Summary
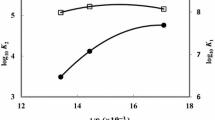
The acidity constants of adenosine-5′-mono- and diphosphate (AMP andADP) were determined at 25.00±0.1°C by potentiometric titration in pure water and different solvent mixtures (methanol, ethanol, N,N-dimethylformamide, dimethylsulfoxide, acetone, and dioxane). The ionization ofAMP andADP depends on both the proportion and the nature of the organic solvent used. ThepK a1 values for bothAMP andADP are slightly influenced as the solvent is enriched in ethanol and methanol and remains practically constant in presence of different amounts ofDMF andDMSO. A pronounced change in thepK a1 values is observed as the solvent is enriched in acetone or dioxane. It is concluded that the electrostatic effect has only a relatively small influence on the dissociation equilibrium, whereas other solvent effects such as solvent basicity, hydrogen bonding and protonsolvent interactions play an important role.
Zusammenfassung
Die Aciditätskonstanten von Adenosin-5′-mono- und -diphosphat wurden bei 25.0±0.1°C in reinem Wasser und in verschiedenen Lösungsmittelgemischen (Methanol, Ethanol, N,N-Dimethylformamid, Dimethylsulfoxid, Aceton und Dioxan) potentiometrisch bestimmt. Der Ionisierungsgrad vonAMP undADP hängt sowohl von der Menge als auch von der Art des organischen Lösungsmittels ab. DiepK a1-Werte vonAMP undADP werden durch Zugabe von Methanol und Ethanol nur wenig, durch verschiedene Mengen vonDMF undDMSO gar nicht, durch Aceton und Dioxan jedoch deutlich beeinflußt. Offensichtlich haben elektrostatische Effekte nur geringe Auswirkungen auf das Dissoziationsgleichgewicht, wogegen andere Faktoren wie Basizität des Lösungsmittels, Wasserstoffbrückenbindungen und Lösungsmittel-Proton-Wechselwirkungen eine bedeutende Rolle spielen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spiro T. G. (1973) Phosphate transfer and its activation by metal ions; Alkaline phosphatase. In: Eichhorn G. L. (ed.) Inorganic biochemistry, vol 1. Elsevier, New York
Cooperman B. S. (1979) Metal ions in biological systems5: 79–125
Mildvan A. S. (1979) Adv. Enzymol. Relat. Areas Mol. Biol.49: 103–126
Sigel H. (ed.) (1979) Nucleotides and derivatives: their ligating ambivalency. In: Metal ions in biological systems. Dekker, New York
Smith R. M., Martell A. E., Chen Y. (1991) Pure Appl. Chem.63: 1015
Levene P. A., Simms H. S. (1925) J. Biol. Chem.65: 519
Taylor H. F. W. (1948) J. Chem. Soc. 765
Alberty R. A., Smith R. M., Bock R. M. (1951) J. Biol. Chem.193: 425
Beers R. F., Steiner R. F. (1957) Nature (London)179: 1076
Wirth T. H., Davidson N. (1964) J. Am. Chem. Soc.86: 4314
Cheney G. E., Freiser H., Fernando Q. (1959) J. Am. Chem. Soc.81: 2611
Lewin S., Tann N. W. (1962) J. Chem. Soc. 1466
Christensen J. J., Izatt R. M. (1962) J. Phys. Chem.66: 1030
Azab H. A. (1987) Bull. Soc. Chim. France 265
Azab H. A. (1992) Talanta39(8): 913
Ahmed Hassan, Azab H. A., El-Gyar S. A., Khafagy Z. A. (1992) Can. J. Chem.70(6): 1684
Azab H. A. (1993) Talanta40(6): 863
Azab H. A., Ahmed Hassan, Khafagy Z. A. (1993) J. Chem. Eng. Data38: 231
Wu G., Izatt R. M., Bruening M. L., Jiang W., Azab H. A., Krakowiak K. E., Bradshaw J. S. (1992) J. Inclusion Phenom13: 121
Azab H. A., El-Gyar S. A., Ahmed Hassan, Khafagy Z. A. (1992) Bull. Fac. Sci. Assiut Univ.21: 79
Azab H. A. (1993) J. Chem. Eng. Data38: 453
Buisson D. H., Sigel H. (1974) Biochem. Biophys. Acta343: 45–63
Rossotti F. J. C., Rossotti H. (1965) J. Chem. Educ.42: 375
Douheret G. (1967) Bull. Soc. Chim. France 1412
Douheret G. (1968) Bull. Soc. Chim. France 3312
May P. M., Williams D. R. (1985) In: Leggett D. J (ed.) Computational methods for the determination of formation constants. Plenum Press, New York, pp 37–70
De Stefano C., Princi P., Rigano C., Sammartano S. (1987) Ann. Chim. (Rome)77: 643
Arena G., Rizzarelli E., Sammartano S., Rigano C. (1979) Talanta26: 1
Rigano C., Grasso M., Sammartano S. (1984) Ann. Chim. (Rome)74: 537
Dixon L. C. W. (1972) Nonlinear optimisation. English Universities Press Ltd., London
Levenberg K. (1944) Quart. App. Math.2: 164
Marquardt D. W. (1963) J. Soc. Indust. Appl. Math.11: 431
Bates R. G. (1964) Determination of pH theory and practice. Wiley, New York, p 198
Hammett L. P. (1928) J. Am. Chem. Soc.50: 2666
Gordon J. E. (1975) The organic chemistry of electrolyte solutions. Wiley, New York
Frank F., Ives D. J. G. (1966) Q. Rev.20: 1
Benneto H. P., Feakins D., Turner D. L. (1966) J. Chem. Soc. 1211
Tomkins R. P. T. (1966) The thermodynamics of ion-solvation in methanol-water mixtures. Thesis, Birkbeck College, University of London
Tremillon B. (1974) Chemistry in non-aqueous solvents. Reidel, Boston, p 68
Arnett E. M. (1963) Prog. Phys. Org. Chem.1: 223
Deno N. C., Wisotsky M. J. (1963) J. Am. Chem. Soc.85: 1735
Coetzee J. F., Padmanobhan G. R. (1965) J. Phys. Chem.69: 3193
Bates R. G. (1969) In: Coetzee J. F., Ritchie C. D. (eds.) Solute-solvent interactions. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 51, 72
Ritchie C. D. (1969) In: Coetzee J. F., Ritchie C. D. (eds.) Solute-solvent interactions. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 219–221, 223, 227
Bjerrum N. K. (1926) Dan. Vidensk. Selsk., Mat.-Fys. Medd. 7, 9
Fuoss R. M., Krausv C. A. (1933, 1935) J. Am. Chem. Soc.55: 2387;57: 1
Kolthoff I. M., Bruckenstein S. (1956, 1957) J. Am. Chem. Soc.78: 1;79: 1; Bruckenstein S., Kolthoff I. M. (1956) J. Am. Chem. Soc.78: 2974
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azab, H.A., El-Nady, A.M. & El-Shatoury, S.A. Acidity constants of adenosine-5′-mono- and diphosphate in various water-organic solvent mixtures. Monatsh Chem 125, 1049–1057 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00811512
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00811512