecturus maculosus: histochemical, biochemical, and electron microscopical studies. J Biophys Biochem Cytol 9:893–908
Hinton DE, Stoner LC, Burg M, Trump BF (1982) Heterogeneity in the distal nephron of the salamander (Ambystoma tigrinum): a correlated structure function study of isolated tubule segments. Anat Rec 204:21–32
Hoshi T, Suzuki Y, Itoi K (1981) Differences in functional properties between the early and the late segments of the distal tubule of amphibian (Triturus) kidney. Jpn J Nephrol 23:889–896
Huber GC (1917) On the morphology of the renal tubules of vertebrates. Anat Rec 13:305–339
Kaissling B, Kriz W (1979) Structural analysis of the rabbit kidney. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol 56:1–123
Lametschwandtner A, Albrecht U, Adam H (1978) The vascularization of the kidneys inBufo bufo (L.),Bombina variegata (L.),Rana ridibunda (L.) andXenopus laevis (D.) (Amphibia, Anura) as revealed by scanning electron microscopy of vascular corrosion casts. Acta Zool 59:11–23
Linss W, Geyer G (1964) Über die elektronenmikroskopische Struktur der Nierentubuli vonRana esculenta. Anat Anz 115:281–296
Maunsbach AB, Boulpaep EL (1984) Quantitative ultrastructure and functional correlates in proximal tubule ofAmbystoma andNecturus. Am J Physiol 246:F710-F724
Möllendorff WV (1930) Der Exkretionsapparat. In: Möllendorff WV (ed) Handbuch der mikroskopischen Anatomie des Menschen, VII/1. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–328
Moodie GEE (1978) Observations on the life history of the caecilianTyphlonectes compressicaudus (Dumeril and Bibron) in the Amazon basin. Can J Zool 56:1005–1008
Morris JL (1981) Structure and function of ciliated peritoneal funnels in the toad kidney (Bufo marinus). Cell Tissue Res 217:599–610
Morris JL, Campbell G (1978) Renal vascular anatomy of the toad (Bufo marinus). Cell Tissue Res 189:501–514
Naito I (1984) The development of glomerular capillary tufts of the bullfrog kidney from a straight interstitial vessel to an anastomosed capillary network. A scanning electron microscopic study of vascular casts. Arch Histol Jpn 47:441–456
Persson B-E, Persson AEG (1981) The existence of a tubulo-glomerular feedback mechanism in the amphiuma nephron. Pflügers Arch 391:129–134
Sakai T, Kawahara K (1983) The structure of the kidney of Japanese newts,Triturus (Cynops) pyrrhogaster. Anat Embryol 166:31–52
Stanton B, Biemesderfer D, Stetson D, Kashgarian, Giebisch G (1984) Cellular ultrastructure ofAmphiuma distal nephron: effects of exposure to potassium. Am J Physiol 247:C204-C216
Starck D (1982) Vergleichende Anatomie der Wirbeltiere auf evolutionsbiologischer Grundlage, Bd 3: Organe des aktiven Bewegungsapparates, der Koordination, der Umweltbeziehung, des Stoffwechsels und der Fortpflanzung. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Stoner LC (1977) Isolated, perfused amphibian renal tubules: the diluting segment. Am J Physiol 233:F438-F444
Taugner R, Schiller A, Ntokalou-Knittel S (1982) Cells and intercellular contacts in glomeruli and tubules of the frog kidney. Cell Tissue Res 226:589–608
Wake WH (1969) Kidney morphology in terrestrial and aquatic caecilians. Anat Rec 163:331
Wake MH (1970) Evolutionary morphology of the caecilian urogenital system. Acta Anat 75:321–358
Welsch U, Storch V (1973) Elektronenmikroskopische Beobachtungen am Nephron adulter Gymnophionen (Ichthyophis kohtaoensis Taylor). Zool Jahrb Anat 90:311–322
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Research fellow of the Alexander von Humboldt foundation: home address: Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, University of Tokyo, Tokyo 113, Japan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakai, T., Billo, R. & Kriz, W. The structural organization of the kidney ofTyphlonectes compressicaudus (Amphibia, Gymnophiona). Anat Embryol 174, 243–252 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00824340
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00824340