Summary
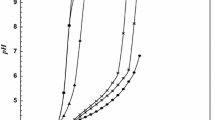
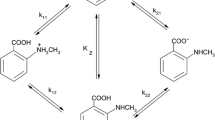
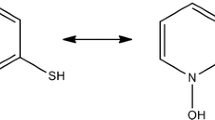
pK a values of 2-hydroxy 3-pyridinol (HHP), 2-mercapto 3-pyridinol (MHP), and 2-carboxy-3-pyridinol (CHP) were determined by potentiometric titration in water/organic solvent mixtures containing 20 mole% of organic solvent at 25±0.1 °C and 0.1M ionic strength (KNO3) applying an empiricalpH correction for mixed aqueous solvents. The influence of the organic solvents on the dissociation constants and tautomeric equilibria of the pyridinol derivatives is discussed. The effect of the molecular structure of the compounds onpK a is also explained. Titrations of a mixture of two weak diprotic acids (HHP andCHP) in a water/dimethylsulphoxide medium containing 20 mole% organic solvent at constant ionic strength were evaluated using theGran method.
Zusammenfassung
DiepK a-Werte von 2-Hydroxy-3-pyridinol (HHP), 2-Mercapto-3-pyriodinol (MHP) und 2-Carboxy-3-pyridinol (CHP) wurden durch potentiometrische Titration in wäßrigen Systemen mit 20 mol% organischem Lösungsmittelanteil bei 25±0.1 °C und einer lonenstärke von 0.1M KNO3 unter Anwendung einer empirischenpH-Korrektur für Lösungsmittelgemische bestimmt. Der Einfluß der organischen Lösungsmittel auf die Dissoziationskonstanten und die tautomeren Gleichgewichte der untersuchten Verbindungen und der Einfluß der molekularen Strukturen auf diepK a-Werte werden diskutiert. Die Titration eines Gemisches von zwei schwachen zweibasigen Säuren (HHP undCHP) in Wasser/Dimethylsulfoxid bei konstanter Ionenstärke wurde mit Hilfe derGranschen Methode ausgewertet.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saleh M. S., Idriss K. A., Abu-Bakr, M. S., Hashem E. Y. (1992) Analyst117: 1003
Saleh M. S. (in course of publication).
Idriss K. A., Saleh M. S., Sedaira H., Seleim M., Hashem E. Y. (1991) Monatsh. Chem.122: 507
Manning P. C. (1966) Can. J. Chem.44: 1471
Fowles G. W., Matthews R. W., Walten R. A. (1968) J. Chem. Soc.A: 1108
Azoo J. A., Reginald G. R., Gupta K. (1975) J. Chem. Soc.C: 1975
Shelke D. N., Jahagirdar D. V. (1979) J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem.41: 929
Aruga R. (1979) J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem.41: 845
Keith B., Ramesh P., Egon M. (1982) Polyhedron1: 269
Couturier Y., Petifaux Ch. (1984) Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr. 72
Saleim M., Idriss K. A., Saleh M. S., Sedaira H. (1987) Analyst112: 1685
Napoli A., Magri A. L. (1989) Ann. Chim. (Rome)77: 783
Bucci R., Carunchio V., Girelli A. M., Messina A. (1985) Polyhedron4: 1433
Idriss K. A., Seleim M. M., Saleh M. S., Hashem E. Y. (1993) Bull. Fac. Sci., Assiut Univ.,22: 109
Magda S., Saleh K. A., Idriss H. A., Azab, Hashem E. Y. Solution Chem. (in press)
Gutmann V. (1968) Coordination Chemistry in Non-aqueous Solutions, Springer, New York
Logowski J. J. (ed.) (1966) The Chemistry of Non aqueous Solvents, Vol. 1. Academic Press, New York
Burger K. (1983) Solvation, Ionic and Complex Formation Reactions in Non-aqueous Solvents. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Gran G. (1952) Analyst77: 661
Guenther W. (1975) Chemical Equilibrium. Plenum Press, New York, p. 106
Serjeant E. P. (1985) Potentiometry and Potentiometric Titrations. Wiley-Interscience, New York, p. 338
Robinson R. A., Stokes R. H. (1959) Electrolyte Solutions, 2nd ed. Butterworths, London, p. 230
Bacarella A. L., Grunwald E. W., Marshall H. P., Purlee L. L. (1955) J. Org. Chem.20: 747
Albert A., Serjeant L. P. (1962) Ionization constants of Acids and Bases. Methuen, London, p. 58
Deligny C. L., Luykx P. E. M., Rehback M., Wieneke A. A. (1960) Rec. Trav. Chim. Pays-Bas.79: 713
Coetzee J. F., Ritchie C. D. (1969) Solute-Solvent interactions. Marcel Dekker, New York, p. 221
Gutmann V. Electrochim. Acta (1976)21: 661; Chimia (1977)31: 1
Elguero J., Marzin C., Katritzky A. R., Linda P. (1976) The Tautomerism of Heterocycles (Edited by A. R. Katritzky). Academic Press, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saleh, M.S. Acid-base equilibria of some pyridinol derivatives in binary water/organic solvent systems. Monatsh Chem 126, 377–384 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00813199
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00813199